Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
37.9025518
139.02309460000004
Collection information
Japan,Niigata Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | カミツレ, Camitsure, Chamomillae Flos (Non-JPS2022), German Chamomile Flower (Non-JPS2022) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | カミツレ花, カモミールジャーマン, ジャーマンカモミール | |||||
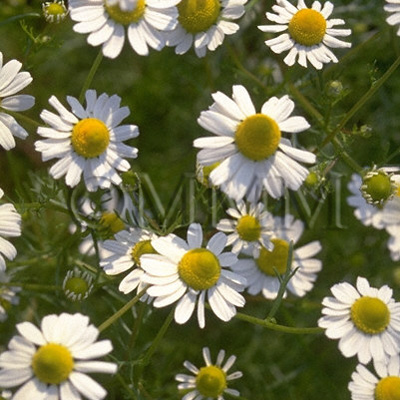
| crude drug image |
| |||||
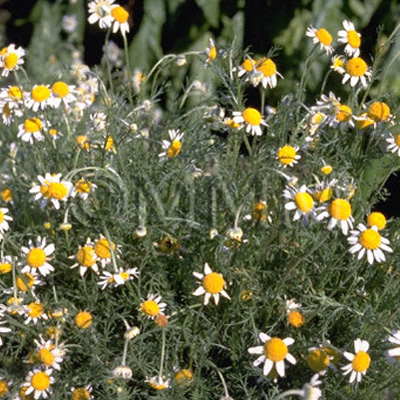
| Original plant name | Matricaria chamomilla Linn., (Kamitsure) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||
| Used part | 頭状花 | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diaphoretic, carminative, anti-inflammatory drug and antispasmodic, Chamomillae Flos is applied for common cold, headache and diarrhea. It is also applied for lack of appetite as aromatic amaroid stomachic, and rheumatism as bath agent. | |||||
| Medical system | Eueropean herbal medicine | |||||
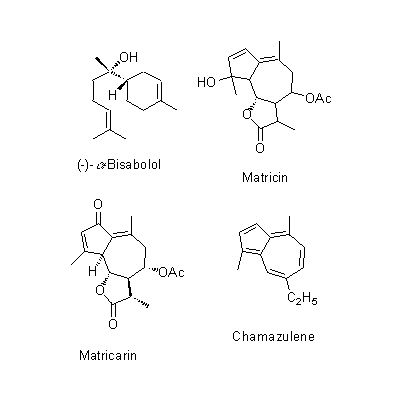
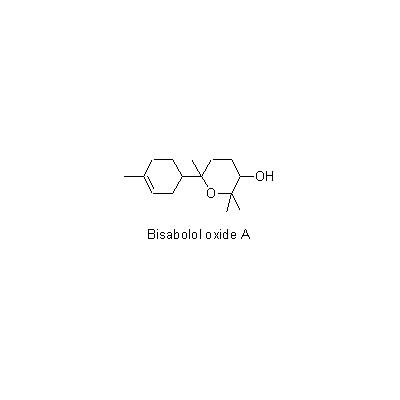
| Chemical constituent | Monosaccharides (*C1): Inositol Sesquiterpenoids (*C1,C2): l-alpha-Bisabolol, l-alpha-bisabolol oxide A, alpha-Farnesene, Matricin, Chamazulene, Matricarin, Chamomilla ester Triterpenoids (*C1): Taraxasterol Flavonoids (*C1,C2): Apigenin, Quercetin, Patulitrin, 5,4'-Dihydroxy-3,6,7,3'-Tetramethoxy-flavone, Luteolin, Patuletin, Chrysoeriol, Isorhamnetin, Apigenin 7-(6-O-acetyl)glucoside, Apigenin 7-glucoside. Coumarins (*C1): Herniarin, Umbelliferone, Esculetin Other aromatic derivatives (*C2): Anisic acid, Vanilic acid, Syringic acid, Caffeic acid | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory(chamazulene),antispasm (herniarin). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AJ296412, AJ296447, AJ009324, U82046, U82047 | |||||
| Disease | Common cold, Headache, Diarrhea, Anorexia, Rheumatism | |||||
| Formulation | not used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | Chamomillae Romanae Flos, Roman Chamomile | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. C1)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 220. C2)Integrated Essentials Parmacognosy, pp 263-264. | |||||
| Remarks | The most common herb in Europe is Chamomile. There are two kinds of Chamomile. One is German chamomile (Jap. name: Kamitsure) which is an annual grass. The other is Roman chamomile, Anthemis nobilis L. (Jap. name: Romakamitsure), which is a herbaceous perennial. The word Chamomile comes from both "Khamai" which means earth and "Melon" which means apple in Greek since its flower has the flavor of apple. The aroma slightly varies between the two varieties. The flower-head of German chamomile is commonly used in Europe especially in Germany. Its infusion has moderate sedating properties and it is applied for irritation and insomnia. It is also used to keep warm for cold constitution, sweating out, and lowering of fever in the first stage of cold and pharyngodynia. Roman chamomile is said to be the genuine Chamomile. In England, the word Chamomile indicates this one. The constituents are similar to German chamomile as well as the benefits. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/19 | |||||