Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 牛膝(中国産), Niuxi, Achyranthis Radix (JP18), Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix (CP2020), Achyranthes Root (JP18), Two-toothed Achyranthes Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 懐牛膝 | ||||||
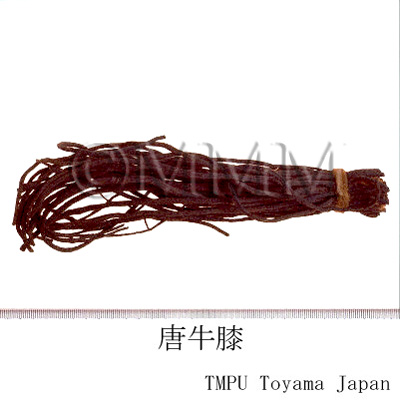
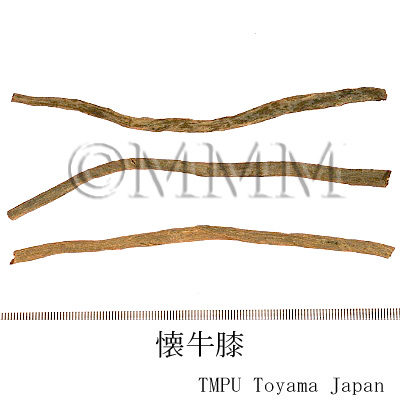
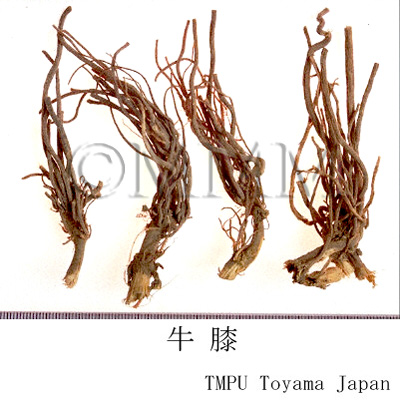
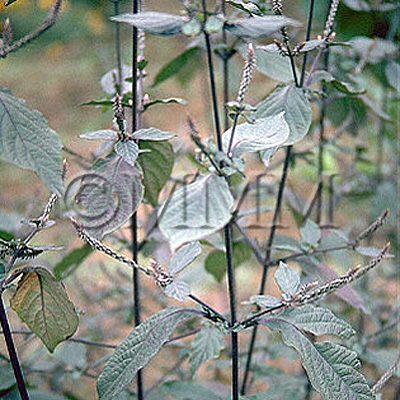
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
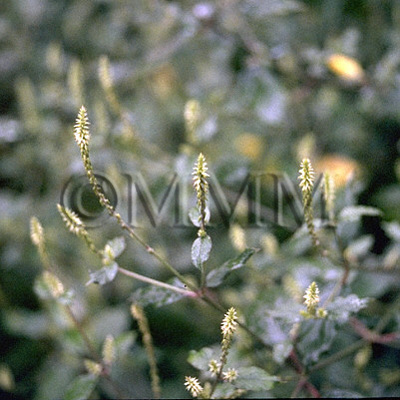
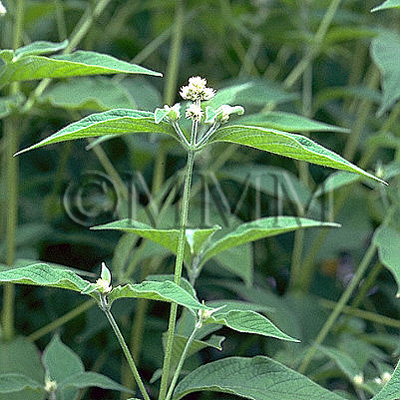
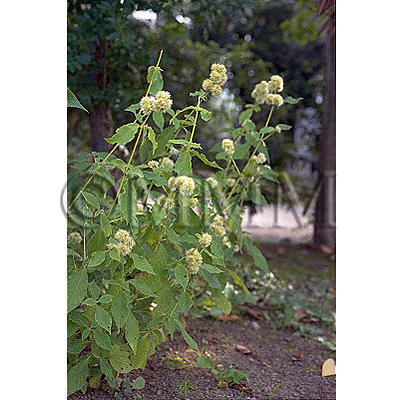
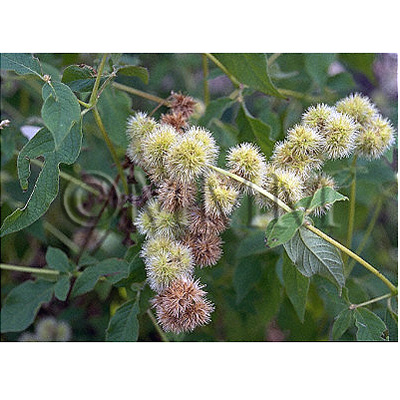
| Original plant name | Achyranthes bidentata Blume, Achyranthes fauriei H. Léveillé et Vaniot1, (Hinanainokozuchi1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Amaranthaceae | ||||||
| Used part | root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Niuxi is long, enlarged, dense, soft and yellowish-white. The Chinese Niuxi is high quality. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a diuretic and painkiller, for removing blood stasis and inducing menstruation, Niuxi is applied for menstrual disorder, blood stasis, arthritis of lumbar and knee joints, paralysis, edema and oliguria. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for invigorating blood circulation | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; bitter, sweet and sour. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and kidney meridians. [Actions] To expel stasis to unblock the meridian, tonify liver-kidney, strengthen sinew and bone, disinhibit urine and relieve stranguria, and conduct blood downward. [Indications] Amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, limp aching in the lower back and knees, lack of strength of sinew and bone, stranguria, edema, headache, dizziness, toothahe, mouth sore, hematemesis, epistaxis. | ||||||
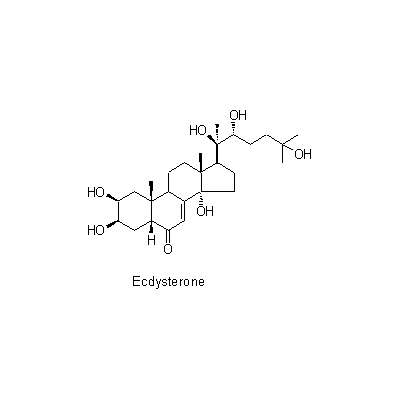
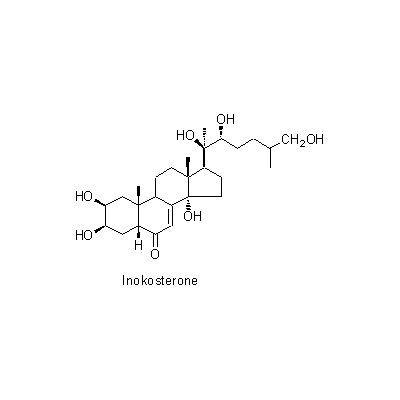
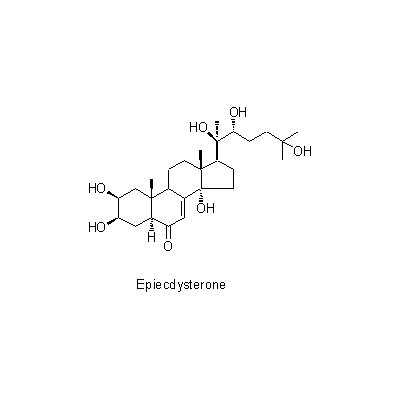
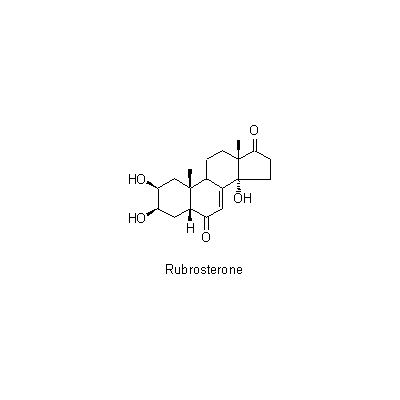
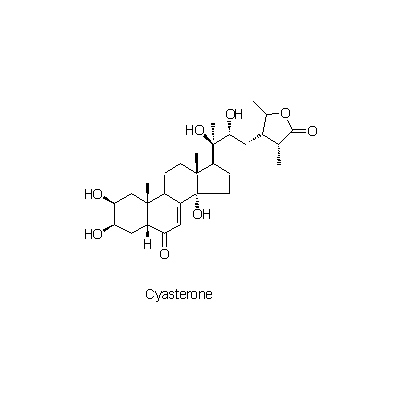
