Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
People's Republic of China
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
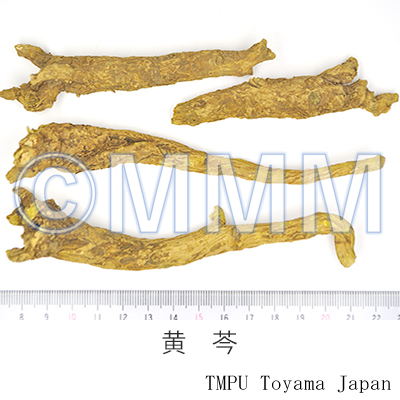
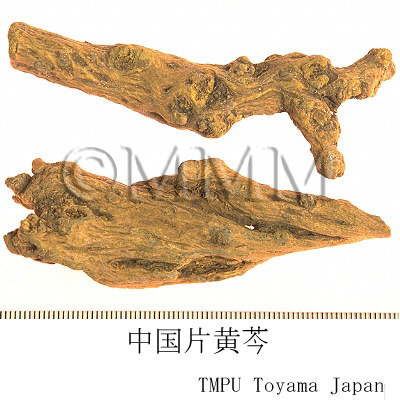
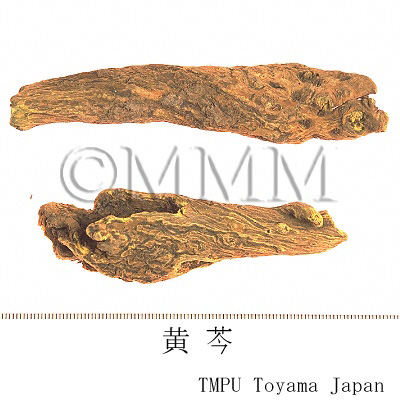
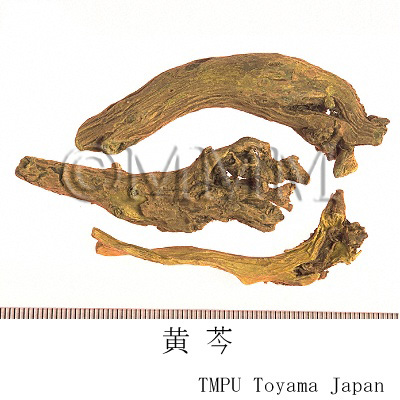
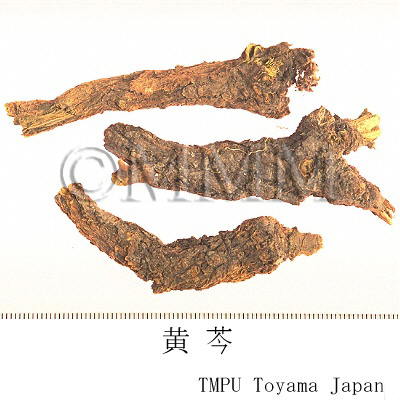
| Common name | 黄芩, Huangqin, Scutellariae Radix (JP18), (CP2020), Scutellaria Root (JP18), Baical Skullcap Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 子芩,尖芩,片芩,山東黄芩 | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
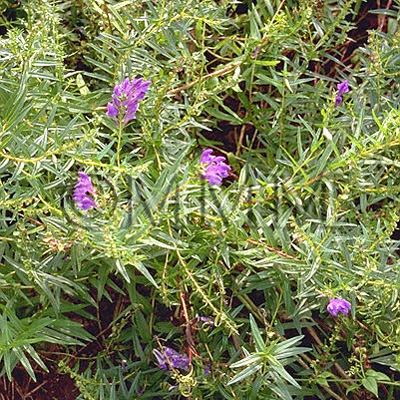
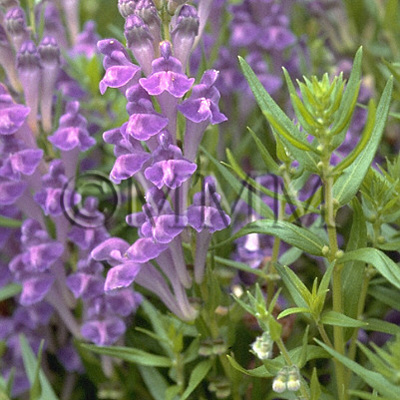
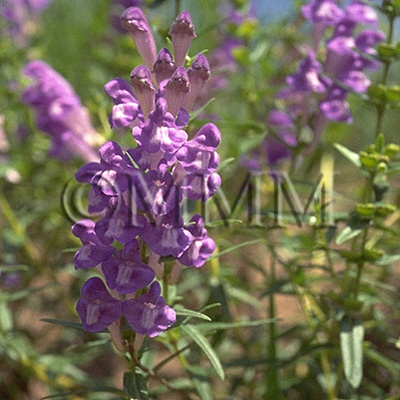
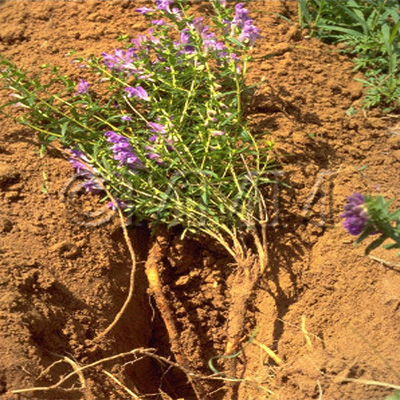
| Original plant name | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, (Koganebana) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Labiatae | ||||||
| Used part | root (without periderm) | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huangqin is thick, long and dense. It is yellow without outer cover. (NI) Shandon-huangqin and Rehe-huangqin are the highest quality. | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As antiinflammatory drug and antifebrile, Huangqin is applied for inflammation, congestion, stuffiness in the abdomen, diarrhea, and stomachache. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for elimination heat and dampness | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, gallbladder, spleen, large intestine and small intestine meridians. [Actions] To clear heat and dry dampness, purge the fire, remove toxin, stop bleeding and prevent miscarriage. [Indications] For discomfort in the chest, nausea and vomiting in epidemic febrile disease caused by damp-heat or summer-heat, feeling of fullness in the abdomen, acute dysentery or jaundice, cough due to heat in the lung, high fever with dire thirst, spitting of blood and epistaxis due to heat in the blood, carbuncle and sores, threatened abortion. | ||||||
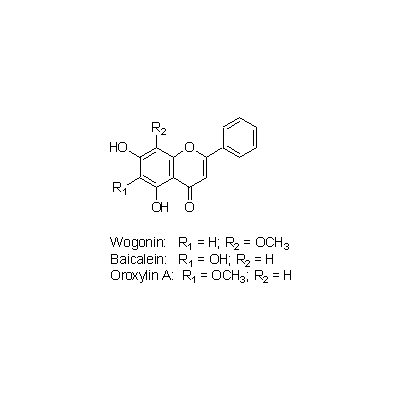
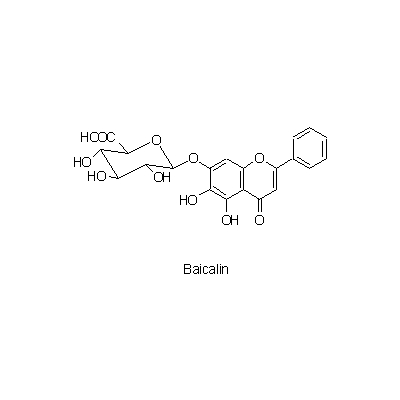
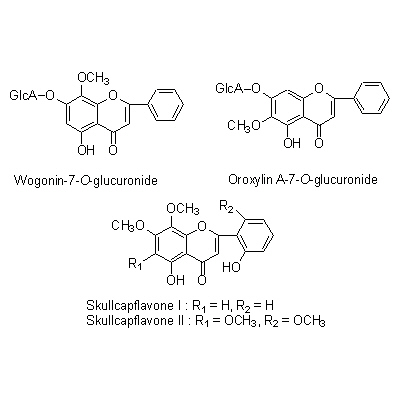
| Chemical constituent | Monosaccharides (*C2): D-Glucose Oligosaccharides (*C2): Sucrose Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, Campesterol, Stigmasterol Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Baicalin, Baicalein, Wogonin, Oroxylin A, 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone, 5,7,2',6-Tetrahydroxyflavone, Skullcapflavone I, Skullcapflavone II, 5,8-Dihydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone, Oroxylin A glucuronide, Koganebananin (*C2): Wogonin-7-O-glucuronide | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antifebrile, detoxicant, enhancement of bile secretion, inhibition of the secretion of gastric juices, antiinflammatory, antiallergic, antibacterial, improvement of lipid metabolism, inhibition of thrombus formation, acts on arachidonic acid metabolic system, etc. (flavonoids). