Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
People's Republic of China
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
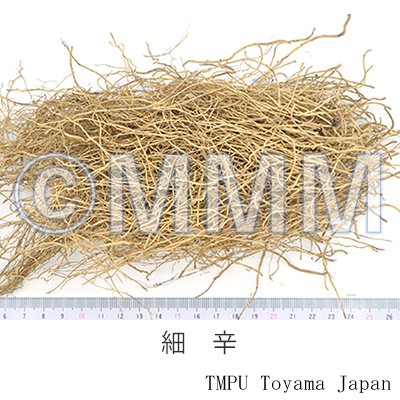
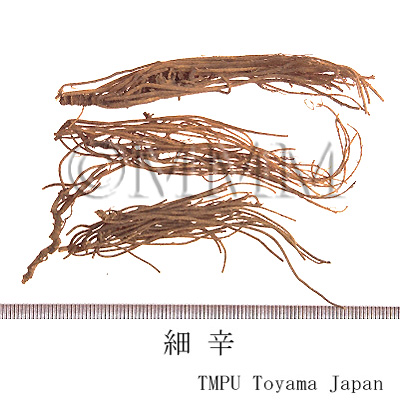
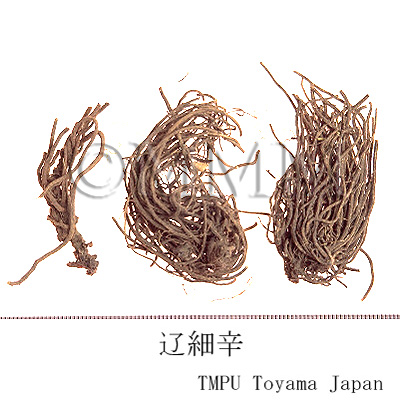
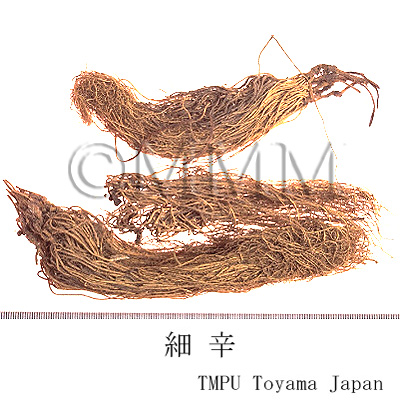
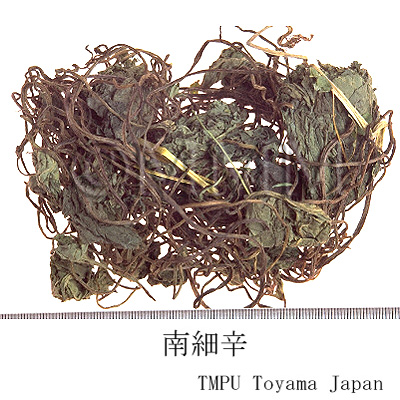
| Common name | 細辛, Xixin, Asiasari Radix (JP18), Asari Radix et Rhizoma (CP2020) , Asiasarum Root (JP18), Manchurian Wildginger Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 華細辛, 北細辛, 漢城細辛, 遼細辛 | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
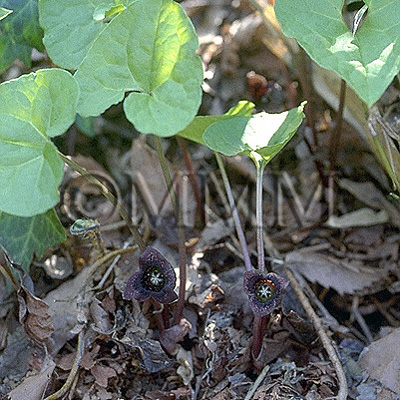
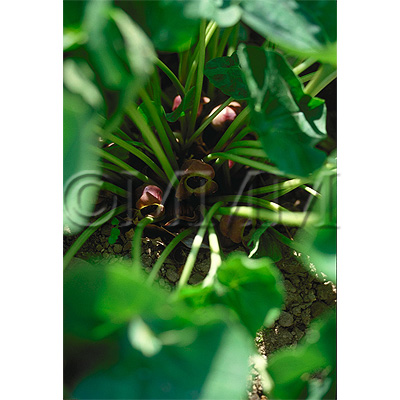
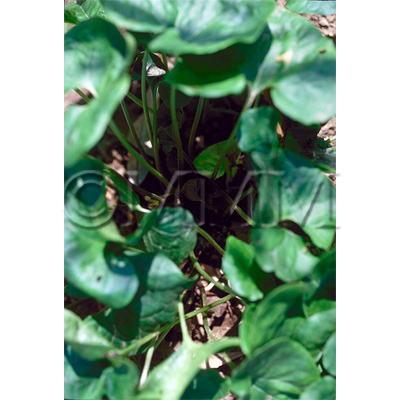
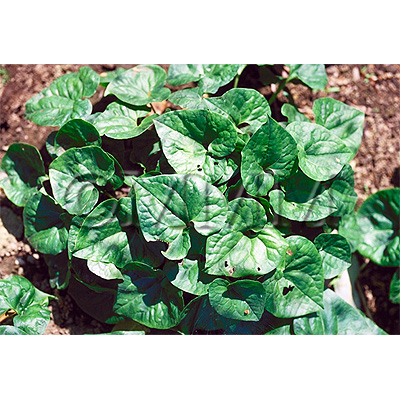
| Original plant name | Asiasarum heterotropoides F. Maekawa var. mandshuricum F. Maekawa1, Asiasarum sieboldii F. Maekawa2, (Keirinsaishin1, Usubasaishin2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Aristolochiaceae | ||||||
| Used part | root & rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Xixin has strong odour and pungency. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antitussive, expectorant, tranquilizer, painkiller and metabolic promoter, xixin is applied for cough with thin sputum due to chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis, frequent cough with headache, chest pain and a feeling of fullness in the chest. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, lung and kidney meridians. [Actions] To release the exterior, dissipate cold, dispel wind,relieve pain, open the orifices, warm the lung and resolve fluid retention. [Indications] Common cold caused by wind-cold, headache, toothache, stuffy and runny nose, allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, wheezing and cough caused by phlegm-fluid retention. | ||||||
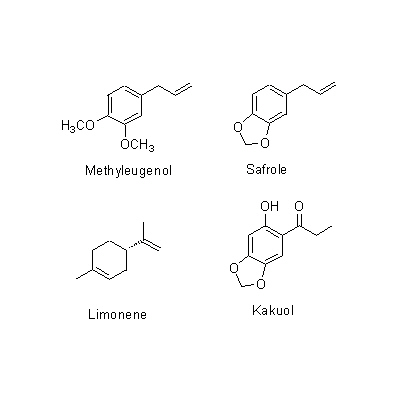
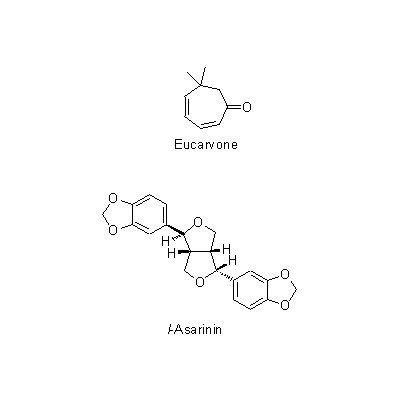
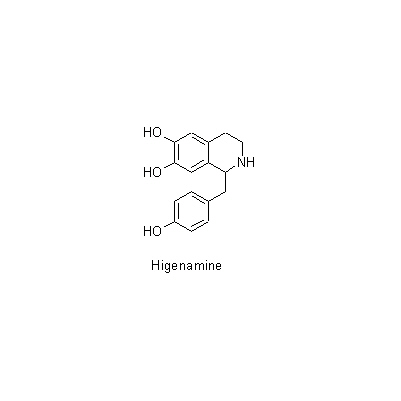
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids A. heterotropoides var. seoulense (*C1): Parmitic acid Monoterpenoids A. sieboldii (*C1): Eucarvone, Limonene, 1,8-Cineole, 3-Caren-2-on-5-ol, 2-Epoxycaran-2-on-3-ol A. heterotropoides var. seoulense (*C1): l-beta-Pinene, Eucarvone Phenylpropanoids A. sieboldii (*C1): Methyleugenol, Elemicin A. heterotropoides var. seoulense (*C1): Methyleugenol, Safrole, Kakuol A. heterotropoides