Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
41.805699
123.43147199999999
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Liaoning Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 升麻, Shengma, Cimicifugae Rhizoma (JP18), (CP2020), Cimicifuga Rhizome (JP18), Largetrifoliolious Bugbane Rhizome (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 黒升麻, 緑升麻 | ||||||
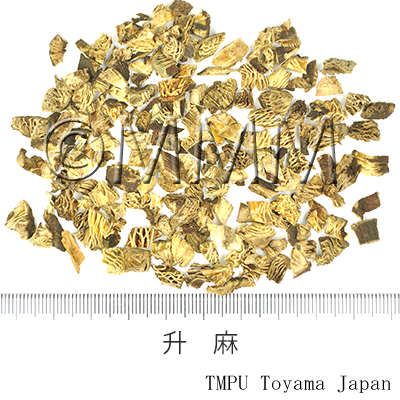
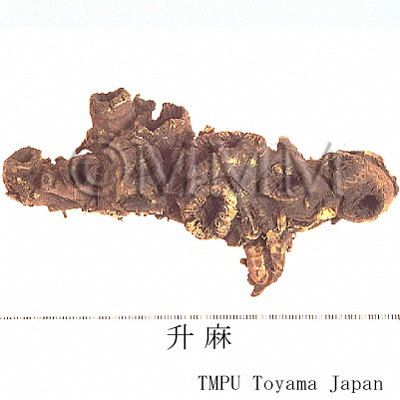
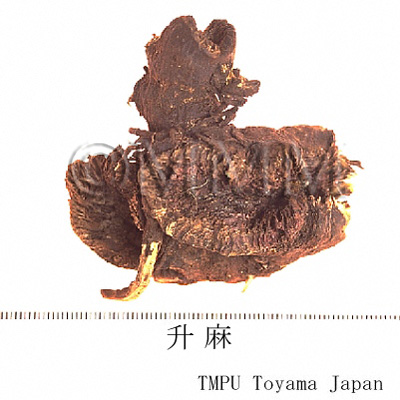
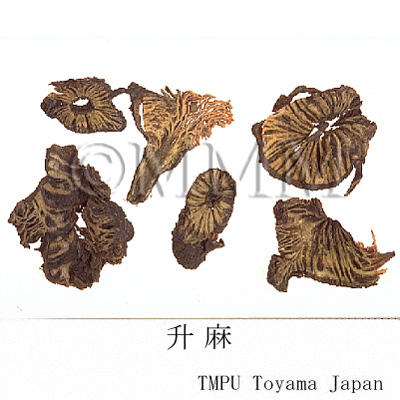
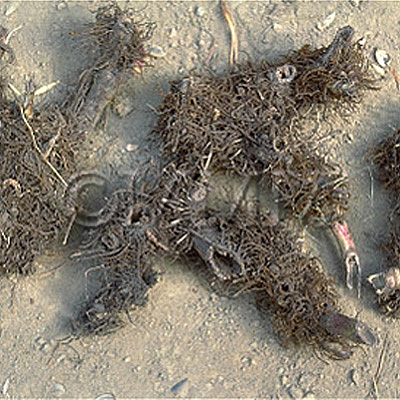
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
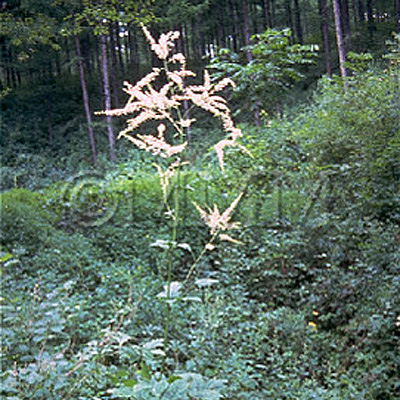
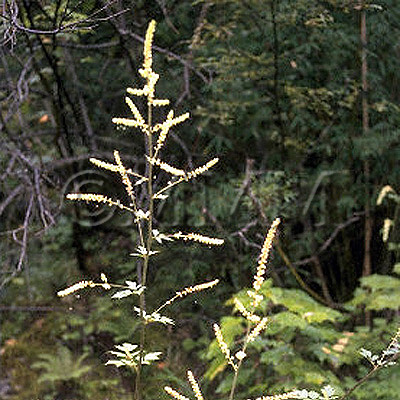
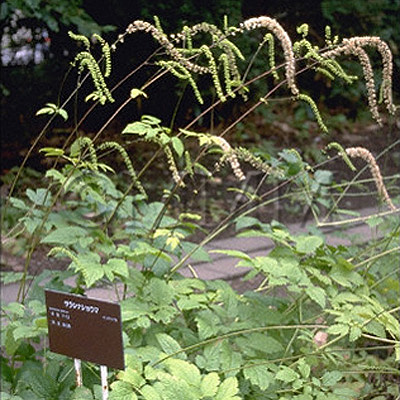
| Original plant name | Cimicifuga dahurica Maximowicz, Cimicifuga heracleifolia Komarov, Cimicifuga foetida Linn. or Cimicifuga simplex Turczaninow1, (Sarashinashoma1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Ranunculaceae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Shengma is large without fine roots and the outer surface is black. The cross section is white or light green. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, antidote, and anti inflammatory drug, Shengma is applied for fever, headache, pharyngitis, cold, measles, and anal prolapse. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with cold property | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; pungent and mild sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, spleen, stomach and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To effuse exterior to promote eruption, clear heat and remove toxin, upraise yang qi. [Indications] Wind-heat headache, toothache, mouth sore, swelling and sore of throat, unerupted measles, macula and papule caused by yang toxin, prolapse of the rectum, uterine prolapse. | ||||||
