Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
38.042805
114.51489300000003
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
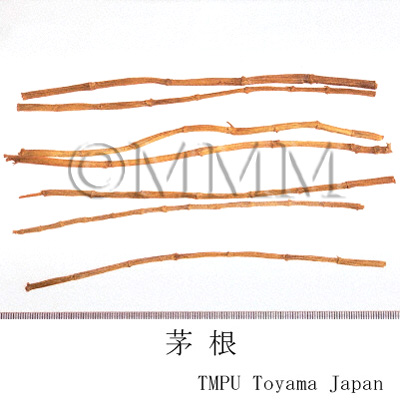
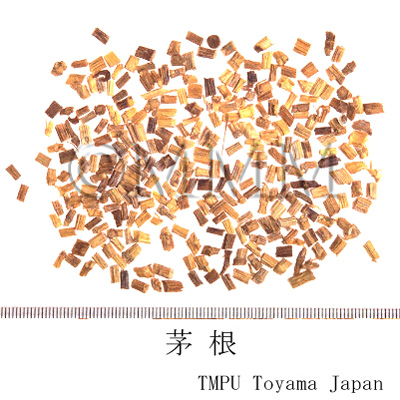
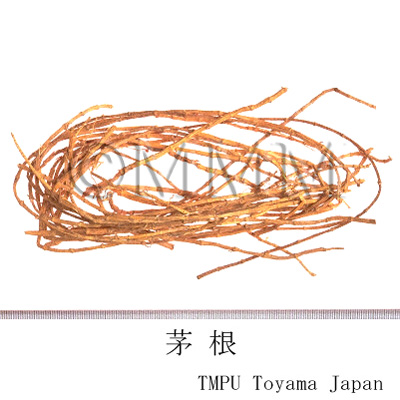
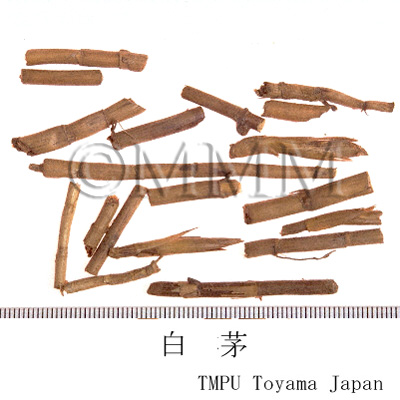
| Common name | 茅根, Maogen, Imperatae Rhizoma (JP18), (CP2020), Imperata Rhizome (JP18), Lalang Grass Rhizome (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 白茅根 (Baimaogen) | |||||
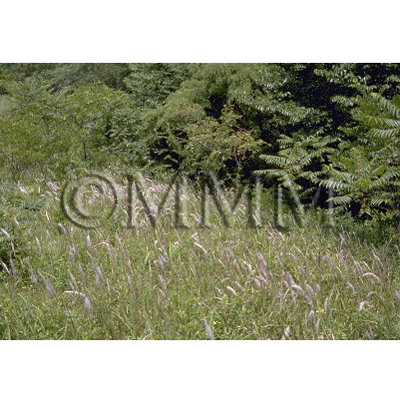
| crude drug image |
| |||||
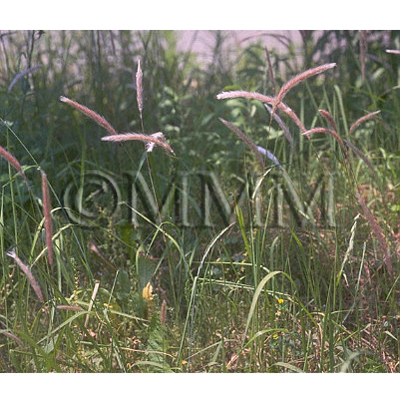
| Original plant name | Imperata cylindrica Beauvois1, Imperata cylindrica P. Beauvios var. koenigii Durand et Schinz, Imperata cylindrica var. major C.E. Hubb., (Chigaya1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Gramineae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Maogen is thick, long and light in color (yellowish-white). (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antiinflammatory diuretic, antifebrile, hemostatic, for clearing blood, maogen is applied for heat disease, hematemesis, epistaxis, hematuria, edema, jaundice, oliguria, thirst, asthma and nausea. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Hemostatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung; stomach and bladder meridians. [Actions] To cool the blood, stanch bleeding, clear heat, and promote urination. [Indications] Hematemesis, epistaxis and hematuria caused by blood heat, vexation and thirst caused by heat disease, dampness-heat jaundice, edema, small quantity of urination, and heat strangury with slow pain. | |||||
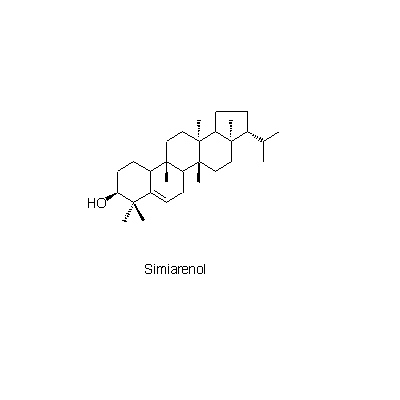
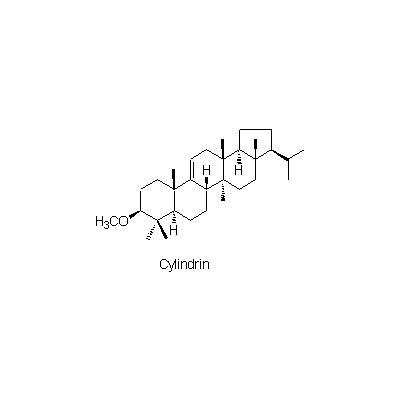
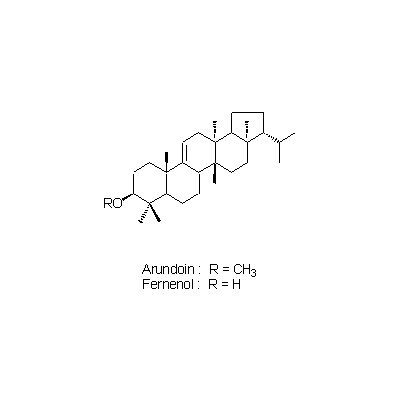
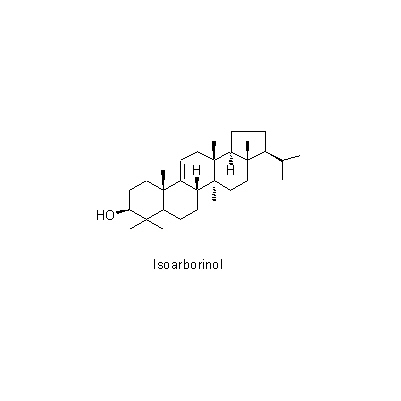
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Citric acid, Malic acid Monosaccharides (*C1): D-Fructose, D-Glucose, D-Xylose Oligosaccharides (*C1): Sucrose Triterpenoids (*C1): Simiarenol, Cylindrin, Arundoin, Fernenol, Isoarborinol Others (*C1): K塩/KCl | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Diuresis (water extract). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF345653, AF092512, AF190764 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematuria, Thirst, Vomitting, Nausea, Hiccup, Measles, High fever, Cough, Jaundice, Acute nephritis, Urodynia, Dysuria | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 98-99. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/02/02 | |||||