Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
34.746611
113.62532799999997
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Henan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
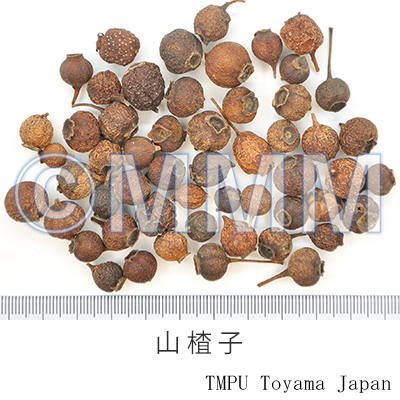
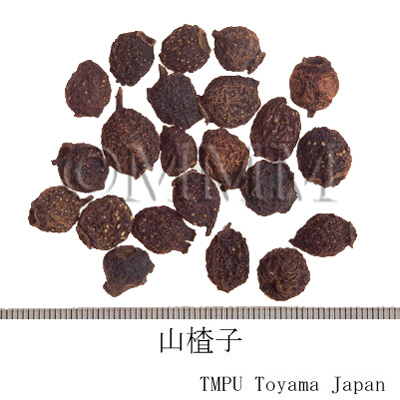
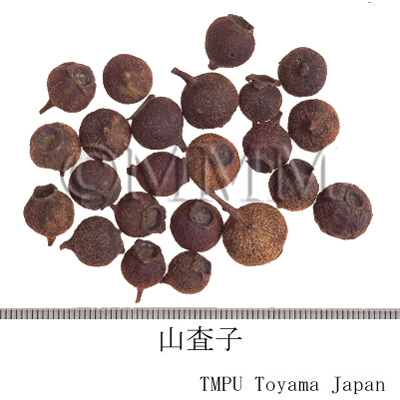
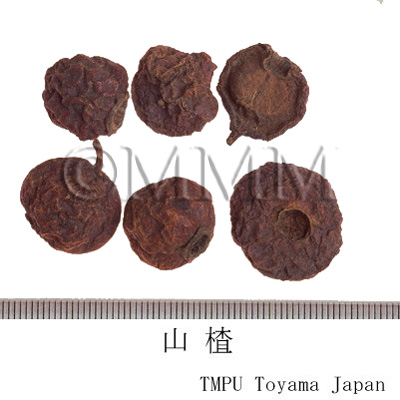
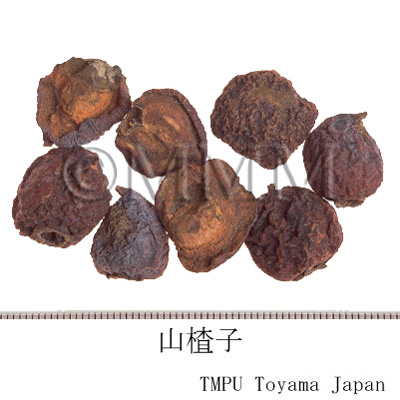
| Common name | 山楂子(山査子), Shanzhazi, Shanzha, Crataegi Fructus (JP18, CP2020), Crataegus Fruit (JP18), Hawthorn Fruit (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 山楂肉 | ||||||
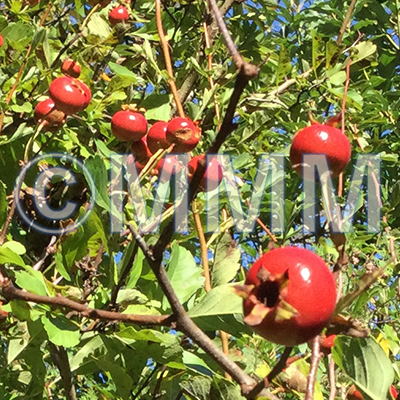
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
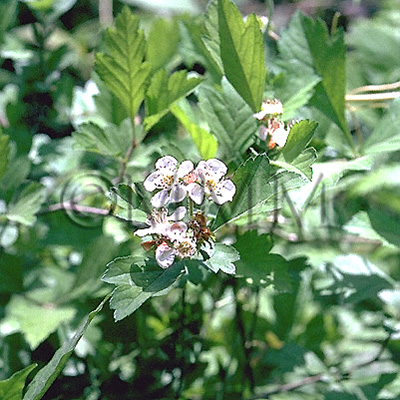
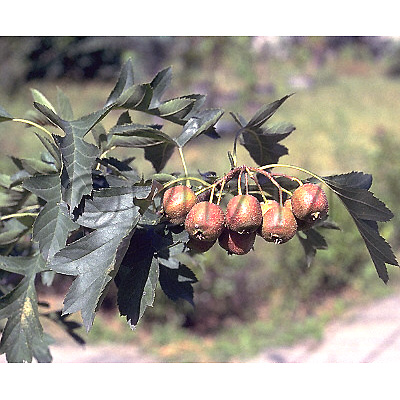
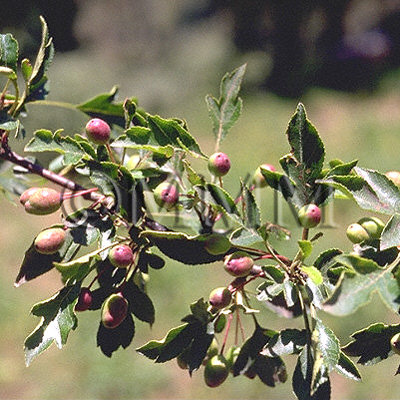
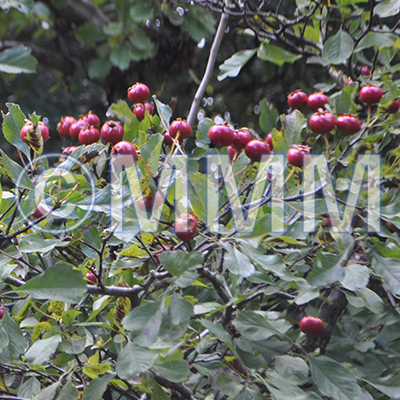
| Original plant name | Crataegus cuneata Siebold et Zuccarini1, Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge var. major N.E. Brown2, (Sanzashi1, Omisanzashi2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Rosaceae | ||||||
| Used part | Pseudocarp | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Shanzhazi is red and large. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JHMC (1989), CP (2020 ed.), JP XVIII | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a remedy for dyspepsia, diarrhea and blood stasis, Shanzhazi is applied for indigestion, stagnation of undigested food with epigastric distention, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gripe, menstrual pain, hyperemesis of after childbirth and hyperlipemia. It is also used for abdominal mass in children, fever, convulsions and peritonitis. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Digestive and evacuants | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; sour, sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach and liver meridians. [Actions] To promote digestion and invigorate the stomach, move qi and dissipate stasis, resolve turbidity and lower lipid. [Indications] Meet food accumulation and stagnation, distention and fullness in the stomach duct, abdominal pain caused by diarrhea and dysentery, blood-stasis amenorrhea, postpartum stasis and obstruction, stabbing pain in heart and abdomen, chest impediment and heart pain, pain caused by genital disease, and hyperlipidemia. | ||||||
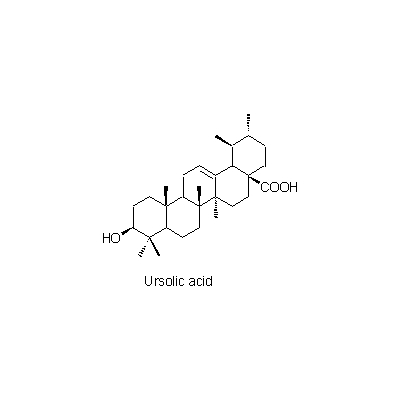
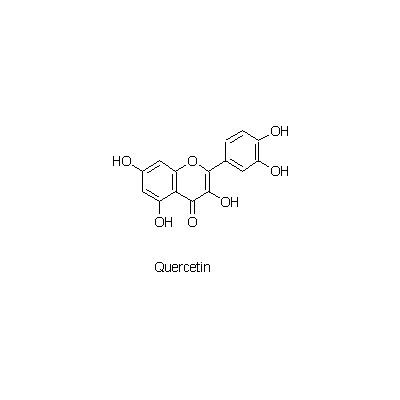
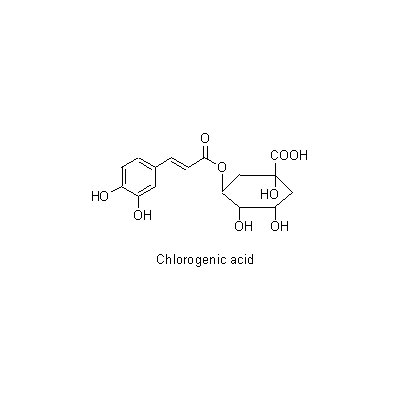
