Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
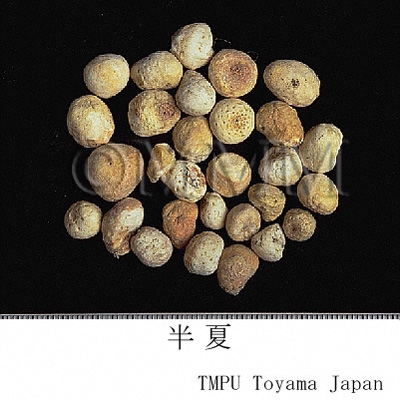
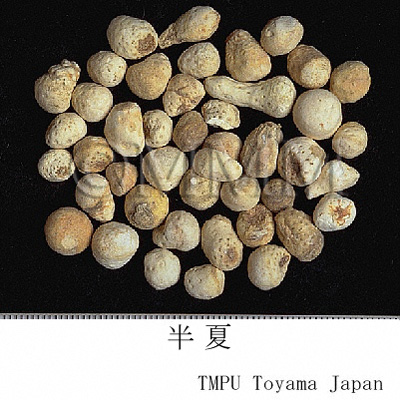
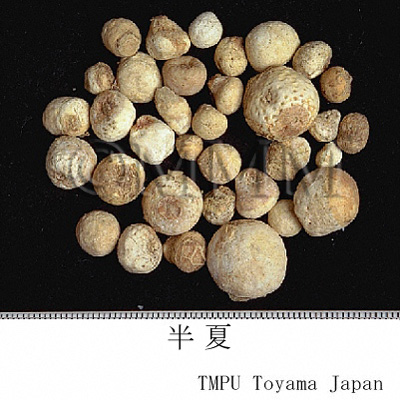
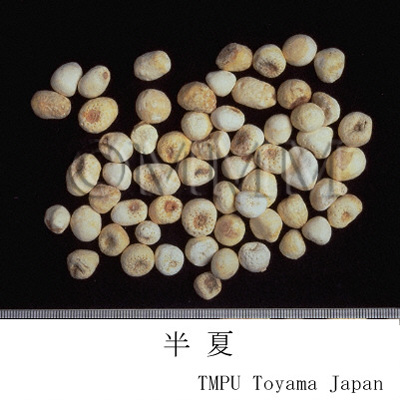
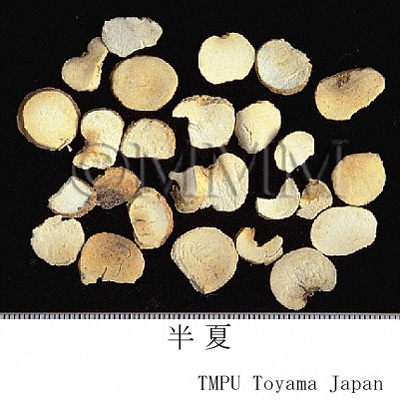
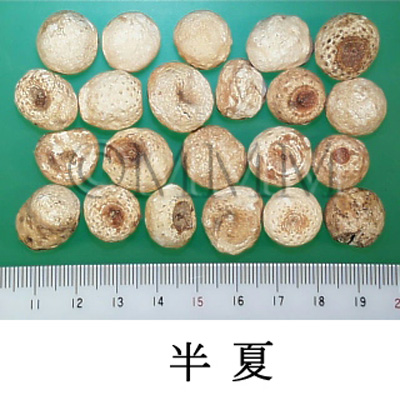
| Common name | 半夏, Banxia, Pinelliae Tuber (JP18), Pinelliae Rhizoma (CP2020), Pinellia Tuber (JP18, CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 珍珠半夏 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
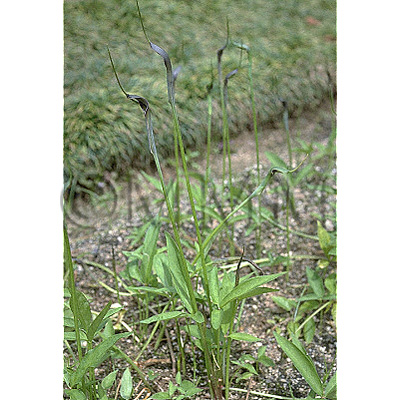
| Original plant name | Pinellia ternata Breitenbach, (Karasubishaku) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Araceae | |||||
| Used part | tuber (without periderm) | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good banxias are big, white and similarly sized. Neither red, black or stiff one is good. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a tranquilizer and expectorant, for relieving vomiting, banxia is applied for nausea with water retention in the stomach followed by ascension of qi, vomiting, cough, palpitation, dazzling, headache, acute intestinal catarrh, hyperemesis and insomnia. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Expectorants | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent; toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach and lung meridians. [Actions] To dry dampness, resolve phlegm, downbear counterflow, stop vomiting, disperse stuffiness and dissipate bind. [Indications] Dampness-phlegm, cold-phlegm, panting, cough, profuse sputum, dizziness caused by phlegm-fluid retention, dizziness caused by wind-phlegm, phlegm syncope, headache, vomiting, regurgitation, chest and epigastric stuffiness and fullness, globus hystericus; topically for swelling abscess and phlegm nodule. | |||||
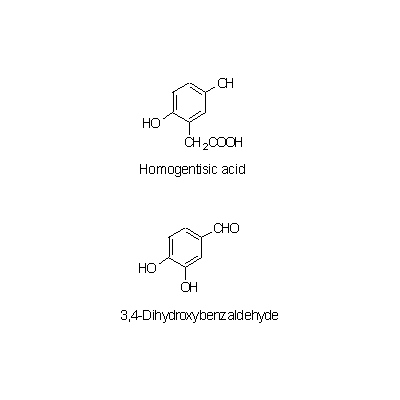
| Chemical constituent | Lipids セロブロシド [Cerebroside](1-O-glucosyl-N-2'-acetoxy palmytoyl-4,8-sphingodienineを主とする脂質) Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): 粘液物質 [mucilaginous substance], Ca-oxalate Monosaccharides (*C1): D-Glucose, Glucuronic acid, L-Rhamnose Polysaccharides (*C1): デンプン [starch], 高分子多糖 [macromolecular polysaccharide] Triterpenoids (*C1): Triterpenoid Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, beta-Sitosteryl glucoside Other aromatic compounds (*C1,C2): Homogentisic acid, Homogentisic acid glucoside, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde diglucoside Amino acids (*C1,C2): Arginine, Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Serine, Glycine Alkaloids (*C1,C2): l-Ephedrine (微量 [a tiny amount]) Other nitrogen compounds (*C1): Choline Others (*C1): 無機質 [mineral] | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiemetic (decoction), stimulation of salivation (decoction: increase in early stage, decrease in later stage). Antitussive (decoction). Suppression of stomach ulcer (water extract). Antiinflammatory (water extract). Antiallergic. | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Cough, A lot of sputum, Nausea, Vomitting, Feeling of pressure in the chest, Vertigo, Palpitation, Insomnia, Headache, Esogastritis, Acute gastritis, Hyperemesis gravidarum | |||||
