Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
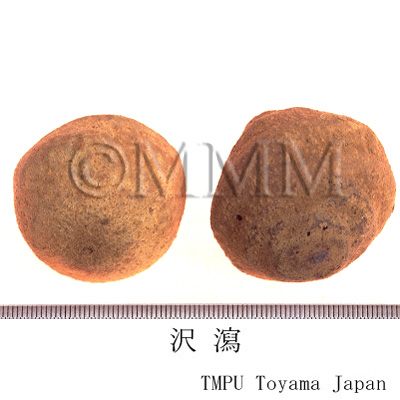
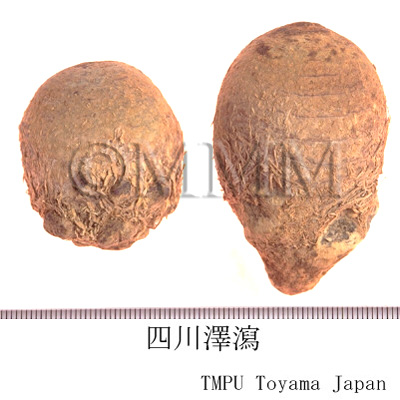
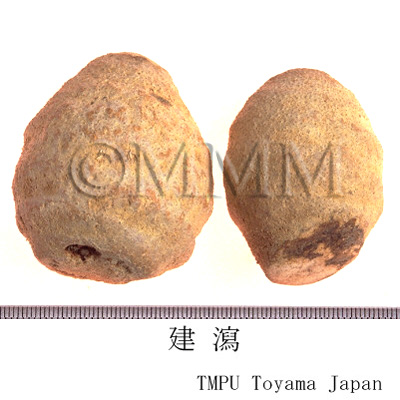
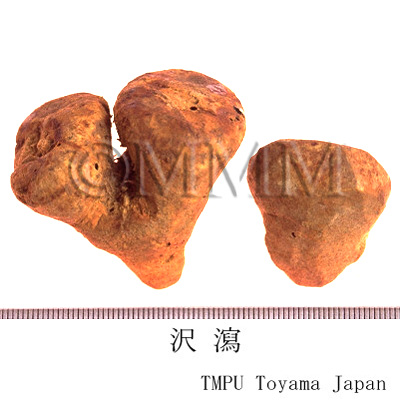
| Common name | 沢瀉, Zexie, Alismatis Tuber (JP18), Alismatis Rhizoma (CP2020), Alisma Tuber (JP18), Oriental Waterplantain Rhizome (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 建沢,川沢 | ||||||
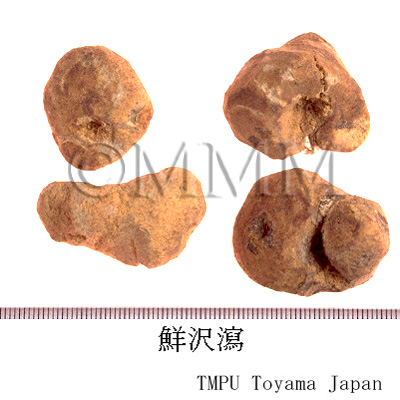
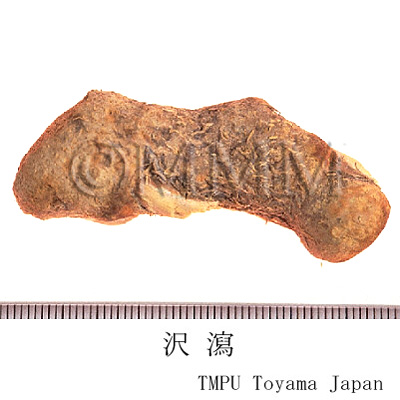
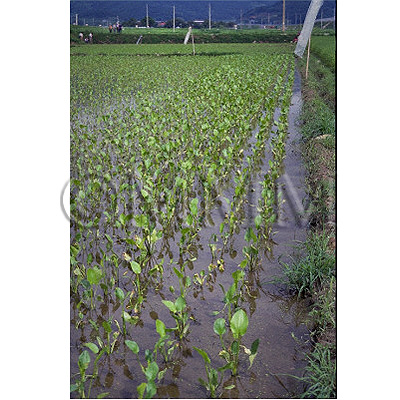
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
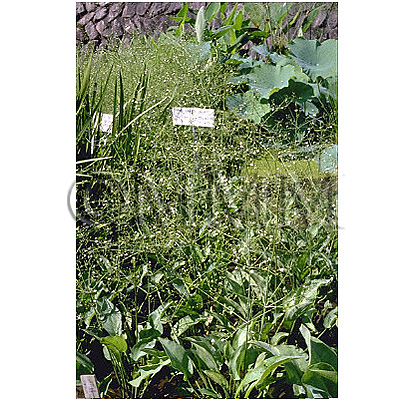
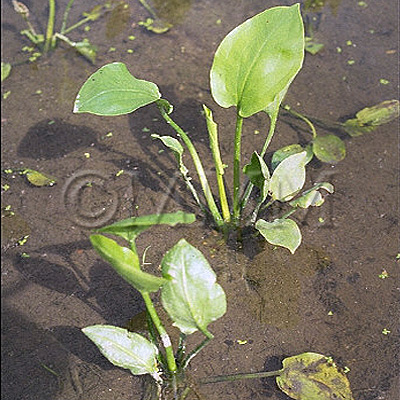
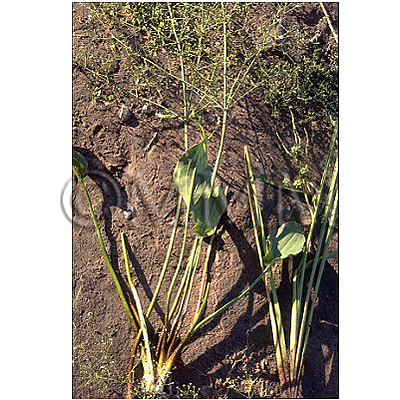
| Original plant name | Alisma orientale Juzepczuk, (Sajiomodaka) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Alismataceae | ||||||
| Used part | tuber (without periderm) | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Zexie is enlarged, spherical and the inside is whitish. The inside of second class is light brown. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a diuretic and antidiarrheal drug, zexie is applied for oliguria, frequent urination, dizziness, thirst and retention of water in the stomach. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diuretics removing dampness | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet and bland. [Meridian Tropism] Kidney and bladder meridians. [Actions] To promote urination, drain dampness, discharge heat, resolve turbidity, and lower lipid. [Indications] Inhibited urination, edema distention and fullness, diarrhea, scanty urination, dizziness caused by phlegm-fluid retention, heat strangury and hyperlipidemia. | ||||||
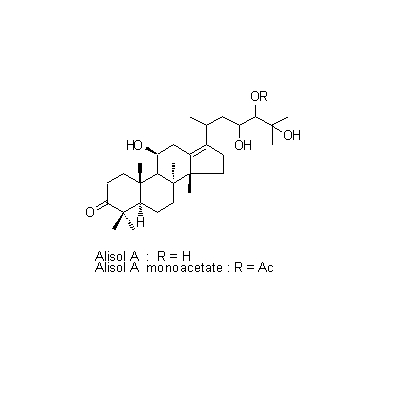
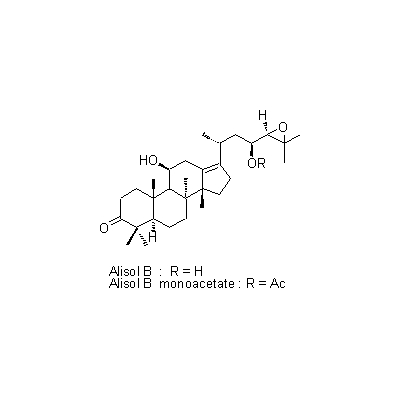
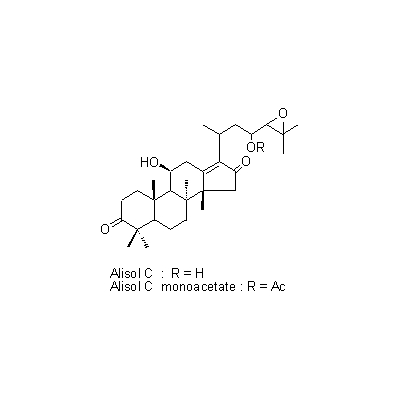
