Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hubei Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
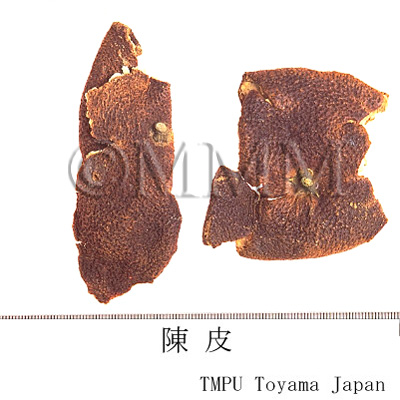
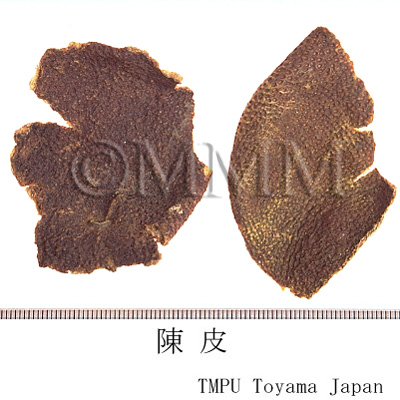
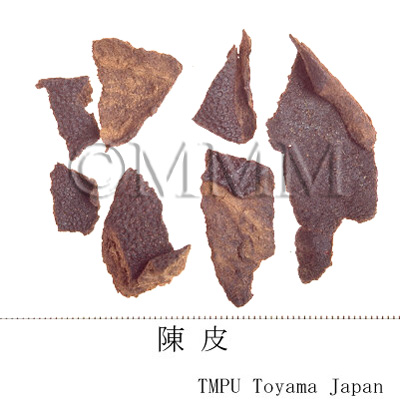
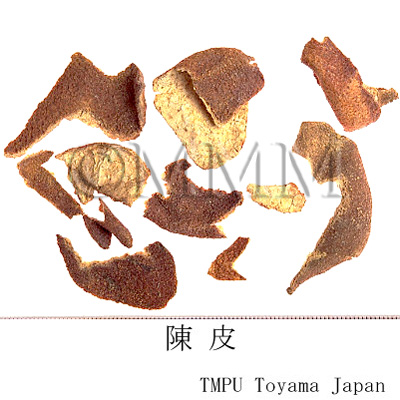
| Common name | 陳皮 (中国産/CN production), Chenpi, Citri Reticulate Pericarpium (CP2020), Dried Tangerine Peel (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 青皮, 化州橘皮, 橘皮 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
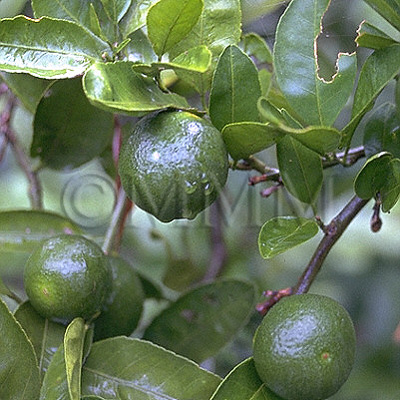
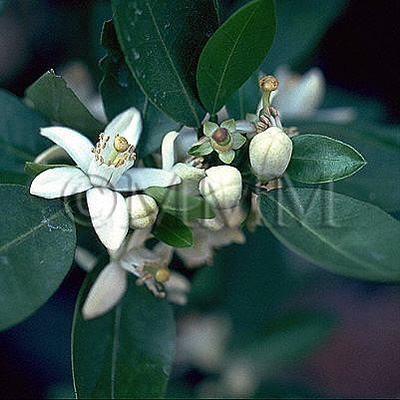
| Original plant name | Citrus unshiu Marcowicz1, Citrus reticulata Blanco2, Citrus grandis Osbeck3, Citrus sinensis Osbeck4, (Unshūmikan1, Ponkan-type2 Buntan3, Amadaidai4) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rutaceae | |||||
| Used part | mature fruit peel | |||||
| Quality for selection | The older the better. The older Chenpi has a milder aroma than the fresh one. It is a kind of liuchen. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As aromatic and bitter stomachic, carminative, expectorant and antitussive, Chenpi is applied for anorexia, vomiting, catharsis, pain and cough. It enters the qi system of lung and spleen, and is applied to upper and middle energizer.. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; bitter and pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and spleen meridians. [Actions] To regulate qi, fortify the spleen, dry dampness and resolve phlegm. [Indications] Distention and fullness in the epigastrium and abdomen, reduced food intake with vomiting and diarrhea, cough and profuse sputum. | |||||
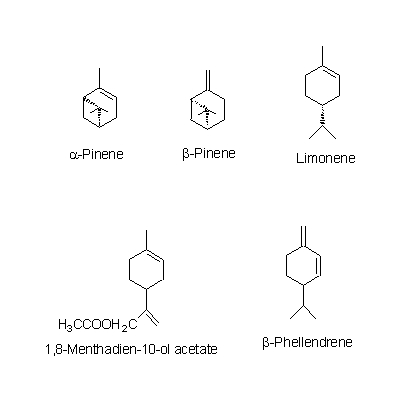
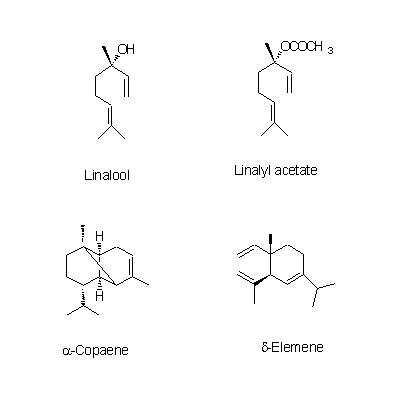
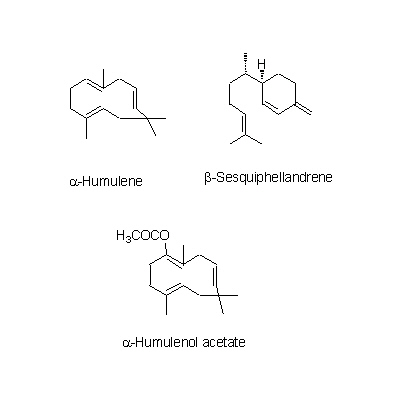
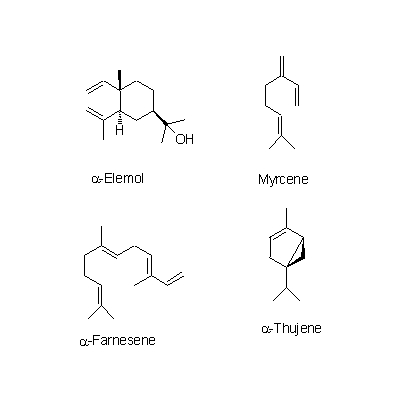
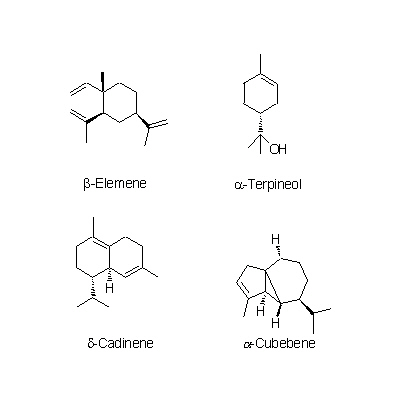
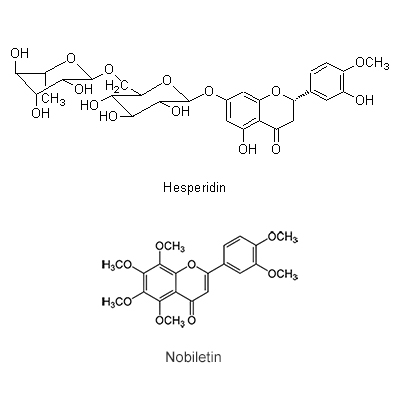
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds C. unshiu (*C1): クエン酸(citric acid) Monosaccharides C. unshiu (*C1): Vitamin C Monoterpenoids C. tangerina (*C1): alpha-Pinene, beta-Pinene, Limonene, beta-Phellandrene, p-Cymene, alpha-Terpinene, Linalool, Linalyl acetate C. unshiu (*C1): Limonene, alpha-Terpinene, alpha-Pinene, beta-Pinene, Linalool, alpha-Thujene, alpha-Terpineol, Myrcene, 1,8-Menthadien-10-ol acetate Sesquiterpenoids C. unshiu (*C1): delta-Elemene, alpha-Copaene, beta-Sesquiphellandrene, alpha-Elemol, alpha-Farnesene, beta-Elemene, delta-Cadinene, alpha-Cubebene Flavones & Flavonols C. unshiu (*C2,C3,C4,C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, (5-Demethylnobiletin) C. reticulata (*C2,C4,C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, Tangeretin, 5-Hydroxy-7,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone, 5-Demethylnobiletin, (Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone) C. sinensis (*C2,C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, tetra-O-Methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin, (3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone) C. grandis (*C2,C5): Tangeretin, Rhoifolin C. tangerina (*C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin, (Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-Hydroxy-7,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone) C. erythrosa (*C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin, Rhoifolin, (Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, 5-Hydroxy-7,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone) Flavanones & Dihydroflavonols C. tangerina (*C1,C5): Hesperidin, Narirutin, (Poncirin, Naringenin) C. unshiu (*C1,C2,C4,C5): Hesperidin, Naringenin, Hesperetin, Narirutin, (Naringin) C. reticulata (*C2,C4,C5): Hesperetin, Narirutin, Hesperidin C. sinensis (*C2,C5): Poncirin, Naringenin, Hesperetin, Narirutin, Hesperidin C. grandis (*C2,C5): Naringenin, Naringin, Hesperetin C. erythrosa (*C5): Poncirin, Narirutin, Hesperidin Coumarins C. grandis (*C2,C5): Meranzin hydrate, Marmin, Isomeranzin, 5-[(6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenyl) oxy]-psoralen, Isoimperatorin, Meranzin C. reticulata (*C4,C5): (Oxypeucedanin, Isoimperatorin) C. tangerina (*C5): (Limettin, Isomeranzin) C. erythrosa (*C5): (Isomeranzin) Alkaloids Citrus spp. (*C6): Synephrine | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedative, inhibition of central nervous system, ileum extirpation, contraction of uterus and peripheral blood vessel, mucosal and local stimulation, increase in inner pressure of gallbladder and hypertonia of Sphincter of Oddi, increase in bile secretion, acceleration of intestinal movement, decrease in the level of cholesterol in liver and serum (d-limonene). antiulcer (nobiletin).Sympathomimetic action (synephrine).Antiinflammatory (naringin,neohesperidin,nobiletin,tangeretin,sinensetin,xanthotoxin),antiallergic(nobiletin,tangeretin,3-methoxynobiletin,sinensetin),inhibition