Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
38.418439
115.32664599999998
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Anguo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 栝楼根, Gualougen, Trichosanthis Radix (JP18, CP2020), Trichosanthes Root (JP18), Snakegourd Root (CP2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 天花粉 (Tianhuafen) | ||||
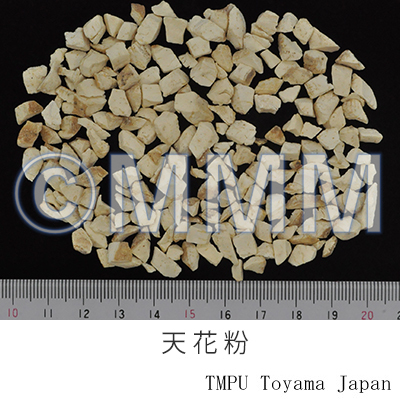
| crude drug image |
| ||||
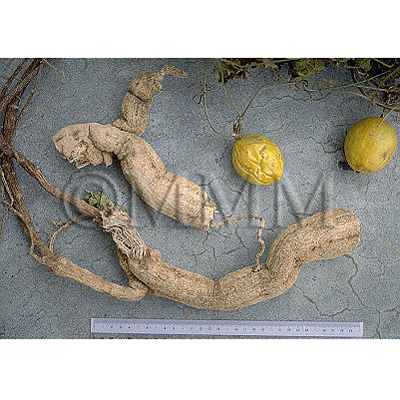
| Original plant name | Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim, Trichosanthes kirilowii var. japonicum Kitamura1, Trichosanthes bracteata Voigt2, (Kikarasuuri1, Ōkarasuuri2) | ||||
| original plant image |
| ||||
| Family name | Cucurbitaceae | ||||
| Used part | root without periderm | ||||
| Quality for selection | Good guaougen is dense. The cross section is white and has floral patterns in the center. (TN) | ||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, antitussive, diuretic, relactagogue, relieving thirst and for draining pus, it is applied to cure thirst of deficiency syndrome, pain due to pharyngeal swelling, respiratory disease, malignant tumor and all. The powder of "gualougen" ("tenkafun" in JP) is used externaly to infantile skin diseases. | ||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for reducing intense internal heat | |||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, purge fire, engender fluids, quench thirst, disperse swelling and expel pus. [Indications] Vexation and thirst caused by heat disease, lung heat and dryness cough, interior heat, wasting-thirst, sore and ulcer, swelling skin infections. | ||||
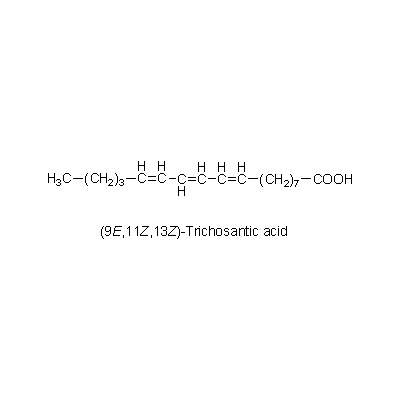
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids (*C1): Trichosantic acid Polysaccharides (*C1): 澱粉/starch Triterpenoids (*C1): 11-Oxo-cucurbit-5-ene-3beta,24,25-triol Sterols (*C1): Stigmasterol, beta-Sitosterol Amino acids (*C1): Citrulline Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): gamma-Aminobutyric acid (*C2): Trichosanthin | ||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hyperglycemia (decoction, water extract) | ||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||
| Disease | Thirst, Dry cough, Hemoptysis, Pyogenic dermatosis | ||||
| Formulation | Ekigento, Karokeishito, Kangento, Saikokyohangekakaroto, Saikokeishikankyoto, Saikoseikansan, Saikoyoeito, Seishinto, Seisoyoeito, Haiyoto, Bakumondoinshi | ||||
| Related drugs | Gualouren (Trichosanthes Semen) | ||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 32-33. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 265. | ||||
| Remarks | In china, "Gualougen" is also called "Tianhuafen". The root of T. rosthornii Herms is used as Chinese "Tianhuafen" as well. "Tenkafun", Japanese pronunciation of "Tianhuafen", is the starch "Gualougen" which is applied externaly on eczema, irritated skin, etc. The root of T. bracteaata Voigt ("Ōkarasuuri" in JP) is also used as Japanese "Gualougen". | ||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/14 | ||||