Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
28.228209
112.93881399999998
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hunan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 黄柏, Huangbo,Phellodendri Cortex (JP18), 関黄柏: Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex, 川黄柏: Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (CP2020), Phellodendron Bark (JP18), 関黄柏: Amur Cork-tree, 川黄柏: Chinese Cork-tree (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 関黄柏, 川黄柏 | ||||||
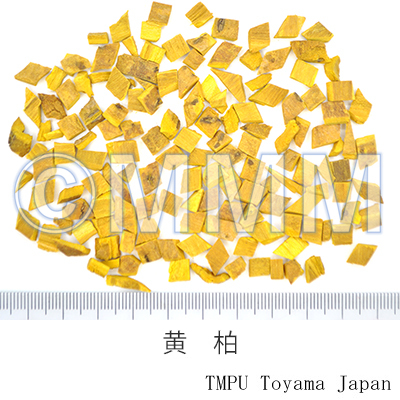
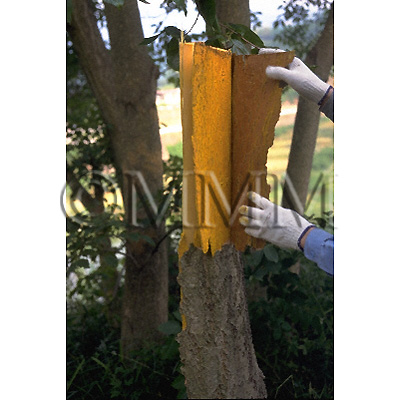
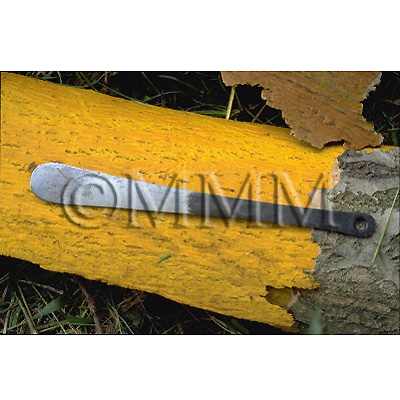
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
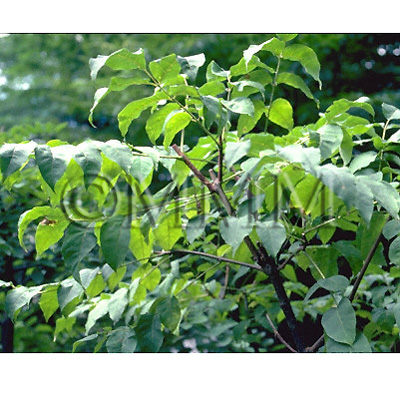
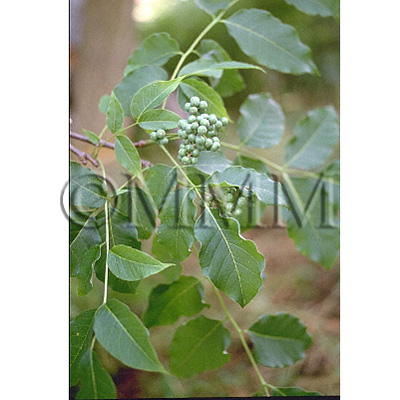
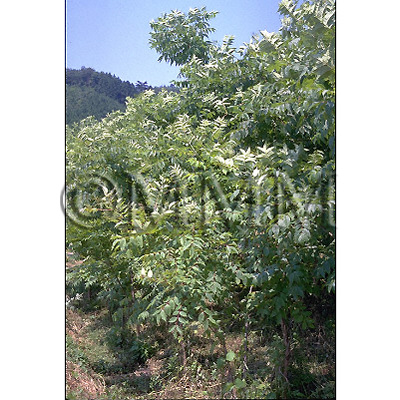
| Original plant name | Phellodendron amurense Ruprecht (incl. its variety)1 or Phellodendron chinense Schneider2, (JP: Kihada, etc.1, CN: Kihada1, Shinakihada2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Rutaceae | ||||||
| Used part | bark (without periderm) | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huangbo is bright yellow and has thick bark. It has a strong bitterness. Good powdered Huangbo becomes sticky right after being kneaded by water. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an amaroid stomachic, antiphlogistic, astringent and for relieving stagnation of intestines, Huanhgbo is applied for gastroenteritis, abdominal pain, jaundice and diarrhea. As an antiinflammatory drug, it is applied to bruises externally. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for elimination heat and dampness | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Kidney and bladder meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, dry dampness, purge fire, relieve steaming, remove toxin and treat sore. [Indications] Diarrhea, dysentery, jaundice with dark urine, abnormal vaginal discharge and pudendal itching, heat strangury with chronic pain, beriberi, leg flaccidity, bone steaming and consumptive fever, night sweating, seminal emission, sore and ulcer, swelling and toxin, eczema, and dampness sore due to dampnes-heat. | ||||||
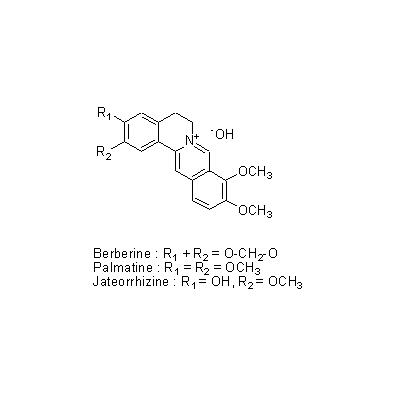
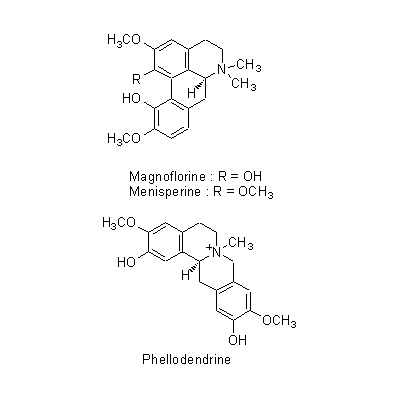
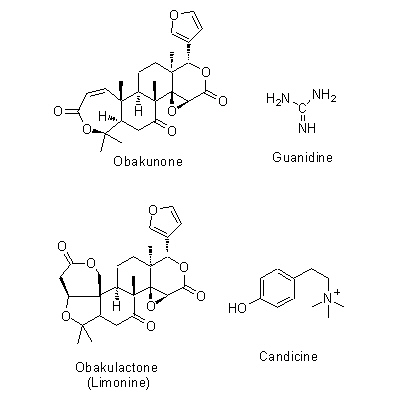
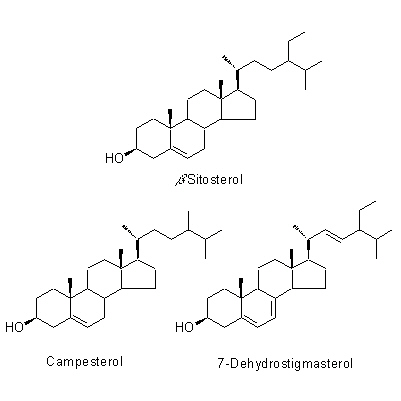
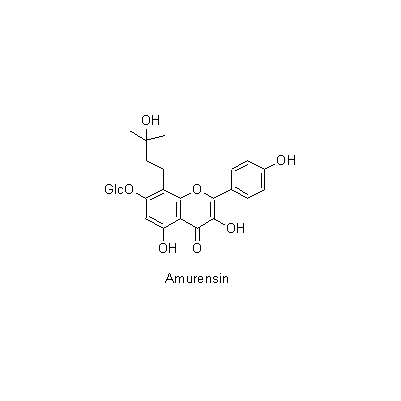
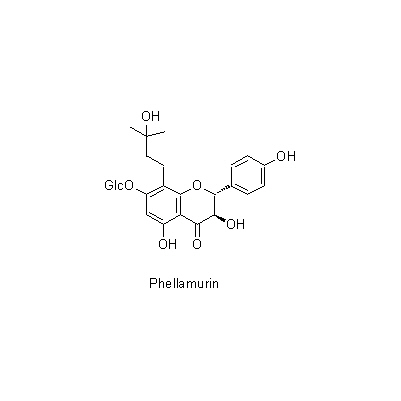