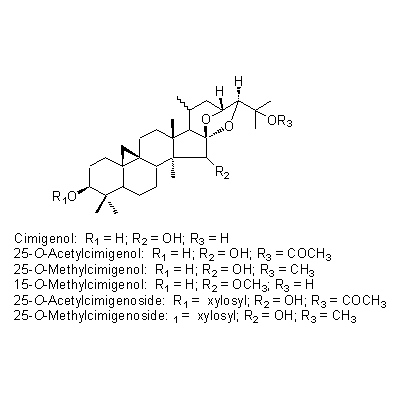
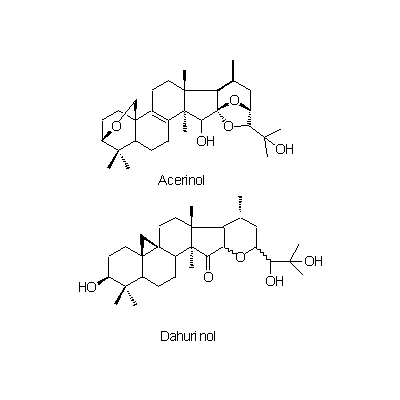
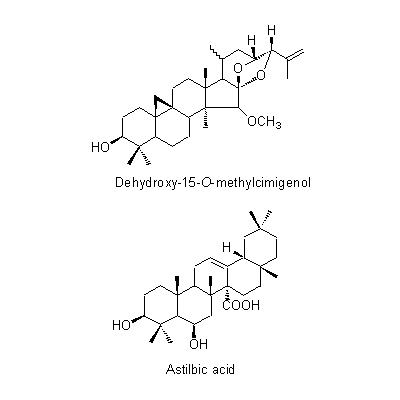
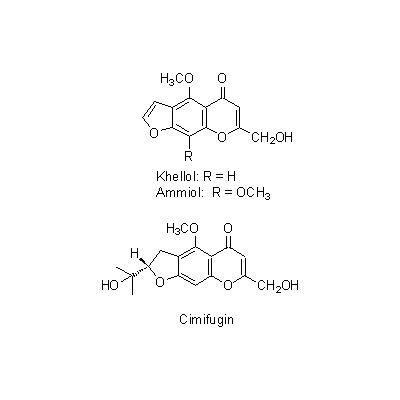
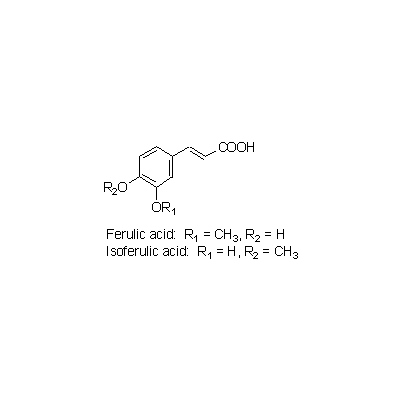
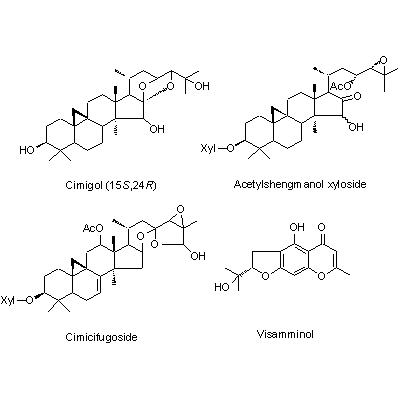
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids C. dahurica (*C1): Cimigenol, Cimigenol xyloside, Dahurinol C. acerina (*C1): Cimigenol, Acerinol, 25-O-Acetylcimigenol, 25-O-Methylcimigenol, Dehydroxy-15-O-methylcimigenol, 15-O-Methylcimigenol, 25-O-Acetylcimigenoside, 25-O-Methylcimigenoside (*C6): Cimigenol 3-arabinoside, Cimigol, Isodahurinol, Acerionol, Cimicifugoside, 26-O-Methylcimifugoside, Cimifugenin A, 26-O-Methylcimifugenin A, Cimicifugenol, Acetylshengmanol xyloside, Friedelin Triterpenoids C. foetida (*C1,C3,C4,C5): Cimicidanol, Foetidinol, Acetylacteol-3-O-arabinoside, 25-Anhydrocimigenol-3-O-beta-xyloside, Cimicidanol-3-O-beta-xyloside, Cimicidol-3-O-beta-xyloside, Cimicifol, Cimicinol, Foetidinol-3-O-beta-xyloside, 15-alpha-Hydroxycimicidol-3-O-beta-xyloside, 15-alpha-Hydroxyfoetidinol-3-O-beta-xyloside Triterpenoids C. heracleifolia (*C1,C2,C3): 24-epi-Acerinol, 25-O-Acetyl-7,8-didehydrocimigenol, 7,8-Didehydrocimigenol, 24-epi-7,8-Didehydrocimigenol, Heracleifolinol 3-keto-24-epi-7,8-didehydrocimigenol, 3'-O-Acetyl-24-epi-7,8-didehydrocimigenol-3-O-beta-xyloside, 2',4'-Di-O-acetyl-24-epi-7,8-didehydrocimigenol-3-O-beta-xyloside, 7,8-Didehydro-24-O-acetylhydroshengmanol-3-O-beta-xyloside, 24-epi-7,8-Didehydrocimigenol-3-O-beta-xyloside Sterols C. dahurica (*C1): beta-Sitosterol C. acerina (*C1): beta-Sitosterol Phenylpropanoids C. dahurica (*C1): Ferulic acid, Isoferulic acid Chromones C. dahurica (*C1): Visnagin C. simplex (*C1): Khellol, Ammiol, Cimifugin (*C6): Visamminol | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antifebrile, analgesic, antiinflammatory (*E1), sedative, antihypertensive, inhibitior of bone resorption (*C3). