Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
31.820591
117.22721899999999
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Anhui Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
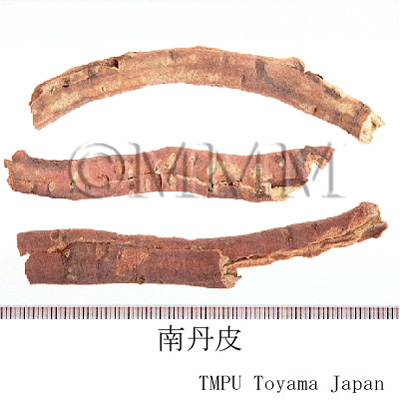
| Common name | 牡丹皮, Mudanpi, Moutan Cortex (JP18, CP2020), Moutan Bark (JP18), Tree Peony Bark (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 鳳凰牡丹皮 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
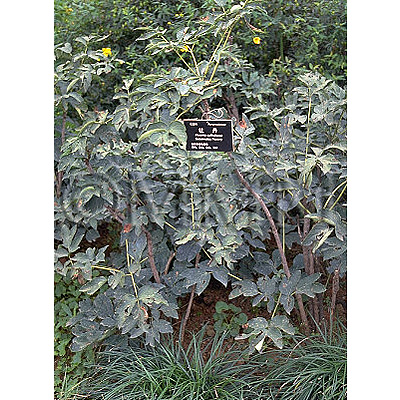
| Original plant name | Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews (= Paeonia moutan Sims), (Botan) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Paeoniaceae | |||||
| Used part | root bark | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Mudanpi has radial thickness without xylem. There are white powders on the cross section. It has strong aroma. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a tranquilizer, painkiller, for removing blood stasis and draining pus, mudanpi is applied for hematogenous disorder (blood circulation stasis) such as headache, abdominal pain, gynecologic disease, menstrual disorder and dysmenorrhea. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for eliminating heat from blood | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; bitter and pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, liver and kidney. [Actions] To clear heat and cool the blood, activate blood to resolve stasis. [Indications] Heat entering nutrient-blood aspects, macula and papule caused by warm toxin, hematemesis, epistaxis, fever at night and cool in the morning, steaming bone fever without sweating, amenorrhea and dysmenorrhea, pain caused by traumatic injuries, swelling abscess, sore and skin infections. | |||||
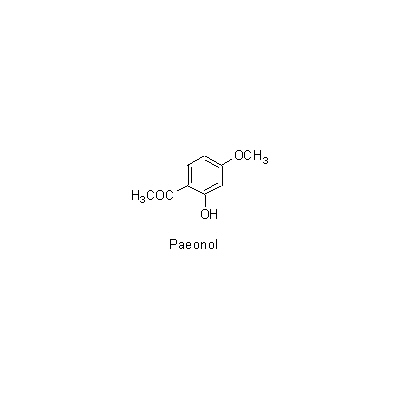
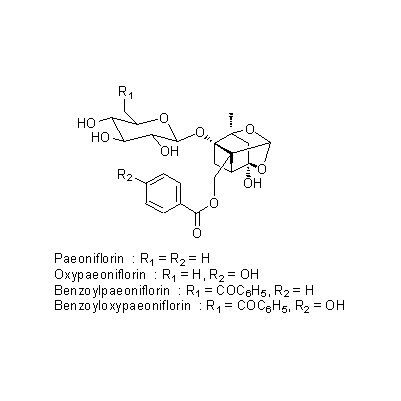
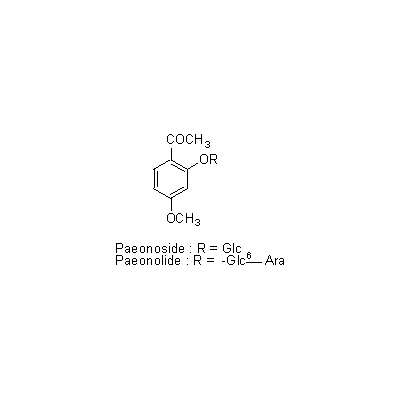
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids (*C1): Paeoniflorin, Oxypaeoniflorin, Benzoylpaeoniflorin, Benzoyloxypaeoniflorin (*C2): Galloyl-paeoniflorin, Galloyl-oxypaeoniflorin Sterols (*C1): Campesterol, beta-Sitosterol Tannins (*C2): Tetragalloylglucose, Pentagalloylglucose Other aromatic derivatives (*C1): Paeonol, Paeonolide, Paeonoside, Benzoic acid (*C2): Suffruticoside A, Suffruticoside B, Suffruticoside C, Suffruticoside D, Suffruticoside E | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory (methanol extract),analgesic,antibacterial (E. coli, S. aureus),antiinflammatory,suppression of gastric juice secretion (paeonol). | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Fever, Internal bleeding, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Amenorrhea, Menorrhalgia, Intra-abdominal tumor, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Appendicitis, Pyogenic dermatosis, Headache, Red eye, Thirst, Irregular menstruation | |||||
| Formulation | Unkeito, Kashininto, Katsuketsusan'oto, Kamishoyosan, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kyukichoketsuin, Keishibukuryogan, Goshitsusan, Goshajinkigan, Saikakujioto, Saikosokanto, Shichikensan, Shaito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Sesshoin, Daiobotampito, Choyoto, Choyotokashakuyaku, Tojinto, Toryuto, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimijiogan, Hachimisenkiho, Hokoeito, Botanpisan, Yokuininto, Rokumijiogan, Kogikujiogan | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 132-133. C2) The Journal of Traditional Sino-Japanese Medicine 15(1), 95-103(1994). | |||||
| Remarks | There are many varieties of peony. The origin of Mudanpi is complicated and the composition of the chemical component varies slightly according to the species. The Mudanpi without core, which is produced in Nara Prefecture, is good quality. The best product in China is produced at Tonglingfenghuangshan in Anhui Prov. which is called "Fenghuangmudanpi" or "Fengdanpi". The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines Mudanpi as the one which contains not less than 1.0%(JP17) but 0.9%(JP18) of Paeonol. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||