Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
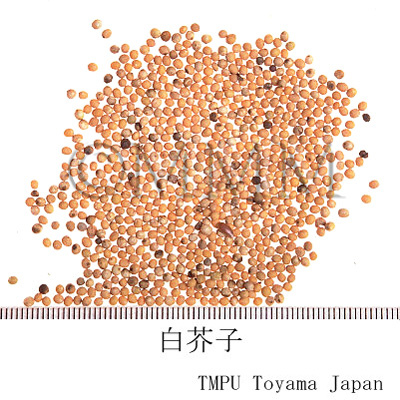
| Common name | 芥子, Jiezi, Sinapis Semen (CP2020), Mustard Seed (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 白芥子, 黄芥子 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
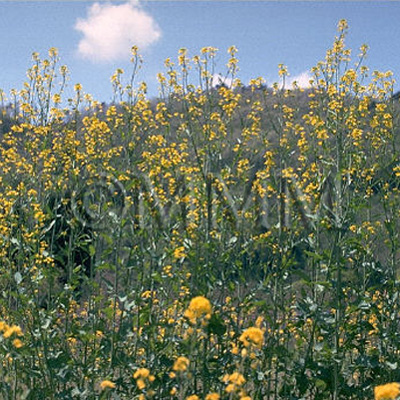
| Original plant name | 白芥子<White Mustard Seed>: Brassica alba (L.) Boiss. (= Brassica hirta Moench)1;黄芥子<Yellow Mustard Seed>: Brassica juncea Coss. (= B. juncea Czern.)2, (Shirogarashi1, Karashi2) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Brassicaceae | |||||
| Used part | seed | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Jiezi is as pungent as possible when chewed. (TN) Baijiezi (Jap. name: Byakugaishi) is said to be of higher quality. | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a stimulant, rubefacient and expectorant, jiezi, defatted and pasted with water, is applied for neuritis and pneumonia transdermally. It is widely used as a raw material for spice and volatile mustard oil. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Expectorants | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Lung meridian. [Actions] To warm the lung and sweep phlegm, disinhibit qi, dissipate binds and unblock the collaterals to relieve pain. [Indications] Cough with cold-phlegm, distending pain in the chest and the hypochondrium, phlegm stagnation in meridians, joint numbness and pain, phlegm-dampness deep multiple abscess,yin flat-abscesses with swelling and toxin. | |||||
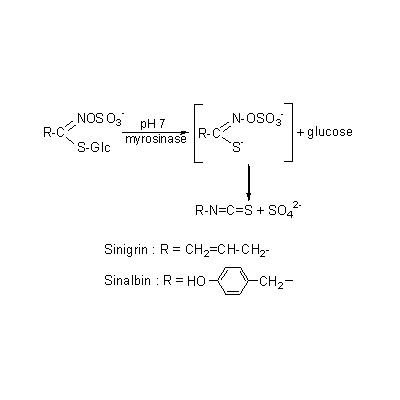
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids (*C2): 脂肪油/fatty oil 30~35%: Erucic acid, Arachidic acid, Linolenic acid Phenylpropanoids B. juncea (*C1,C2): Sinapic acid, Sinapine, Glucosinolate B. hirta (*C1): Sinalbin 2.5~5%.(酵素 myrosinase により p-Hydroxybenzoyl isothiocyanateを生成) B. juncea (*C1): Sinigrin(酵素 myrosinase により Allyl isothiocyanate を生成) B. nigra (*C1): Sinigrin 1~2.5% (同上) Others B. juncea (*C1,C2): Myrosinase | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Skin and mucosal stimulation (mustard seed oil). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF264734, AF267640, M88342, AF128093, AF128094, D10840, X05060 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Neuralgia, Pneumonia, Sputum, Cough, Swelling and pain of joint | |||||
| Formulation | Seishitsuketanto, Haiyoto | |||||
| Related drugs | Black Mustard Seed | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 232-233. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 293. | |||||
| Remarks | Jiezi (Jap. name: Gaishi) had been listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia until 1971(8th revised edition). It defines the seed of B. juncea and congeners. As a comprehensive term, Karashi, B. juncea (n=18), is amphidiploid, a natural cross between Aburana, B. rapa L (n=10), and Kurogarashi, B. nigra (L.) W. D. J. Koch (n=8). The place of its origin is said to be the Middle East or Central Asia. In China, besides narrow-defined Karashi (var. juncea) which is the material for Jiezi, the following are also used as food.: - Hakarashina (var. integrifolia Sinskaya or var. multisecta L. H. Bailey) is the pungent leaf or stem. - Nekarashina (var. megarrhiza Tsen et Lee) is the root. - Zāsai (var. tumida Tsen et Lee) is the swollen base of leaf-blade and petiole. Kurogarashi is cultivated in the Middle East and Mediterranean region as a vegetable or medicinal plant like Karashi. The seed of Kurogarashi is called Kokugaishi. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||