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Feeling of pressure in the chest, Vomitting, Full stomach, Diarrhea, Cough, High fever, Swelling and pain of the throat, Pyogenic dermatosis, Threatened abortion, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage | ||||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Unseiin, Ogesan, Ogonto, Ogonkahangeshokyoto, Odoto, Oren'akyoto, Orengedokuto, Orengedokuto, Orenshodokuin, Otsujito, Kagenshahakusan, Kagenshosaikoto, Kagenryokakusan, Kagenryokakusan'ippo, Kakkon'oren'ogonto, Kakkonkahangeto, Kamisaikakujioto, Kankyooren'ogon'ninjinto, Kangento, Kanzoshashinto, Kanroin, Kufushokutsuto, Kumisaikoto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Keishigomotsuto, Gohekiin, Kowashakuyakuto, Gorinsan, Saikatsugekito, Saikanto, Saikokaboshoto, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, Saikokyohangekakaroto, Saikokeishito, Saikokeishikankyoto, Saikoshimotsuto, Saikoseikansan, Saikoyoeito, Saibokuto, Saireito, San'oshashinto, San'oshashinto (brewing), San'oto, Sammotsuogonto, Jijintsujito, Shakuyakuto, Shakuyakushimotsugekito, Shadojindaioto, Shahito, Shahitokaryukotsuboreito, Junchoto, Shokyoshashinto, Shosaikoto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shosaikotokakikyosekko, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shozokumeito, Shobaishashinto, Shoyosankato, Jokinritsuansan, Shin'iseihaito, Seiishakato, Seiinrikakuto, Seishitsuto, Seishitsuketanto, Seijokentsuto, Seijobofuto, Seishinrenshiin, Seihaito, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Daisaikoto, Daizokumeito, Daibyakuchuin, Jizutsuippo, Chimobukuryoto, Tokisan, Tokinentsuto, Tokibyakujutsusan, Tokirokuoto, Tonsonto, Naisoorento, Nisento, Nyoshinsan, Baimoto, Haiyoto, Hangeshashinto, Bofutsushosan, Hokikenchuto, Hochujishitsuto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Honposhakuyakuto, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryutan-shakan-to, Rengyoto, Rengyoto, Rokumotsuogonto | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 152-154. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 236-237. | ||||||
| Remarks | New roots with a dense internal part are called "Zigin" ("Tiaogin", "Zhigin" and "Wanzhou"). The apexes of the roots are called "Jiangin". "Sugin" and "Kugin" are the old roots, partially rotted with hollows. The flakes are called "Piangin" or "Pingshou". | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | ||||||