Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
33.870422
109.94047699999999
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Shangluo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
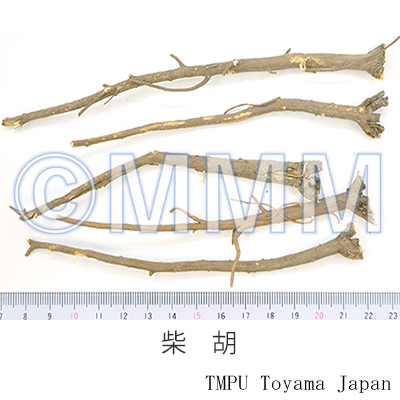
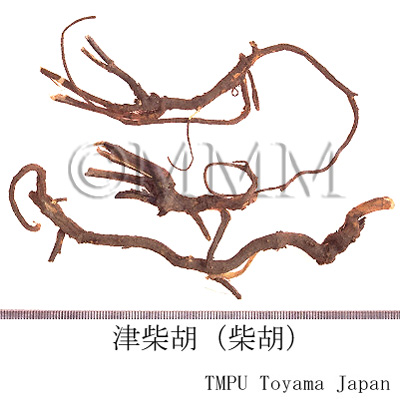
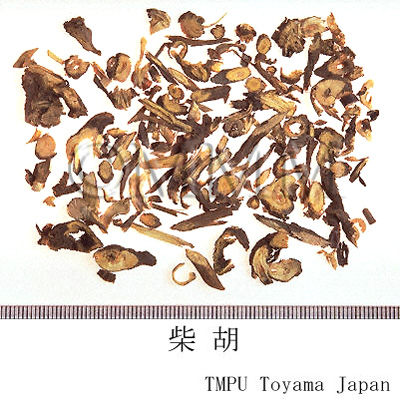
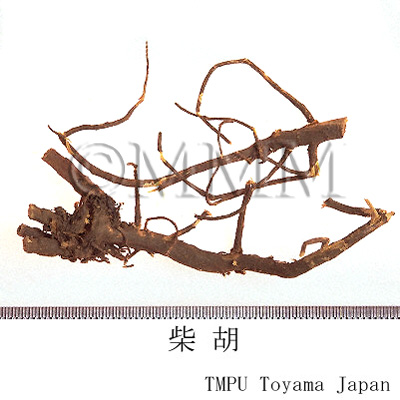
| Common name | 柴胡, Chaihu, Bupleuri Radix (JP18), (CP2020), Bupleurum Root (JP18), Chinese Thorowax Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 北柴胡,津柴胡,植柴胡 | |||||
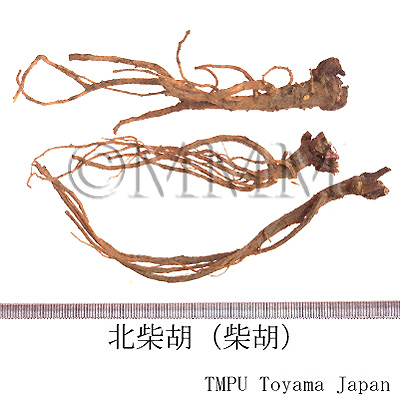
| crude drug image |
| |||||
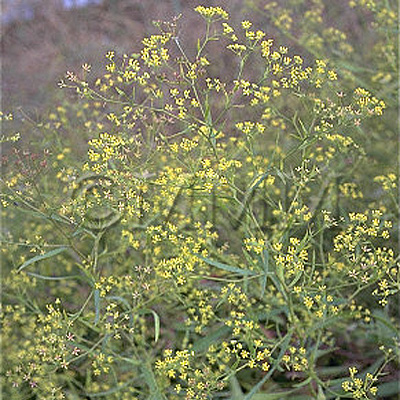
| Original plant name | Bupleurum falcatum Linn., (Mishimasaiko) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Quality for selection | The large roots which are moist and have few fragments of subterranean stems or leaves are good quality. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, antidote, painkiller, and anti-inflammatory drug, Chaihu is applied for discomfort in the hypochondrium, alternate chills and fever such as malaria, jaundice, chronic hepatitis, chronic nephritis, metabolism disorder. Chaihu is known as the main medicine for Shaoyang disease. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with cold property | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; pungent, bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, lung, heart and kidney meridians. [Actions] To disperse and reduce fever, soothe the liver to resolve depression, upraise yang qi. [Indications] Common cold with fever, alternating chills and fever, distending pain in the chest and the hypochondrium, menstrual irregularities, uterine prolapse, and prolapse of the rectum. | |||||
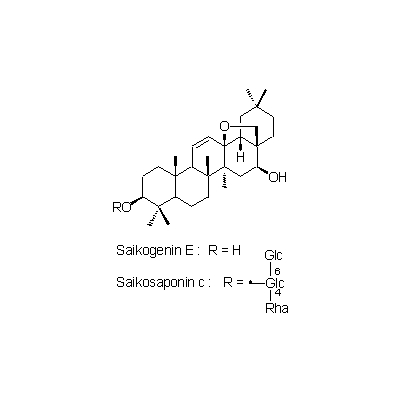
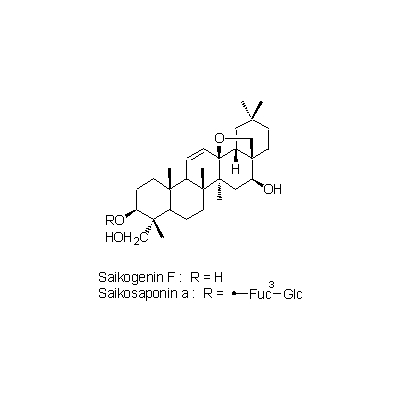
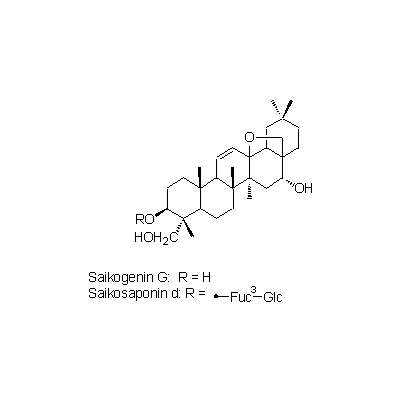
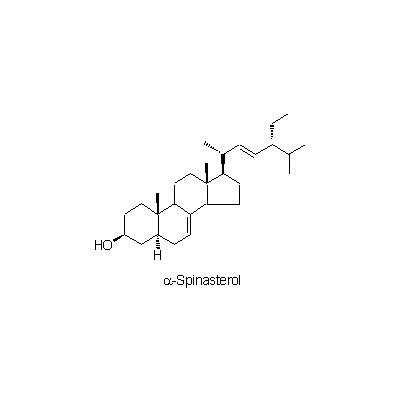
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids (*C1): Stearic acid, Oleic acid, Linolic acid, Linolenic acid Sugar (*C1): Adonitol Triterpenoids (*C1): Saikogenin E, Saikogenin F, Saikogenin G B. falcatum (*C2,C3,C4): Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Prosaikogenin A, Prosaikogenin D, Saikogenin F, Saikogenin G, Saikogenin A, Saikogenin D, Saikogenin E Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Saikosaponin a, Saikosaponin b, Saikosaponin c, Saikosaponin d, Saikosaponin e, Saikosaponin f B. falcatum (*C2,C3,C4): Saikosaponin a, Saikosaponin d, Saikosaponin b1, Saikosaponin b2, Saikosaponin c Sterols (*C1): α-Spinasterol, Stigmasterol, ⊿7-Stigmastenol, ⊿22-Stigmastenol | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Crude saponin fraction:Suppression of central nervous system, analgesic, antitussive, antifebrile, antiinflammatory, inhibition of stress ulcer, diuresis. Saikogenin A: suppression of central nervous system, analgesic, antitussive, antifebrile, antiinflammatory. Methanol soluble and water soluble fractions: analgesic, antiulcer. Saikogenin A, D: antiinflammatory, enhancement of protein synthesis in the liver, increase of the amount of glycogen in the liver, suppression of the increase in concentration of cholesterol, triglycerol and phospholipids. