Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
22.5519759
120.5487597
Collection information
Taiwan,Pingtung
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
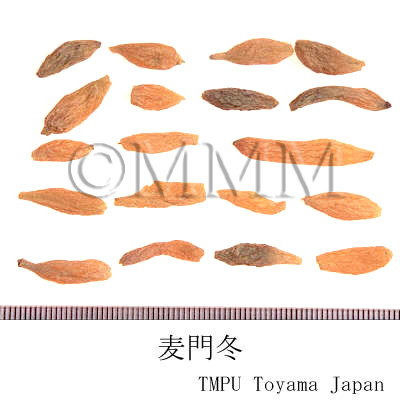
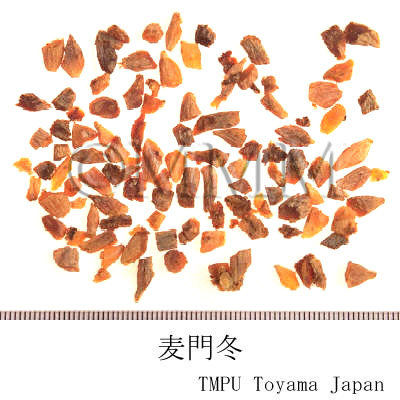
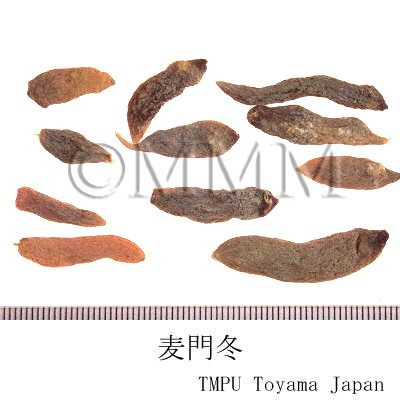
| Common name | 麦門冬, Maimendong, Maidong, Ophiopogonis Radix (JP18, CP2020), Ophiopogon Root (JP18), Dwarf Lilyturf Tuber (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
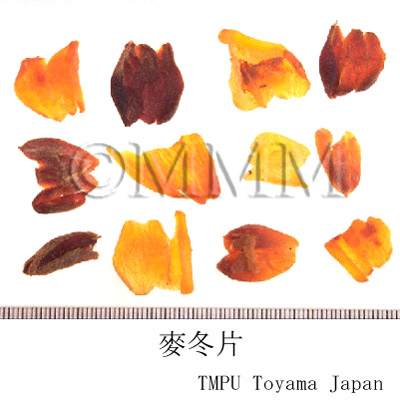
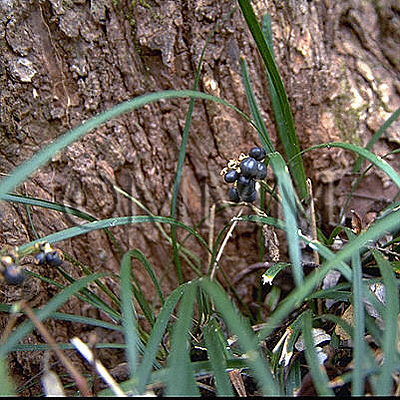
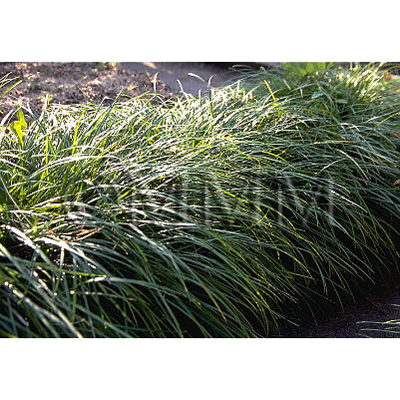
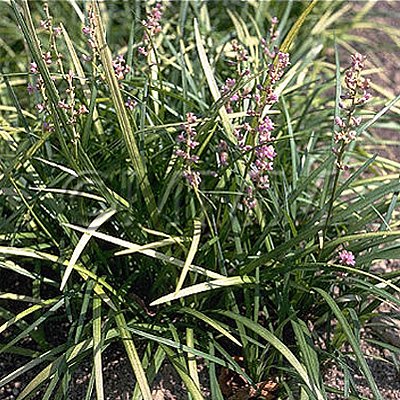
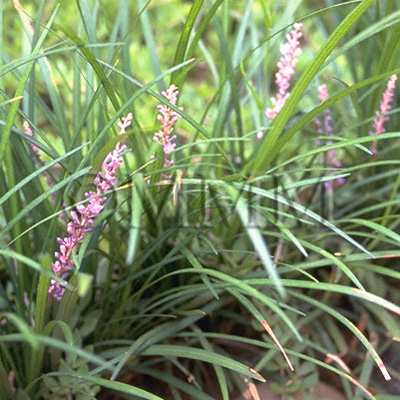
| Original plant name | Ophiopogon japonicus Ker-Gawler (= Ophiopogon ohwii Okuyama), Janohige, (Nagabajanohige) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | ||||||
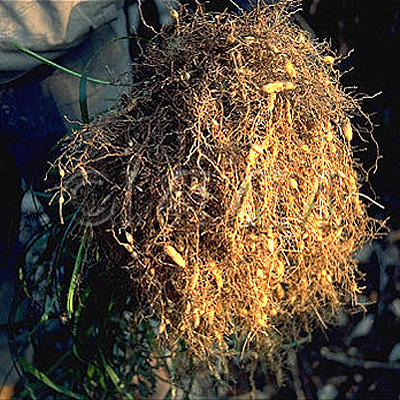
| Used part | tuberous root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Maimendong is enlarged, rich in moisture and pale yellow. It looks heavy. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a mucous and synovial antiinflammatory drug, tonic, antitussive, expectorant, diuretic, for strengthening the constitution, maimendong is applied for nourishing the stomach, to remove reversed flow of qi and feeling of hot flushes. It has a strong cardiotonic and diuretic effects for the parson who has a hot flush tendency. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Yin-vital essence | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To nourish yin, engender fluid, moisten the lung, and to clear the heart. [Indications] Dry cough caused by lung dryness, cough caused by yin consumptive disease, throat impediment and sore throat, thirst caused by fluid consumption, interior heat wasting-thirst, insomnia caused by vexation, constipation caused by intestinal dryness. | ||||||
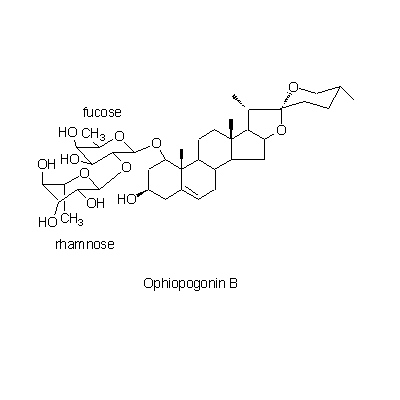
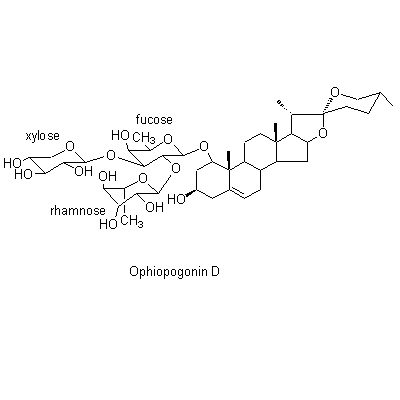
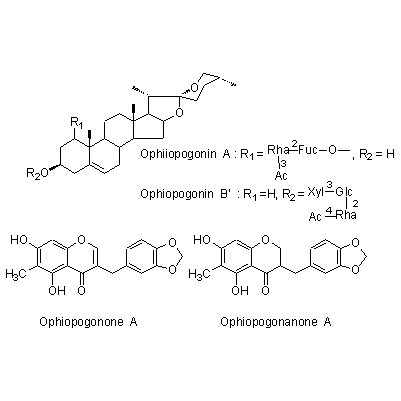
