Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
Taiwan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
25.0329694
121.56541770000001
Collection information
Taiwan,Taipei City
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
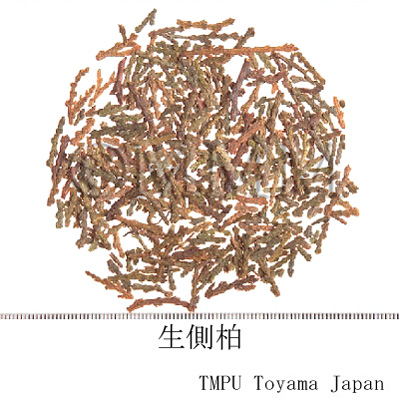
| Common name | 側柏葉, Cebaiye, Platycladi Cacumen (CP2020), Thujae Orientalis Folium et Ramulus, Chinese Arborvitae Twig and Leaf (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
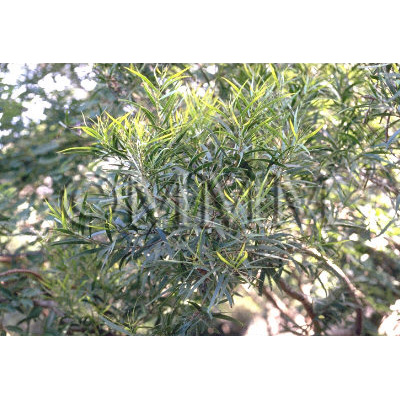
| Original plant name | Thuja orientalis Linn. (= Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco), (Konotegashiwa) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Cupressaceae | |||||
| Used part | blanch with leaf | |||||
| Quality for selection | The good one is bitter and has a strong odor. The lasher and fresher are better (NI). | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an astringent, analgesic and hemostatic, it is applied for hemorrhage and wind-damp with spleen pain such as hematemesis, epistaxis, hematochezia, hematuria, dysentery and abnormal uterine bleeding. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Hemostatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter and astringent. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, liver and spleen meridians. [Actions] To cool the blood to stanch bleeding, resolve phlegm and suppress cough , promote hair growth and blacken hairs. [Indications] Hematemesis, epistaxis, hemoptysis, bloody stool, flooding and spotting, cough caused by lung-heat, hair loss caused by blood heat, premature graying. | |||||
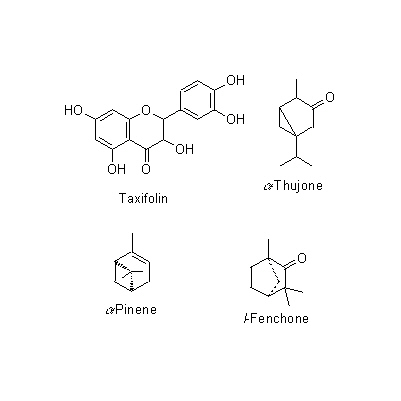
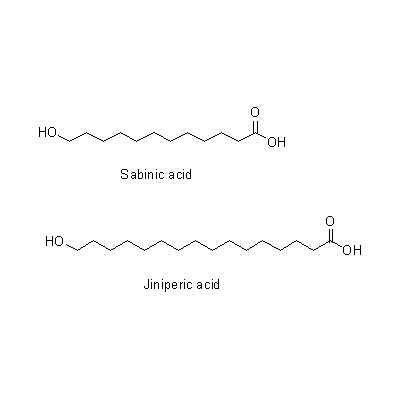
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids Chamaecyparis obtusa (*C1): estolide型臘成分(leaves) Other aliphatic and related compounds T. ovientalis (*C1): Juniperic acid, Sabinic acid (leaves) Monoterpenoids Chamaecyparis obtusa (*C1): alpha-Pinene, Limonene, d-Bornylacetate, d-Terpinylacetate (leaves) T. occidentalis (*C1): alpha-Pinene, l-Fenchone, alpha-Thujone (leaves) Sesquiterpenoids Chamaecyparis obtusa (*C1): Sesquiterpene-alchol, Hinokiic acid (leaves) Flavanones & Dihydroflavonols T. ovientalis (*C1): Taxifolin (wood) Tannins T. ovientalis (*C1): Tannin (wood) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Unknown. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF152208 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hemoptysis, Hematochezia, Hematuria, Hemorrhagic diarrhea, Melena or hematochezia | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. Ⅱ, pp 89-91. | |||||
| Remarks | In the Japanese market mostly imported Cebaiye (側柏葉) are circulated. The domestic ones are infrequently distributed and mixed with the branches and leaves of Chamaecyparis obtusa Sieb. et Zucc., ap. Endl. (Jap. name: Hinoki). The ones in the Hong Kong market are the leaves of Podocarpus annamiensis N. E. Gray of family Podocarpaceae mainly. Beyond that, the branches and leaves of Cupressus funebris Endlicher of family Cupressaceae is thought to be used under the name of Cebaiye as well. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/28 | |||||