var. mandshuricum (*C1): Kakuol Lignans & Neolignans A. sieboldii (*C1): l-Asarinin A. heterotropoides var. seoulense (*C1): l-Sesamin (*C2): Asatone Isoquinoline alkaloids A. heterotropoides var. mandshuricum (*C1): Higenamine Capsaicins A. heterotropoides var. mandshuricum (*C1): Pellitorine, 2E,4E,8Z,10E,-N-Isobutyl-2,4,8,10-dodecatetraenamide, 2E,4E,8Z,10Z-N-Isobutyl-2,4,8,10-dodecatetraenamide | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory, antihistaminic (water extract), sedative, antipyretic, analgesic (essential oil). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF061499, AF061500, AF061501, AF061502; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Cough, Chronic bronchitis, Bronchiectasis, Headache, Nasal obstruction, Sinusitis, Dyspnea, Somatic pain, Swelling and pain of joint, Toothache, Chill, Common cold | ||||||
| Formulation | Kagenshahakusan, Kufushokutsuto, Keikyososooshinbuto, Keishikyoshakuyakukamaobushisaishinto, Kobokumaoto, San'oto, Shakukan'oshinbuto, Shadojindaioto, Shoseiryuto, Shoseiryukasekkoto, Shoseiryugomakyokansekito, Shin'isan, Seijokentsuto, Sekiganryo (keihi), Sekiganryo (hange), Daiobushito, Daisangoshichisan, Tokishigyakuto, Tokishigyakukagoshuyushokyoto, Dokkatsukiseito, Maobushisaishinto, Meiroin, Yakammaoto, Rikkosan, Ryokankyomishingeto, Ryokankyomishingeninto, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Ryokangomikyoshinto | ||||||
| Related drugs | Tuxixin (Duheng) [see "Remarks"] | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 14-15. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 298-299. | ||||||
| Remarks | - Both Chinese Xixin (Asiasarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum, Jap. name: Keirinsaishin and others) and the Xixin of Korean peninsula (A. heterotropoides var. seoulense F. Maekawa, Jap. name: Usugesaishin) are made of the whole plant including roots. - The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines it as the root & rhizome of Asiasarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum (Jap. name: Keirinsaishin) or A. sieboldii (Jap. name: Usubasaishin). Though, both the root and rhizome don't contain Aristolochic acid, the aerial part does. It is known that aristolochic acid induces renal damages. Tuxixin is A. kooyanum Makino var. nipponicum (F. Maekawa) Kitam. It is a kind of (Japanese) "Kan'aoi". | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/28 | ||||||