※Click on the image to enlarge it.
| Common name | 苦木, Kumu, Picrasmae Lignum (JP18), Picrasmae Ramulus et Folium (CP2020), Picrasma Wood (JP18), Indian Quassiawood (CP2020) |
|---|
| crude drug image | 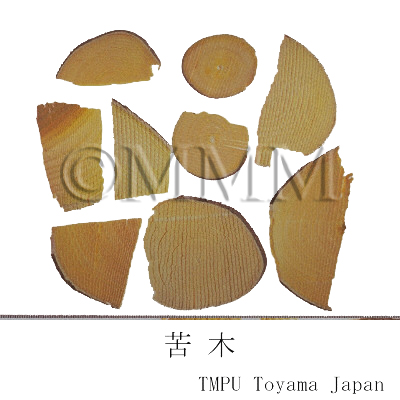 |
※Click on the image to enlarge it. |
|
|---|
| Original plant name | Picrasma quassioides Bennet , (Nigaki) |
|---|
| original plant image |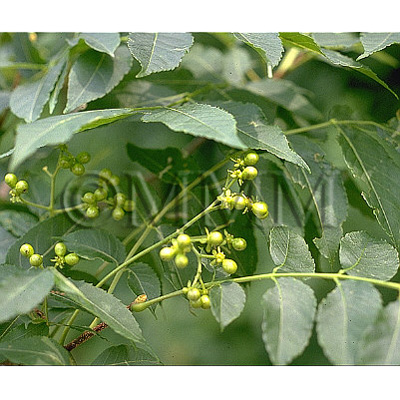  |  |
※Click on the image to enlarge it. |
|
|---|
| Family name | Simaroubaceae |
|---|
| Used part | wood (without bark) |
|---|
| Quality for selection | Good Kumu has a strong bitterness and no contamination of bark. (TN) |
|---|
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) |
|---|
| Clinical application | As an amaroid stomachic, its powder, tink or decoction is used to treat indigestion, diarrhea and gastroenteritis. It is also insecticidal and good for scabies. |
|---|
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine |
|---|
Drug effect in
traditional medicine | Traditional
classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs |
|---|
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter; slighlty toxic.
[Meridian Tropism] Lung and large intestine meridians.
[Actions] To clear heat and remove toxin, and dispel dampness.
[Indications] Common cold caused by wind-heat, swollen sore throat, dampness-heat diarrhea and dysentery, eczema, sore an d deep-rooted boil, bite wound of insect, worm or snake. |
|---|
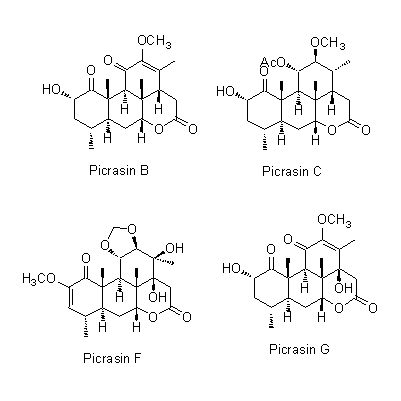
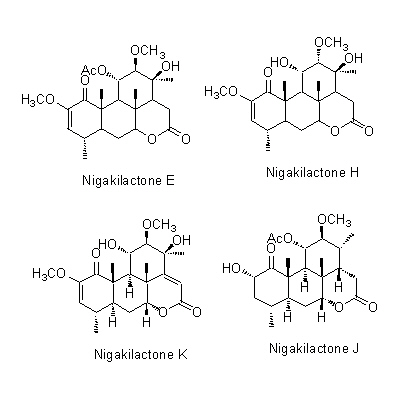
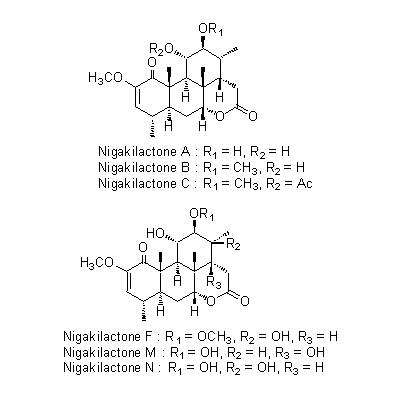
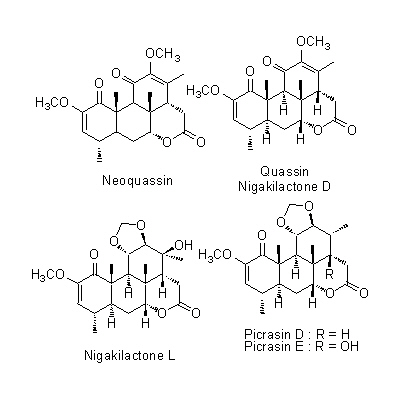
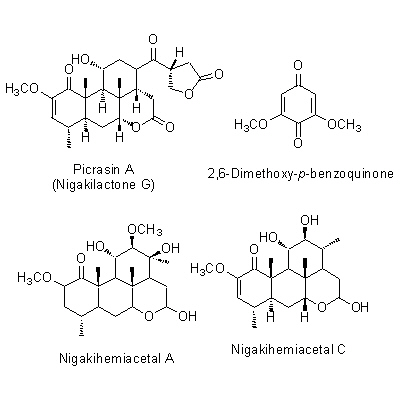
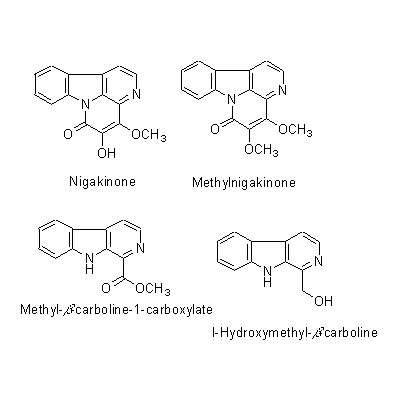
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids
(*C1):
Nigakilactone A, Nigakilactone B, Nigakilactone C, Nigakilactone D(=Quassin), Nigakilactone E, Nigakilactone F, Nigakilactone G(= Picrasin A), Nigakilactone H, Nigakilactone I, Nigakilactone J, Nigakilactone K, Nigakilactone L, Nigakilactone M, Nigakilactone N, Nigakihemiacetal A, Nigakihemiacetal C, Neoquassin, Picrasin A, Picrasin B, Picrasin C, Picrasin D, Picrasin E, Picrasin F, Picrasin G
Benzoquinones
(*C1):
2,6-Dimethoxy-p-benzoquinone
Indole alkaloids
(*C1):
Nigakinone, Methylnigakinone, 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, beta-Carbolin 誘導体/derivatives
|
|---|
| Chemical structure | |
|---|
| Disease | Dyspepsia, Diarrhea, Gastroenteritis |
|---|
| Formulation | |
|---|
| Related drugs | Jamaica quassia, Surinam quassia |
|---|
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi.
C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 177-178. |
|---|
| Remarks | Jamaica quassia is the heart wood of Picrasma excelsa Planchon (Jap. name: Jamaicanigaki). Surinam quassia is the heart wood of Quassia amara L. Both are used as an amaroid stomachic. In Japan, Kumu is substituted for these Quassiae Lignums. The branch and leaf are used for removing toxic heat in China. |
|---|
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 |
|---|
| | |
|---|