Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
24.880095
102.83289100000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Yunnan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
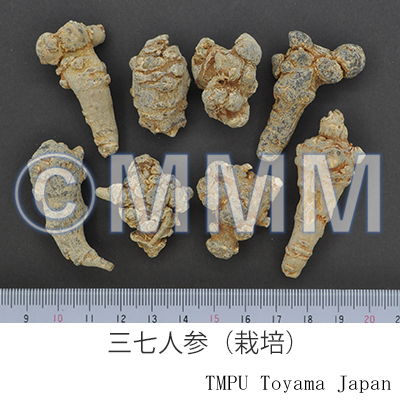
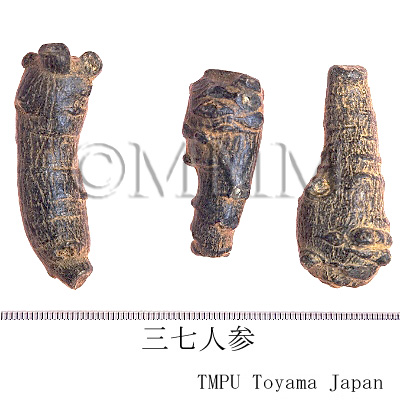
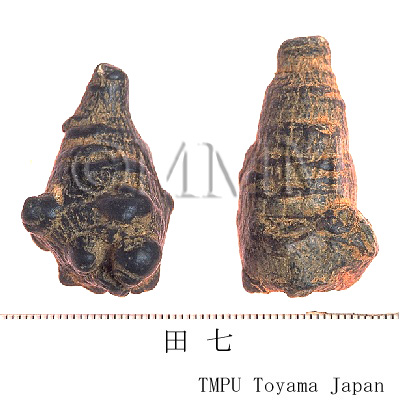
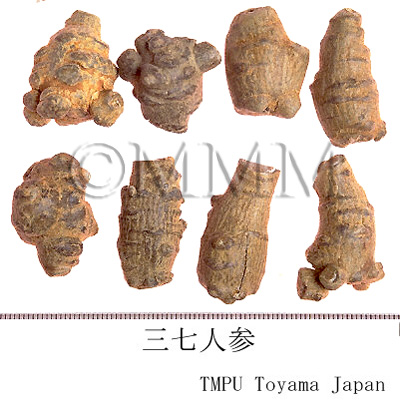
| Common name | 三七人参, Sanqirenshen, Panacis Notoginseng Radix (Non-JPS2022), Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma (CP2020), Panax Notoginseng Root (Non-JPS2022), Sanchi (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 田七, 田三七 | ||||||
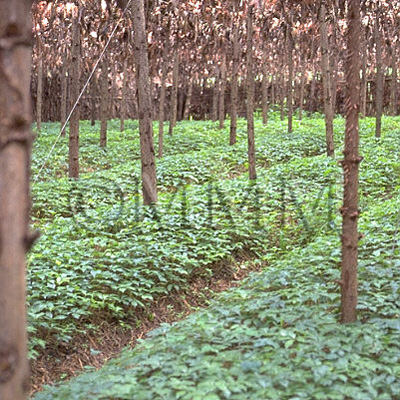
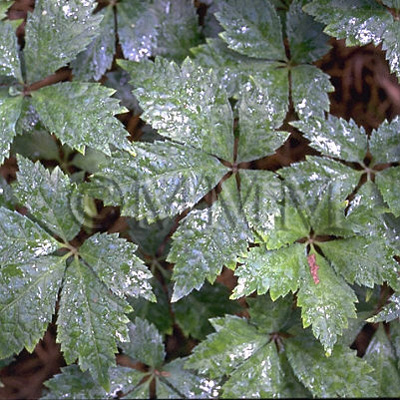
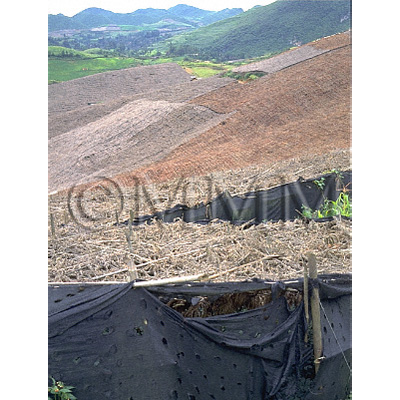
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
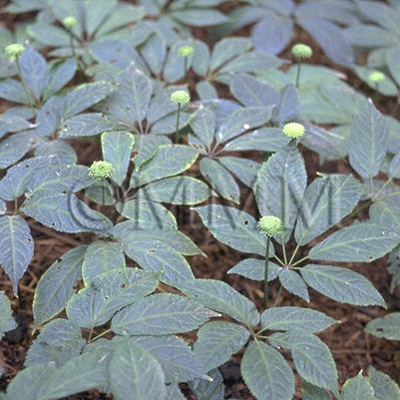
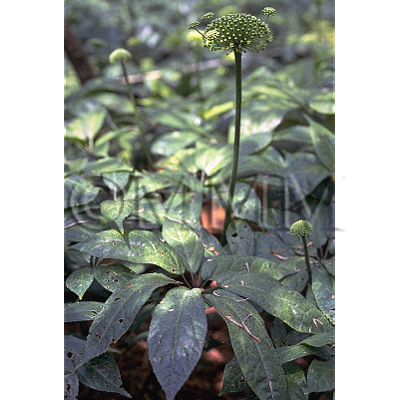
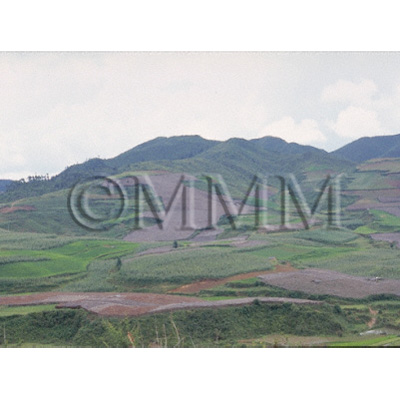
| Original plant name | Panax notoginseng Feng Hwai Chen | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Araliaceae | ||||||
| Used part | root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Chunqi has higher quality than Donqi. Good Sanqirenshen has a big main root. | ||||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | To stop bleeding, relieve swelling, alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, relieve fatigue, and as cardiant: For bruise, various kinds of bleeding such as swelling with pain, hematemesis. epistaxis, metrorrhagia, tumid bleeding, hematemesis, epistaxis, women's metrorrhagia and merostaxis, hyperemesis and stomachache of after childbirth, coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, hypertension, liver disorder and all. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Hemostatics | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and kidney. [Actions] To dissipate stasis and stanch bleeding, disperse swelling and relieve pain. [Indications] Hemoptysis, hematemesis, epistaxis, hematochezia, menstrual flooding and spotting, traumatic bleeding, stabbing pain in the chest and abdomen, swelling and pain caused by traumatic injuries. | ||||||
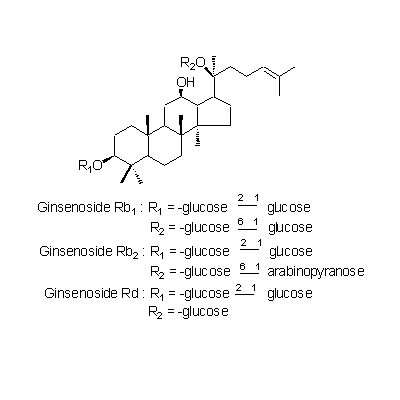
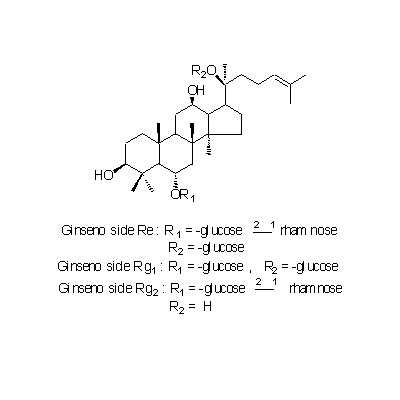
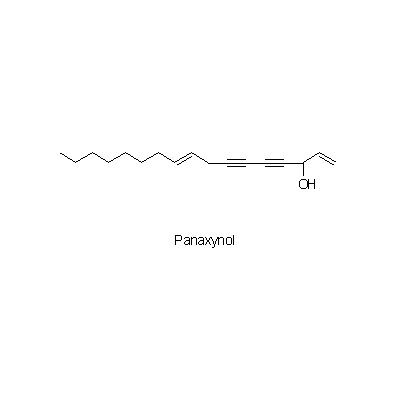
