Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.572815
104.06680099999994
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Sichuan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 枇杷葉, Pipaye, Eriobotryae Folium (JP18, CP2020), Loquat Leaf (JP18, CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 蘇杷葉, 広杷葉 | |||||
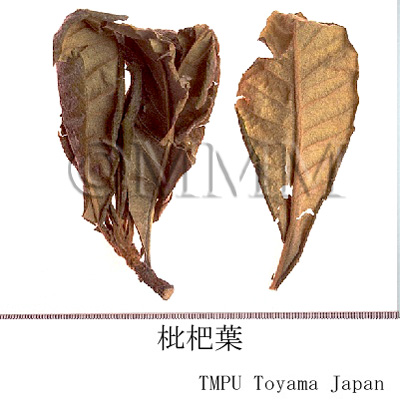
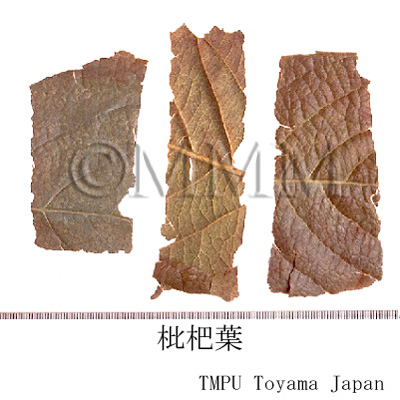
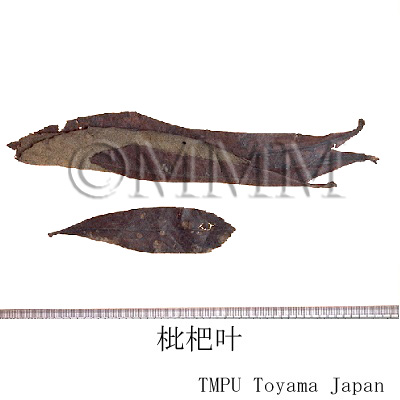
| crude drug image |
| |||||
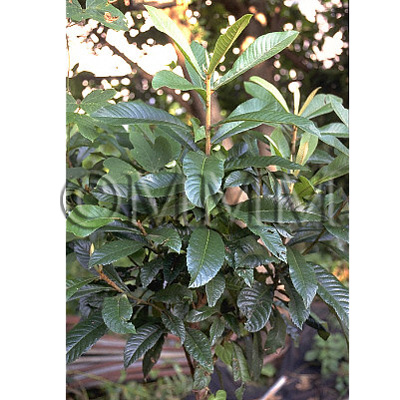
| Original plant name | Eriobotrya japonica Lindl., (Biwa) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rosaceae | |||||
| Used part | leaf | |||||
| Quality for selection | Pipaye is preferably greenish. It should be as fresh as possible. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS(1989), CP(2020 ed.), JP XVIII | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antitussive, expectorant, diuretic and stomachic, for relieving vomiting and removing heat, pipaye is applied for chronic cough, heat exhaustion and edema. The poultice of its decoction is used for dermatitis and heat rash in folk. Pipaye is also used as a bath agent. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Antitussives and antiasthmatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold ; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To clear the heat to suppress cough, downbear counterflow to check vomiting. [Indications] Cough caused by lung-heat, panting caused by qi counterflow, vomit ing and hiccup caused by stomach heat , heat vexation and thirst. | |||||
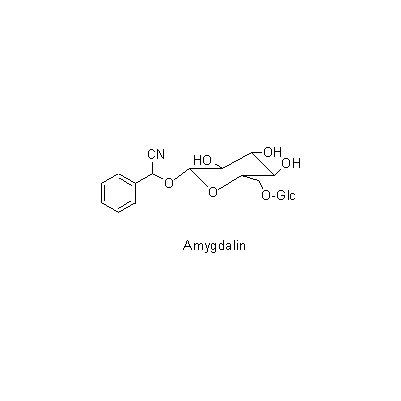
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids (*C1,C2): Ursolic acid, Oleanolic acidの配糖体,maslinic acid Tannins (*C1): タンニン Cyanogenic compounds (*C1): Amygdalin Sulfur containing alkaloids (*C1): Vitamin B1 Others (*C2): Tartaricacid, Citricacid | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (decoction: Staphylococcus aureus). | |||||
| DNA sequence | U06800, U16192 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Cough, Dyspnea, Dry throat, Pertussis, Nausea, Vomitting, Thirst, Heat exhaustion, Edema | |||||
| Formulation | Shin'iseihaito, Kanroin | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 80-82. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook,p289. | |||||
| Remarks | Usage of Pipaye: At first, the underside hairs of the leaf are eliminated. It is roasted for antitussive and expectorant uses. In order to regulate the stomach and relieve vomiting, the raw leaves are used. In Edo Period, the formulation "Biwayoto", of which the main ingredient is dried leaves of Biwa [Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl.] without hairs, was used to beat the summer heat. It is consisted of Huoxiang, Muxiang, Wuzhuyu, Rougui, Pipaye, Gancao and Ezhu. Though it is said to be a Japanese formulation, it dates back to Chinese Ming Dynasty. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||