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Oleanolic acidをゲニンとするサポニン/ saponin, whose genin is Oleanolic acid Sterols (*C2): beta-sitosterol,stigamasterol Ecdysones & Phytoecdysones A. bidentata, A. longifolia (*C1): Ecdysterone, Inokosterone C. officinalis (*C1): Cyasterone Others (*C2): K-Succinate,K-Oxalate,gamma-Aminobutyric acid | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiallergy, antiosteoporosis. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 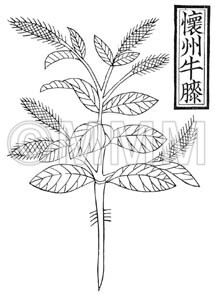 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Menorrhalgia, Extension of menstrual cycle, Amenorrhea, Intra-abdominal tumor, Dystocia, Retention of the placenta, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Swelling and pain of joint, Heaviness and powerlessness in lumber and knee, Lower back pain, Edema, Urodynia, Dysuria, Hematuria, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematemesis, Hemoptysis, Swelling and pain of the root of tooth, Stomatitis, Bleeding from root of tooth, Headache, Vertigo, Stagger | ||||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Ishoho, Kamishimotsuto, Kamihassento, Goshajinkigan, Jokinritsuansan, Sesshoin, Sokeikakketsuto, Daibyakuchuin, Daibofuto, Dokkatsukiseito, Hointo | ||||||
| Related drugs | Chuanniuxi, Tuniuxi and Wagoshitsu (Japan) | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 27-29. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 312. | ||||||
| Remarks | - Sengoshitsu (Chuanniuxi, Cyathulae Radix) is the root of Cyathula officinalis Kuan of family Amaranthaceae. It is both cultivated and found wild in Sichuan Province. It is listed in the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (2020 edi.). It is used for activating blood and restoring menstruation, strengthening joints, and curing strangury by inducing diuresis. It is applied to treat amenorrhea with mass formation in the abdomen, retention of placenta caused by stagnation of blood stasis, palsy of joints, weakness in the legs and muscle, hematuria and bruises. Chuanniuxi is also called Quantianniuxi, Mixinniuxi, Yunniuxi, Guainiuxi and Tianniuxi. Many plants of genus Achyranthes are used as Nuixi locally, which are called Tuniuxi. - The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 18th edi. defines the root of Achyranthes bidentataor A. fauriei (Jap. name: Hinatainokozuchi) as Goshitsu (Niuxi). Goshitsu cultivated in Tochigi and Nara prefectures was called Hitachi-goshitsu and wild Goshitsu was called Yabu-goshitsu. At present, no Japanese Goshitsu is produced. Botanically, Hinatainokozuchi is a variant of A. bidentata (= A. japonica Nakai), (Jap. name: Inokozuchi or Hikageinokozuchi). Therefore, the nomenclature of Hinatainokozuchi is A. bidentata Blume var. tomentosa (Honda) H. Hara. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/29 | ||||||