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB012612, AB029374, AB029375, AB029376, AB029377, AB029378, AB029379, AB029380; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Urticaria, Anal fistula, Pruritus, Hematochezia due to proctoptosis, Descent of the uterus, Measles, Erosion of the root of tooth, Bad breath, Stomatitis, Swelling and pain of the throat, Headache, Chronic diarrhea | ||||||
| Formulation | Ioto, Otsujito, Kumihangeto, Shakuyakushimotsugekito, Shunrinshakusekishito, Shomakakkonto, Joshitsuhokito, Joyowaketsuto, Shin'isan, Shin'iseihaito, Jingyobofuto, Jintanto, Seiishakato, Seinetsuhokito, Tokinentsuto, Hochuekkito, Hochujishitsuto, Rikkosan, Rengyoto | ||||||
| Related drugs | Hongshengma, Guangshengma (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1)Nat.Med.,50,222(1996);51,148(1997). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 30-31. C2)Chem.Pharm.Bull,41,832(1993). C3)J.Trad.Med.,13,50(1996). C4)Tetrahedron,51,1143(1995). C5)Tetrahedron Lett.,35,4575(1994). C6)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 306. E1)J.Med.Pharm.Soc.WAKAN-YAKU,10,110(1997). | ||||||
| Remarks | The roots of Serratula chinensis S. Moore of family Compositae are used in southern China (Guangshengma). The rhizome of Aruncus sylvester Kostel of family Rosaceae may dilute Shengma derived from genus Cimicifuga rhizoma. Care should be taken with the rhizome of Strobilanthes forrestii Diels of family Acanthaceae that has been distributed as Shengma (fake) in China recently. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | ||||||