| Chemical constituent | Monosaccharides (*C1): Sucrose, D-Fructose, D-Glucose Oligosaccharides (*C1): Oligosaccharide Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, beta-Sitosterol-beta-D-glucoside, Stigmasterol Steroid saponins & Sapogenins (*C1): Ophiopogonin A, Ophiopogonin B, Ophiopogonin C, Ophiopogonin D, Ophiopogonin B', Ophiopogonin C', Ophiopogonin D' Neoflavanoids & Homoisoflavonoids (*C1): Ophiopogonone A, Ophiopogonone B, Methylophiopogonone A, Methylophiopogonone B, Ophiopogonanone A, Methylophiopogonanone A, Methylophiopogonanone B | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hypoglycemic (water extract). Antiinflammatory (ethanol extract). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB029789, AB029790, AB029841, AB029842; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Dry cough, Few sputum, Thirst, Lack of energy, Weak pulse, Mlaise, Insomnia, Fret, Constipation | ||||||
| Formulation | Unkeito, Kamishimotsuto, Kanroin, Kufushokutsuto, Kochinmuyusan, Jiinkokato, Jiinshihoto, Shiinsen, Shakanzoto, Shomyakusan, Shoyosankato, Shin'iseihaito, Seijokentsuto, Seishoekkito, Seishinto, Seishinrenshiin, Seinetsuhokito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Chikujountanto, Chikuyosekkoto, Chimobukuryoto, Chotosan, Teizento, Dosuibukuryoto, Ninjinsan, Bakumondoto, Bakumondoinshi, Byakugokokinto, Bukuryhoshinto, Fuhishomyakusankabyakukyu, Hokikenchuto, Hochujishitsuto, Hohaito, Mankeishisan, Mibakuekkito, Ryukotsuto | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 67-68. | ||||||
| Remarks | Both The Japanese Pharmacopoeia and The Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China define O. japonicus as the original plant. Besids, in China, O. ohwii (Jap. Name: Sekkojanohige) and O. chekiangensis Kimura et Migo are circulated. The latter is cultivated in Zhejiang Province. Some say that it must be disinguished from O. japonicus because it has slender rhizome. Korean "Maimendong" is the enlarged roots of Liriope spicata Lour. (Jap. Name: Koyaburan) or L. platyphylla Wang et Tang., which is called "Tumaimen" in China. Its quality is not good. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | ||||||