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Obakunone, Obakulactone(= Limonin) Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, Campesterol, 7-Dehydrostigmasterol 及びその/and the linolate, palmitate Flavones & Flavonols 葉/leaf (*C1): Amurensin, Phellamurin Isoquinoline alkaloids (*C1): Berberine, Palmatine, Magnoflorine, Jateorrhizine, Phellodendrine, Candicine, Menisperine Others (*C1): Guanidine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (Phellodendron Bark powder, berberin: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc.). Antiinflammation (methanol extract). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF066804, AF025523; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Gastroenteritis, Abdominal pain, Jaundice, Diarrhea, Hematochezia, Leukorrhea, Urodynia, Cloudy urine, Swelling and pain of the lower limb, Night sweats, Pyogenic dermatosis, Itching | ||||||
| Formulation | Ishoho, Unseiin, Ekigento, Ogesan, Orengedokuto, Orengedokuto, Orenshodokuin, Kamishimotsuto, Kamihachimyakusan, Keigairengyoto, Saikoseikansan, Jiinkokato, Shishishito, Jijintsujito, Shichimotsukokato, Joshitsuhokito, Jingyobofuto, Jintanto, Seishitsuto, Seishoekkito, Seichuankaito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Tokirokuoto, Hakutooto, Hakutookakanzoakyoto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Hointo, Ryutan-shakan-to, Compound Phellodendron Powder for Cataplasm, Phellodendron, Albumin Tannate and Bismuth Subnitrate Powder | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 147-150. | ||||||
| Remarks | The variants of Kihada, the original plant of Japanese huangbo, are Phellodendron amurense Rupr. var. sachalinense Fr. Schm. (Jap. name: Hirohanokihada), P. amurense Rupr. var. japonicum (Maxim.) Ohwi (Jap. name: Ōbanokihada, Kekihada) and P. amurense Rupr. var. lavallei (Dode) Sprague (Jap. name: Miyamakihada). In Japan it is also used as an ingredient for domestic medicines such as "Daranisuke" in Nara Prefecture or "Hyakusou" in Nagano Prefecture. In addition, there are variety of uses as the materials for berberine. They are cultivated in Niigata, Nagano, Nara, Kumamoto and other prefectures. The bark is removed and they are processed at the end of the rainy season. The share of Japanese Huangbo in total domestic consumption is about 20%. The remain is imported from China. In China, the bark of P. chinense is called "Chuanhuangbo" and the bark of P. amurense is called "Guanhuangbo". Generally, the content of alkaloids is higher if it is produced in southern districts. Kampo Medicine defines Huangbo as a drug for eliminating damp-heat of the lower body. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/10 | ||||||