Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
22.2799907
114.15879829999994
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
37.9025518
139.02309460000004
Collection information
Japan,Niigata Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
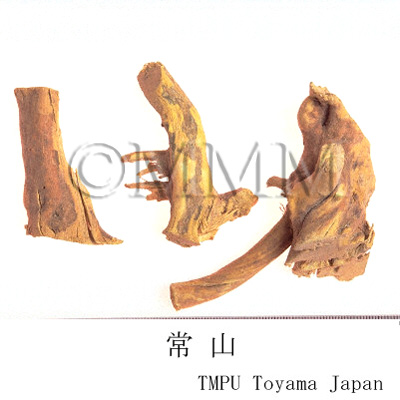
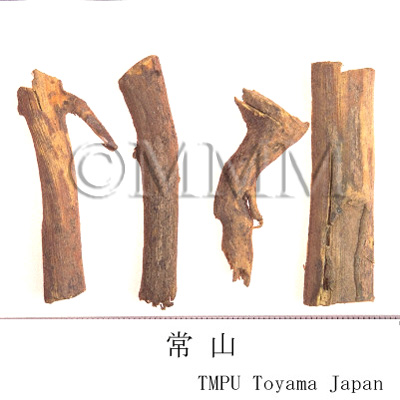
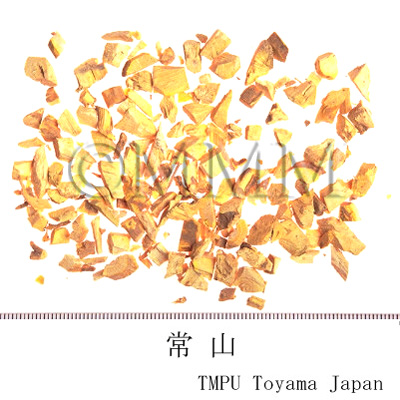
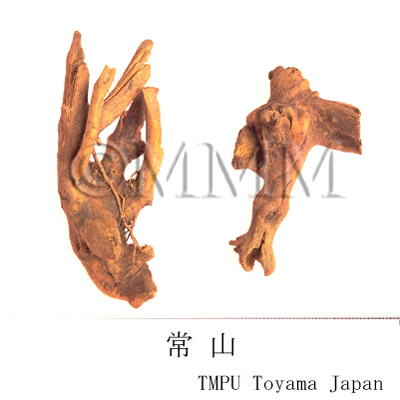
| Common name | 常山, Changshan, Dichroae Radix (CP2020), Antifeverile Dichroa Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
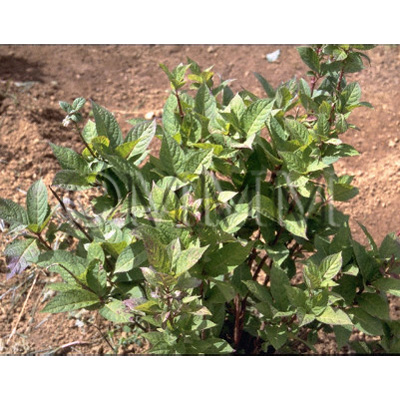
| Original plant name | Dichroa febrifuga Loureiro, (Jōzan'ajisai) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Saxifragaceae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Changshan is the root of Kokusagi (Jap. name), a small tree and tinged with yellow.(NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Changshan is an important drug for malaria. As an antifebrile and phlegm-raising, it is applied for various malarial related diseases, hypochondriac distention, and accumulation of persistent phlegm. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for vomit | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter, pungent; toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, liver and heart meridians. [Actions] To induce vomiting of phlegm and slobber, and interrupt malaria. [Indications] Phlegm-fluid retention, stuffiness in the chest and the diaphragm, and malaria. | |||||
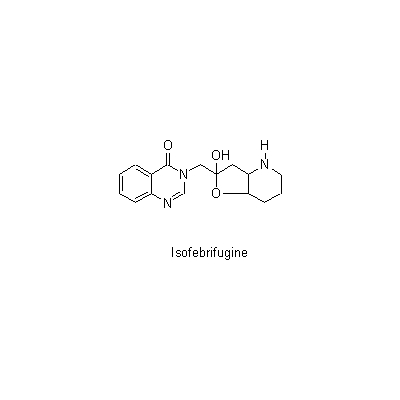
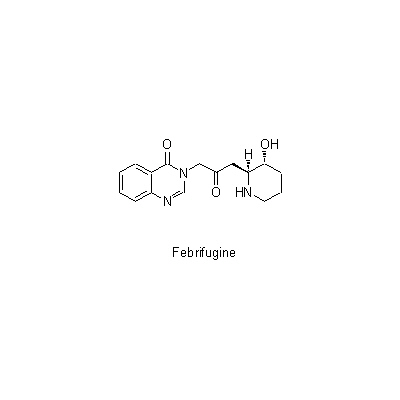
| Chemical constituent | Coumarins (*C1): Umbelliferone Alkaloids アルカロイド約 / alkaloids about 0.1% (*C1): alpha-Dichroine, beta-Dichroine, gamma-Dichroine, Dichroidine, Febrifugine, Isofebrifugine Other nitrogen compounds (*C1): 4-Quinazolone | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antimalaria (water leaching, beta-dichroine, gamma-dichroine). Cardiotonic and antipyretic (decoction). | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Feeling of pressure in the chest, Impossible to expectorate sputum, Alternating cold and fever | |||||
| Formulation | Kyugyakuto, Keishikyoshakuyakukashokushitsuryukotsuboreikyugyakuto, Jobinto, Boreito | |||||
| Related drugs | (see "Remarks") | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 146-149. | |||||
| Remarks | There are many different plants under the name of Changshan. - Japanese Changshan and Syūjōzan: The root of Orixa japonica Thunb. of family Rutaceae (Jap. name: Kokusagi). - Hakujōzan: The root of family Rubiaceae, Mussaenda parviflora Miq. or M. divaricata Hutch. - Kaishūjōzan: The root of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. of family Verbenaceae (Jap. name: Kusagi). - Dojōzan: The root of Hydrangea aspera Buch.-Ham. ex D.Don or H. strigosa Rehd. of family Saxifragaceae and other congeners. Dojōzan also includes the roots of Symplocos chinensis Druce of family Symplocaceae (Jap. name: Taiwansawahutagi), Vitex negundo L. and V. cannabifolia Sieb. et Zucc. (Jap. name: Ninjinboku) of family Verbenaceae. - Sanjōzan: The root of Berberis sibirica Pallas of family Berberidaceae and other Berberis species. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||