| Chemical constituent | Sugar (*C1): Sucrose Monosaccharides (*C1): D-Glucose, D-Fructose Polysaccharides (*C1): 澱粉 [polysaccharides] Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): セスキテルペン [sesquiterpene] Triterpenoids (*C1): Alisol A, Alisol B, Alisol C Other aromatic compounds (*C1): Furfural Amino acids & Peptides (*C1): アミノ酸 [amino acids], たんぱく質 [protein substance] Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Acetylcholine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Anti-fatty liver(Oriental Waterplantain Rhizome powder).Suppression of hepatopathy induced by carbon tetrachloride(benzene-acetone soluble fraction).Decrease in the cholesterol level in the liver and blood (arisol A,arisol A-24-monoacetate,arisol B-23-monoacete, arisol C-23-monoacetate) | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB040179, AF197585, L08759, AJ012291; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 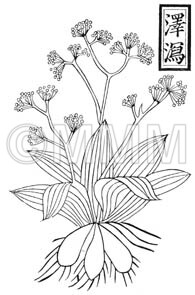 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Oliguria, Muddy and watery stool, Urodynia, Dysuria, Vertigo | ||||||
| Formulation | Ireito, Inchingoreisan, Inchinsan, Ureitsukito, Orenshodokuin, Kagen'ireito, Kamihachimyakusan, Kumihangeto, Keihito, Goshajinkigan, Gorinsan, Goreisan, Saireito, Jippito, Shogedokuto, Shohito, Shireito, Jin'en'ippo, Jingyobofuto, Jintanto, Seishitsuto, Takushato, Jiohanho, Choreito, Choreitogoshimotsuto, Tokishakuyakusanryo, Tokinentsuto, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Haikanpo, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimijiogan, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Bukuryotakushato, Fushinto, Bunshoto, Hokikenchuto, Hochujishitsuto, Mibakuekkito, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryutan-shakan-to, Rokumijiogan, Kaishun'inchinsan, Kogikujiogan | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 99-101. | ||||||
| Remarks | The one produced in Fujian Prov. is called "Jianze (建沢)" and the one produced in Sichuan Prov. is called "Chuanze (川沢)". Their outlines are different due to the difference of their cultivation methods. However, their origins are the same. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | ||||||