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Tartaric acid Triterpenoids (*C1): Ursolic acid Phenylpropanoids (*C1): Chlorogenic acid Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Quercetin Tannins (*C2): (-)-Epicatechin 3-O-gallate, (-)-Epicatechin, Gallic acid, Pyrogallol, 1-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(2",4"6"-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol, 1-(3'-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-(2",4",6"-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol, 5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)gamma-valerolactone, 5-(3'-Hydroxyphenyl)gamma-valerolactone, 5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)valeric acid, 5-(3'-Hydroxyphenyl)valeric acid, (3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, (3'-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 5-(3'-Methoxyphenyl)valeric acid, 2",3"-Dihydroxyphenoxyl 3-(3',4'-dihydroxyphenyl)propionate, (+)-Catechin, (-)-Epigallocatechin, (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate, 1-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(2",4",6"-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol, 1-(3'-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-(2",4",6"-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol Peptide (*C1): 脂肪分解酵素 / lipolytic enzyme Cyanogenic compounds (*C1): Amygdalin | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Enhanced secretion of gastric juices, antibacterial (dysentery bacillus). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | U06799, U16190 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Diarrhea, Lochiometra, Menorrhalgia, Hyperemesis after childbirth, Lower abdominal pain, Measles, Bacterial diarrhea | ||||||
| Formulation | Keihito, Ureitsukito, Kagen'ireito, Gyokusuito | ||||||
| Related drugs | Crataegi Folium cum Flore (Hawthorn leaf/flower), Crataegi Fructus (Hawthorn berry) | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 196-197. C2) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,45,888(1997). | ||||||
| Remarks | - In China, the fruit of Crataegus cuneata Sieb. et Zucc. (Jap. name: Sanzashi) is called Nanshanzha. The fruits of C. pinnatifida Bunge (Jap. name: Ōsanzashi) and C. pinnatifida Bunge var. major N.E. Brown (Jap. name: Ōmisanzashi) are called Beishanzha. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia difines Sanzashi and Ōmisanzashi, while the Chinese Pharmacopoeia defines Ōmisanzashi and Ōsanzashi. There are many agrotypes in Ōsanzashi, which are used for food. - In Europe, the extract of leaves and flowers of C. monogyna Jacq. and C. laevigata (Poiret) DC. (both are not classified in Japan and called just Seiyōsanzashi) are used as cardiac, antihypertensive and antiasthenic drug. It is applied to treat coronary artery diseases, arteriosclerosis, senile diseases and so on. The fruit of Seiyōsanzashi is also used in the same way. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/10/25 | ||||||