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF077877, AJ131344, U50224, U58552, D63489; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 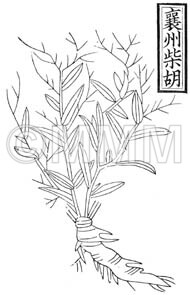 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Liver cirrhosis, Fever, Alternating cold and fever, Feeling of bitter in the mouth, Depression, Restlessness, Pain due to flatulence of hypochondrium, Irregular menstruation, Chronic diarrhea, Hematochezia due to proctoptosis, Descent of the uterus | |||||
| Formulation | Ioto, Ekkiyoeito, En'nenhangeto, Ogibekkoto, Orengedokuto, Otsujito, Kairosan, Kagenshosaikoto, Kamikihito, Kamishoyosan, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kangento, Kippihangeto, Kumisaikoto, Kumihangeto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Saikatsugekito, Saikanto, Saikokaboshoto, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, Saikokyohangekakaroto, Saikokeishito, Saikokeishikankyoto, Saikokobokuto, Saikoshimotsuto, Saikoseikansan, Saikosokanto, Saikobekkoto, Saikoyoeito, Saishakurikkunshito, Saibokuto, Saireito, Jiinshihoto, Shigyakusan, Jijintsujito, Shisoshito, Jumihaidokuto, Shunrinshakusekishito, Shosaikoto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shosaikotokakikyosekko, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shoyosan, Shoyosankato, Joshitsuhokito, Joyowaketsuto, Jingyobekkoto, Jingyobofuto, Jintanto, Shimpito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Daisaikoto, Chikujountanto, Chimobukuryoto, Tonsonto, Ninjinsan, Ninjin-yoei-to, Haidokuto, Baimoto, Hachimishoyosan, Hochuekkito, Yohaito, Yokukansan, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Reiyoukakuin | |||||
| Related drugs | Yinchaihu (Stellariae Radix) | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 121-124. C2)J.Trad.Med.,14,34(1997). C3)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,20,1274(1997). C4)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,21,588(1998). | |||||
| Remarks | The Pharmacopoeia of The People's Republic of China (2020) defines "Chaihu" (柴胡) as dried roots of both Bupleurum chinense DC., known as "Bei-chaihu" or "Jin-chaihu" (Jap. name: "Manshūmishimasaiko") and B. scorzonerifolium Willd., known as "Nan-chaihu" or "Hong-chaihu" (Jap. name: Hosobamishimasaiko) . The Japanese Pharmacopoeia (1st appendix of the14th edition) defines both B. chinense and B. scorzonerifolium as the roots of B. falcatum following the theory that they were the same species. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | |||||