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Panaxynol Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): サポニン配糖体 [saponin glycosides] 3~8%: Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg2, Ginsenoside Ra, Ginsenoside Rb2, Ginsenoside Rd, Ginsenoside Re, (Ginsenoside Ro) Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol Amino acids (*C2): Dencichine (beta-N-oxalo-L-alpha-beta-diaminopropionic acid) | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hemostatic,cardiotonic,analgesic,sedative,antiinflammatory,immunomodulatory etc.The powder of Notoginseng increases the blood flow of animal coronary arteries and reduces the oxygen consumption of cardiac muscle. Therefore reduces the stress on the heart, in addition, decreases the blood lipid and cholesterol. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | 18SrRNA: D85171,AB027524, matK: AB027526, AB027527, ITS: U41684, U41685; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Disease | Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematochezia, Irregular vaginal bleeding, Bleeding, Myocardial infarction, Angina pectoris, Hypertension, Chronic hepatitis, Acute hepatitis, Contusion | ||||||
| Formulation | |||||||
| Related drugs | Renshen (Ginseng), Hongshen (Red Ginseng), Zhujieshen (Panax Japonicus Rhizome), Guangdongrenshen (American Ginseng) | ||||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 5-8. C2)Yakugaku Zasshi, 101, 629(1981). | ||||||
| Remarks | It is found in specific area, from Southeast Yunnan Prov. to Southwest Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region. It has been cultivated there since the Qing dynasty. It was also called "Jinbuhuan" and has been prized since ancient times. Now, it is not only blended into the formulation of Chinese medicine, "Yunnan-baiyao" and "Pianzaihuang" but also distributed as a health food. It is divided into "Chunqi" and "Dongqi" according to the season of harvest. Literature refers to "Chunqi" as being harvested in autumn (before the efflorescence). However, our 1999 research in Yunnan found that "Chunqi" was the root of the plant from which stems had been picked off before flowering, in middle July, and harvested in middle September. "Dongqi" was the root which had been harvested from November to December after collection of the seeds. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/19 | ||||||