of c-AMP phosphodiesterase (nobiletin,tangeretin,3-demethylnobiletin).Strengthening of capillary(hesperidin), and antioxidant(3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF312228; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 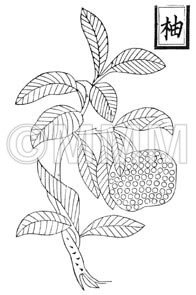 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Vomitting, Diarrhea, Anorexia, Feeling of pressure in the chest, Cough, A lot of sputum | |||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Ioto, Ikosan, Ireito, Untanto, Orenshodokuin, Kagen'ireito, Kagenshahakusan, Kagenshosaikoto, Kakkoshokisan, Kamiuntanto, Kamihassento, Kyukichoketsuin, Kumihangeto, Kumibinroto, Keihito, Kokikososan, Koshaheiisan, Kosharikkunshito, Kososan, Kochinmuyusan, Goshakusan, Saikokobokuto, Saishakurikkunshito, Jiinkokato, Jiinshihoto, Shisoshito, Shisowakiin, Jippito, Junkiwachuto, Shunrinshakusekishito, Shokitenkoto, Shohito, Shoyosankato, Jokinritsuansan, Jin'en'ippo, Jingyobofuto, Jinsoin, Shimpito, Seishitsuketanto, Seishoekkito, Seisoyoeito, Seineitsugeutsuto, Seihaito, Zenshikunshito, Sogento, Sokeikakketsuto, Soshikokito, Chikujountanto, Chokoshiteito, Chokobukuryoto, Chotosan, Tsudosan, Tokiyoketsuto, Dotaitsukeito, Nijutsuto, Nichinto, Ninjin-yoei-to, Hachimitaikaho, Hangekobokushichimotsuto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Fukankinshokisanryo, Bukuryoin, Bukuryhoshinto, Bunshoto, Bunshinkiin, Heiisan, Hointo, Hokikenchuto, Hochuekkito, Hochujishitsuto, Mibakuekkito, Mokutsusan, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Rikkunshito, Rokuutsuto, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Chinpi (Citrus Unshiu Peel produced in Japan), Qingpi (Green Tangerine Peel), Chengpi (Bitter Orange Peel), Zhiqiao (Orange Fruitproduced in China), Zhishi (Immature Orange Fruit) | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 257-260. C2)Nat.Med.,51,231(1997). C3)Nat.Med.,51,84(1997). C4)Nat.Med.,50,114(1996). C5)Nat.Med.,51,205(1997). C6)Shoyakugaku Zasshi,46,150(1992). | |||||
| Remarks | 80-90% of essential oil is limonene. It is more abundant in ripe fruit peel (Chenpi) than peel of immature fruit (Qingpi). Though the older Chenpi is more appreciated, the components of its essential oil will have changed. Aging increases the relative content of limonene. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||