Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
21.9181199
110.85338
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Gaozhou, Maoming, Guangdong
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 藿香, Huoxiang, Pogostemoni Herba (JP18), Pogostemonis Herba (CP2020), Pogostemon Herb (JP18), Cablin Patchouli Herb (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 広藿香 Guanghuoxiang | |||||
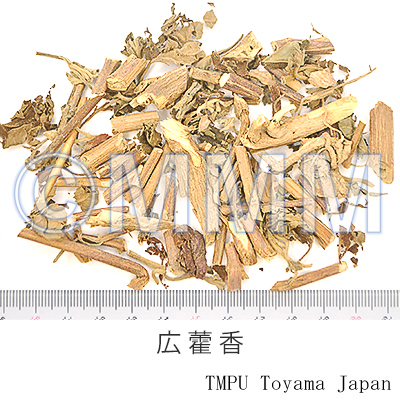
| crude drug image |
| |||||
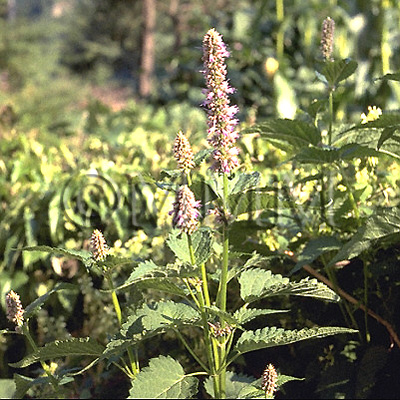
| Original plant name | Pogostemon cablin Bentham, (Pacholi) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Labiatae | |||||
| Used part | aerial part or leaf | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huoxiang has big leaves and a bluish tinge. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an aromatic stomachic and for relieving exterior syndrome, Huoxiang is applied for indigestion, lack of appetite, affection due to heat, and headache due to cold and heat. It is also used for vomiting and diarrhea, since it has antinauseant and constipating action. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Aromatic drugs for resolving dampness | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, liver meridians. [Actions] To resolve turbidity with aromatic medicinal, harmonize the middle and check vomiting, release the exterior and summer-heat. [Indications] Dampness-turbidity obstruction in the middle, epigastric stuffiness vormtmg, summer heat-dampness exterior pattern, beginning of dampness-warmth, fever, fatigue, uncomfortable caused by oppression in the chest, cold-dampness blocking summerheat, vomiting and diarrhea with abdominal pain, sinusitis and headache. | |||||
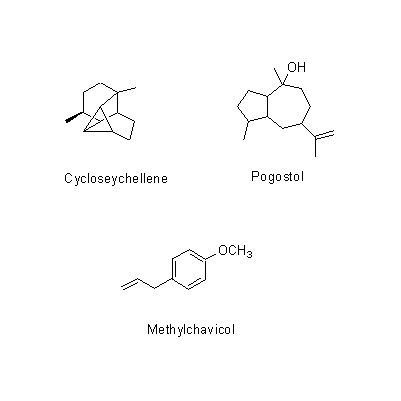
| Chemical constituent | Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Patchouli alcohol, Cycloseychellene, Pogostol Phenylpropanoids (*C1): Methylchavicol (= Esdragol) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Enhanced secretion of gastric juices. | |||||
| DNA sequence | L14406 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Anorexia, Full stomach, Dyspepsia, Mlaise, Chill, Fever, Headache, Heat exhaustion, Nausea, Vomitting, Hyperemesis gravidarum, Sinusitis, Diarrhea | |||||
| Formulation | Kakkoshokisan, Koshaheiisan, Kosharikkunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Chokoshiteito, Kagenshosaikoto, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Chuseito | |||||
| Related drugs | Dokakko, Senkakko | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 58-60. | |||||
| Remarks | Houxiang (Jap. name: Kakkō or Kōkakkō) is a medicine of Indian origin. The plant name Pachouli is from Hindi. It was carried to Guangzhou by Chinese abroad more than 100 years ago and cultivated there. Since it is produced mainly in Guangdong and Hainan, it is called Kōkakkō in Japan (Japanese pronunciation of Guang'広' is Kō.). The one produced in Sichuan Prov. is the whole plant of Agastache rugosa (Fisch. et Mey.) O. Kuntze of family Labiatae (Jap. name: Kawamidori). It is called Dokakkō or Senkakkō. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/29 | |||||