| Formulation | Unkeito, Untanto, Eppikahangeto, En'nenhangeto, Ogibekkoto, Ogonkahangeshokyoto, Orento, Kaikyushokushoto, Kagenshosaikoto, Kashokuyohito, Kakkoshokisan, Kakkonkahangeto, Kabinto, Kamiuntanto, Kamishokankyoto, Kamihassento, Karoto, Kankyoninjinhangegan, Kanzuihangeto, Kanzoshashinto, Kanchuto, Kippihangeto, Kumisaikoto, Kumihangeto, Kosharikkunshito, Kochinmuyusan, Kobokushokyohangekanzoninjinto, Kobokumaoto, Goshakusan, Saikatsugekito, Saikanto, Saikokaboshoto, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, Saikokeishito, Saikoshimotsuto, Saishakurikkunshito, Saibokuto, Saireito, Shisoshito, Shahito, Shahitokaryukotsuboreito, Junkiwachuto, Shokankyoto, Shokyoshashinto, Shosaikoto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shosaikotokakikyosekko, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shoseiryuto, Shoseiryukasekkoto, Shoseiryugomakyokansekito, Shobaishashinto, Shohangeto, Shohangekabukuryoto, Shohito, Jokinritsuansan, Jin'en'ippo, Jinsoin, Seishitsuketanto, Senkonto, Sempukukataishasekito, Soshikokito, Daisaikoto, Daihangeto, Danrito, Chikujountanto, Chikuyosekkoto, Jizutsuippo, Chimobukuryoto, Chuseito, Chokoshiteito, Chokobukuryoto, Chotosan, Teizento, Tokito, Tokibyakujutsusan, Tokibyakujutsuto, Nijutsuto, Nichinto, Haikanpo, Bakumondoto, Hangesanryo, Hangekankyosan, Hangeto, Hangekobokuto, Hangekobokushichimotsuto, Hangeshashinto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Bushikobeito, Bunshinkiin, Henseishinkiin, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonbukuryoto, Yakammaoto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Rikakuto, Rikkunshito, Ryokankyomishingeto, Ryokankyomishingeninto, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Ryokito, Rokuutsuto, Rokumotsuogonto, Fukankinshokisanryo | |||||
| Related drugs | Shuibanxia, the tuber of Typhonium sp. (see "Remarks") | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 45-47. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 327. | |||||
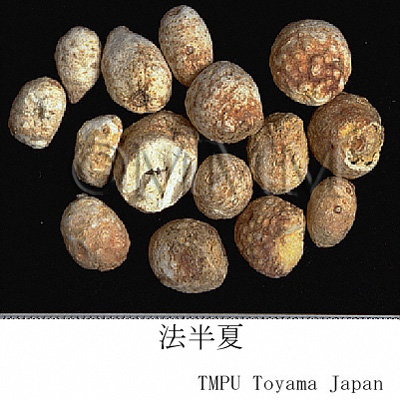
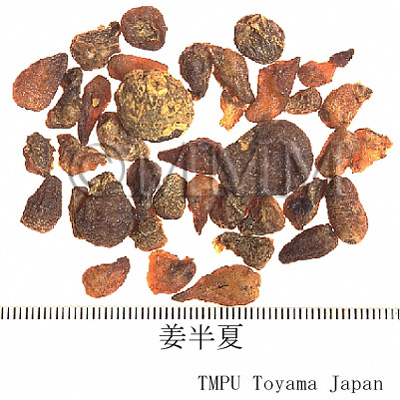
| Remarks | "Banxia (半夏)" is sometimes used after being processed. Processed "Banxia" consists of "Fabanxia (法半夏)" and "Jiangbanxia (姜半夏)". "Fabanxia (法半夏)" is processed with "Gancao (glycyrrhiza/liquorice)" and burnt lime. It is often used for eliminating dampness and resolving phlegm. "Jiangbanxia (姜半夏)" is processed with "Shengjiang (fresh ginger)" and alum. It is often used for lowering the adverse flow of qi to stop vomiting. In rare cases, the tuber of Pinellia pedatisecta Schott, P. tripartita Schott (Jap. name: Ōhange) or Arisaema spp. are blended into Chinese Banxia in the market. "Shuy-banxia (水半夏)" is the tuber of Typhonium sp. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||