Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
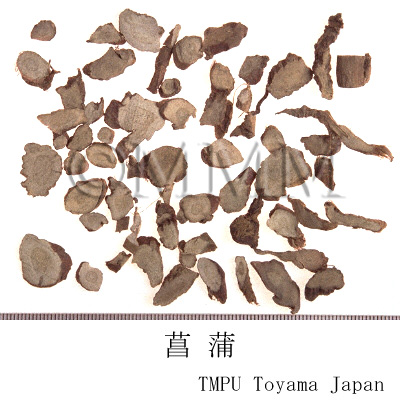
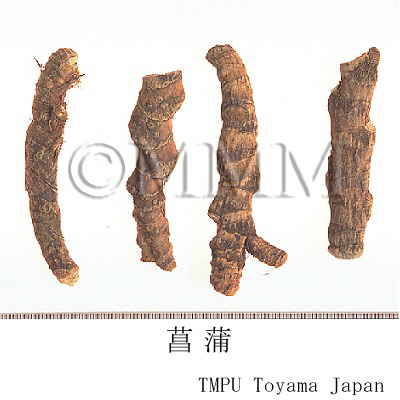
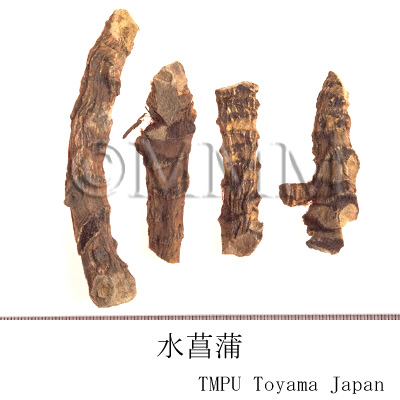
| Common name | 菖蒲, Changpu, Acori Calami Rhizoma (CP2020), Tibet Sweetflag Rhizome (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 菖蒲根,水菖蒲,蔵菖蒲 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Acorus calamus Linn. (= Acorus calamus Linn. var. asiaticus Pers.), (Shōbu) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Araceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | It is an aromatic stomachic (not commonly used because it induces nausea and vomiting) remedy. The rhizome and leaves are used as bath agent in folk. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Stimulants | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Pungent; bitter. [Actions] To warm the stomach yang, diminish inflammation and relieve pain. [Indications] Tonifying stomach yang, dyspepsia, food accumulation and stagnation, diphtheria, anthrax, etc. | |||||
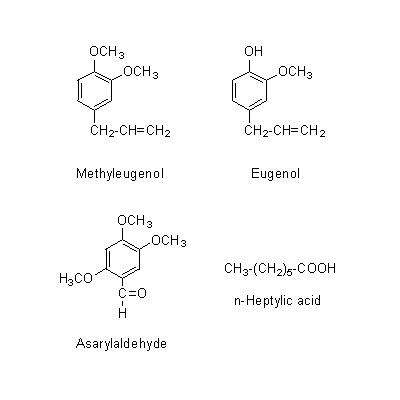
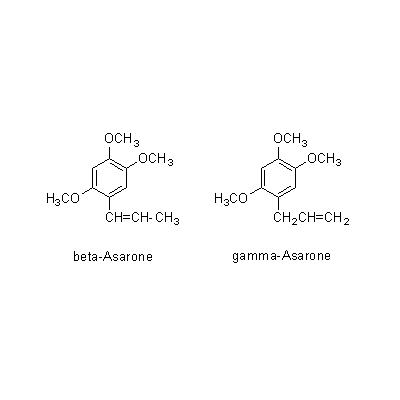
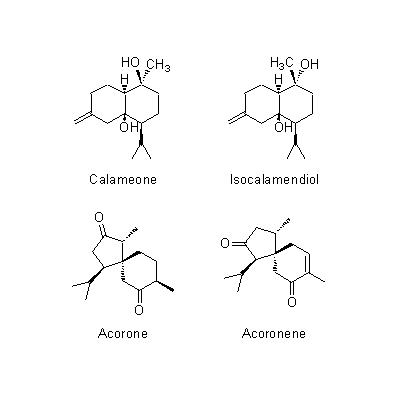
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids A. calamus (*C1): n-Heptylic acid Sesquiterpenoids A. calamus (*C1): Calameone, Isocalamendiol, Acorone, Acoronene Phenylpropanoids A. calamus (*C1): Methyleugenol, Eugenol, beta-Asarone, gamma-Asarone, Other aromatic derivatives A. calamus (*C1): Asarylaldehyde | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (cutaneous fungus), sedation (Asarone). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF209786, AB040154, D28865, L24078 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Anorexia, Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Diarrhea | |||||
| Formulation | ||||||
| Related drugs | Acori Graminei Rhizoma, Acori Graminei Radix, Vacha (Ayurveda), Shu-dag (Tobet) | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 145-146 | |||||
| Remarks | In Japan, it has been used since Heian Period. On the day of the Boys' Festival, Changpu (Jap. name: Shōbu) is hung under the eaves with Tansy, or put it in a bathtub for medicinal bath. It is widely distributed among Eurasian Continent (including Japan, China and India), Malaysian tropical zone and North America, and used as medicine. In Ayurveda (India), it is called Vacha and applied to treat abdominal pain, vomiting, memory decline, intelligence impairment, bronchitis, rhinogenous headache and mental disorder. The composition of the essential oil differs largely depending on its production area (possibly, because of differentiations in the chromosome number). The main composition of Indian Changpu is asarone. As it is said to cause liver disease and malignant tumor, some countries control or prohibit its import. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/10/13 | |||||