Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
43.0620958
141.3543763
Production area information
Japan,Hokkaido Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 川芎, Chuanxiong, Cnidii Rhizoma (JP18), Chuanxiong Rhizoma (CP2020), Cnidium Rhizome (JP18), Szechwan Lovage Rhizome (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 仙台川芎 | ||||||
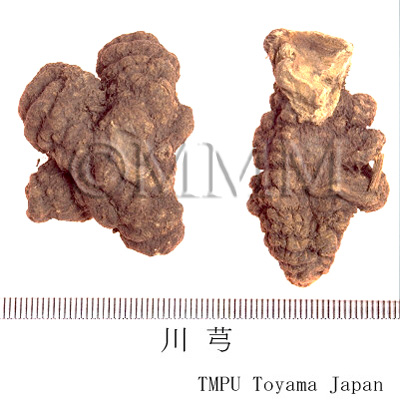
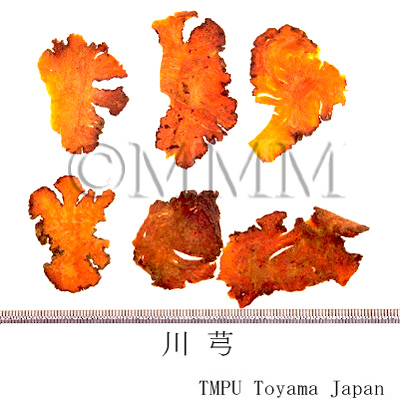
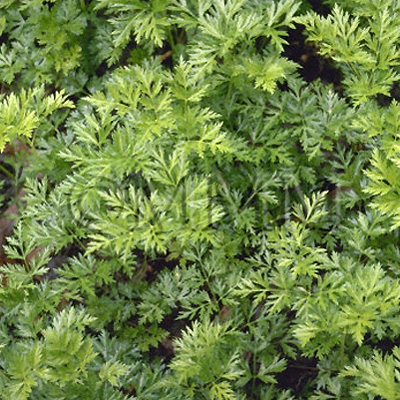
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
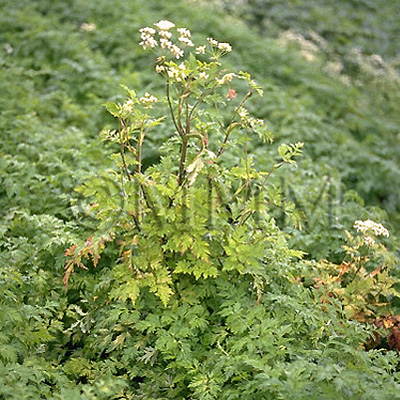
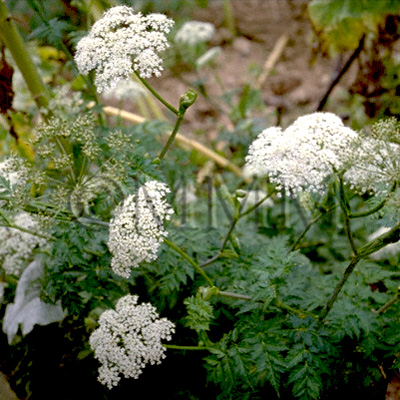
| Original plant name | Cnidium officinale Makino1, Ligusticum chuanxiong Hortorum2, (JP products: Senkyū1, CN products2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The cortex of good Chuanxiong is dark brown and the inside is pale yellow. It is large and has a intense pungency. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | For tonifying the blood and removing blood stasis, as a tonic, tranquilizer, painkiller, chuanxiong is applied for poor circulation, anemia and dysmenorrhea. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for invigorating blood circulation | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, gallbladder and pericardium. [Actions] To activate blood, move qi, dispel wind, and relieve pain. [Indications] Chest impediment with heart pain, stabbing pain in the chest and the hypochondrium, swelling and pain caused by traumatic injuries, menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea and dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain and masses, headache, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness. | ||||||
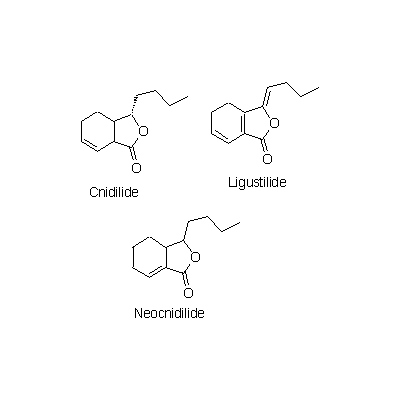
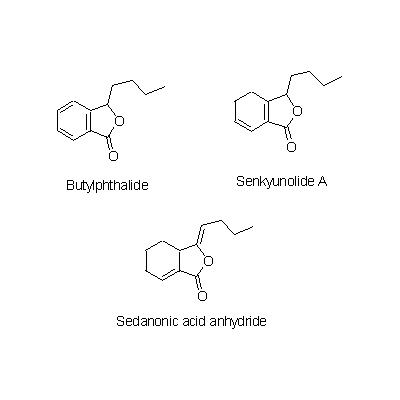
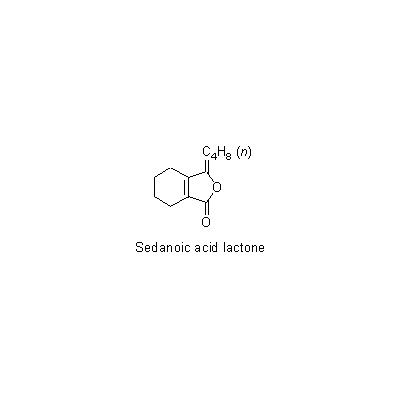
| Chemical constituent | Phenylpropanoids L. chuanxiong (*C1): Ferulic acid C. officinale (*C1): Coniferyl ferulate, Ferulic acid Phthalides L. chuanxiong (*C1): 3-Butylidene-7-hydroxyphthalide, cis-6,7-Dihydroxyligustilide, trans-6,7- Dihydroxyligustilide, Wallichilide, Butylphthalide, Butylidenephtalide, Ligustilide, Senkyunolide A, Neocnidilide C. officinale (*C1): Cnidilide, Ligustilide, Neocnidilide, Butylphtalide, Sedanonic acid anhydride, Senkyunolide A, Senkyunolide B, Senkyunolide C, Senkyunolide D, Senkyunolide E, Senkyunolide F, Senkyunolide G, Senkyunolide H, Senkyunolide I, Senkyunolide J Phenol derivatives C. officinale (*C1): Vanillin Alkaloids L. chuanxiong (*C1): 油状のアルカロイド [oily alkaloids] Other nitrogen compounds L. chuanxiong (*C1): Tetramethylpyrazine C. officinale (*C1): Tetramethylpyrazine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedative (water extract,ether extract).Estrous enhancement (extract).Mucocutaneous stimulation(the oil of Cnidii Rhizoma:external use).Effects on vasomotor center and respiratory center (the oil of Cnidii Rhizoma, produced in China:low doses;excitation, high doses;suppression).Central relaxation of the muscles,relaxation of the smooth muscles(ligustilide). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | D83027, D44586, D83028, D44572, U78388, U78448 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Irregular menstruation, Menorrhalgia, Amenorrhea, Dystocia, Retained placenta, Chest pain, Pain of lateral sides of trunk, Anginal pain, Pyogenic dermatosis, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Headache, Swelling and pain of joint | ||||||
| Formulation | Ifuto, Uyakujunkisan, Unkeito, Unseiin, Ekkiyoeito, Kagawagedokuzai, Kagenhachimotsuto, Katsuketsugedokuto, Katsuketsusan'oto, Kakkontokashin'isenkyuto, Kamishimotsuto, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kamihassento, Kikyogedokuto, Kibanto, Gyakubanto, Kyukikyogaito, Kyukichoketsuin, Kyukihochuto, Kyoseihatekigan, Kufushokutsuto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Kokikososan, Kokyuto, Kokonrokukenzokumeito, Goshakusan, Gomotsudaioto, Saikoshimotsuto, Saikoseikansan, Saikosokanto, Sansoninto, Shikonboreito, Jijintsujito, Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Shisowakiin, Shichimotsukokato, Shimotsuto, Shimotsutokakibansetsuketsumei, Shimotsutokakkekagen, Shaito, Juzentaihoto, Jumizasan, Jumihaidokuto, Jurokumiryukiin, Junhaito, Shozokumeito, Jokinritsuansan, Shin'isan, Jinkimeimokuto, Seijokentsuto, Seijobofuto, Seineitsugeutsuto, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Sesshoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Senkyuchachosan, Zokumeito, Sokeikakketsuto, Daizokumeito, Daibyakuchuin, Daibofuto, Jidabokuippo, Jizusoippo, Chimobukuryoto, Choreitogoshimotsuto, Tokiinshi, Tokisan, Tokishakuyakusanmatsu, Tokishakuyakusanryo, Tokiyoketsuto, Dokkatsukiseito, Naitaku-san, Naitaku-san, Nyoshinsan, Haidokuto, Hachimitaikaho, Hachimotsuto, Hacchinto, Bofutsushosan, Hojinto, Botanpisan, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonbukuryoto, Yokukansan, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Ryutan-shakan-to, Reiyoukakuin, Rengyoto, Rengyoto, Renjuin, Rokuutsuto | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 23-24. | ||||||
| Remarks | The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines it as the rhizome of C. officinale. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | ||||||