Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
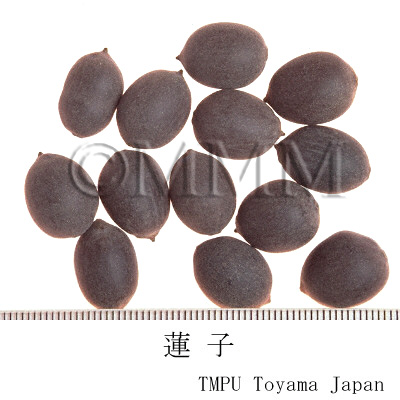
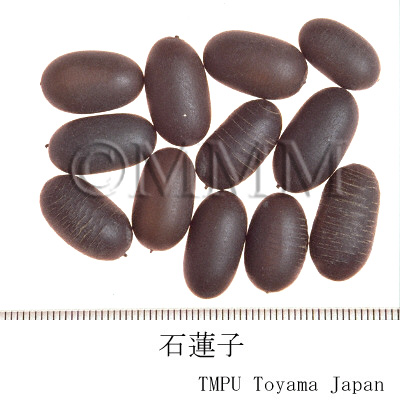
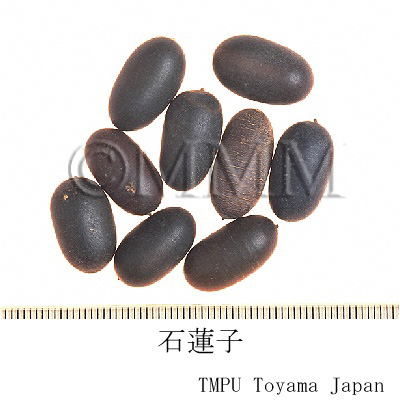
| Common name | 石蓮子, Shilianzi, Nelumbinis Fructus, Lotus Fruit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 蓮実 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Nelumbo nucifera Gaertner, (Hasu) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Nymphaeaceae | |||||
| Used part | mature fruit | |||||
| Quality for selection | Shilianzi produced in Hunan Prov. is high quality. | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2015 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Shilianzi is applied for a complete lack of appetite due to diarrhea or vomiting. Generally, it is used as Lianzi (Jap. name: 蓮肉-Renniku) after removing its seed coat and kernel. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Astringents and haemostatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet, astringent. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, kidney and heart meridians. [Actions] To tonify spleen to check diarrhea, check vaginal discharge, tonify kidney to astringe essence, nourish the heart to tranquilize the mind. [Indications] Diarrhea caused by spleen deficiency, vaginal discharge, seminal emission, palpitation and insomnia. | |||||
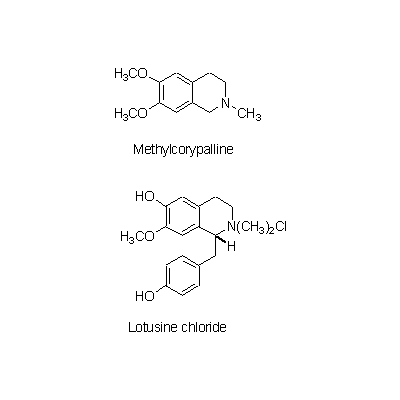
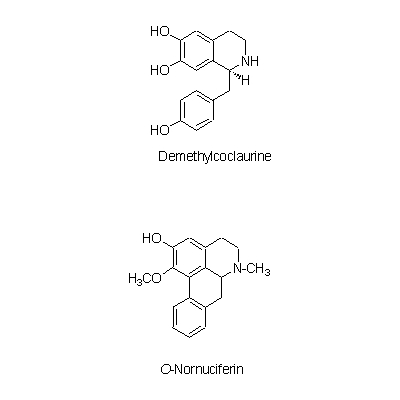
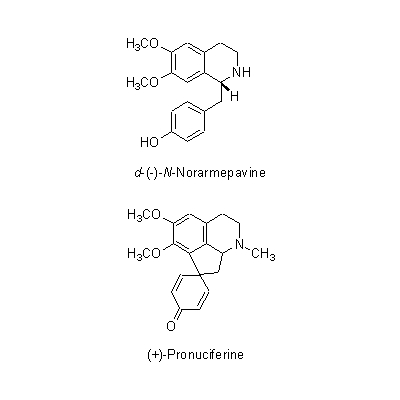
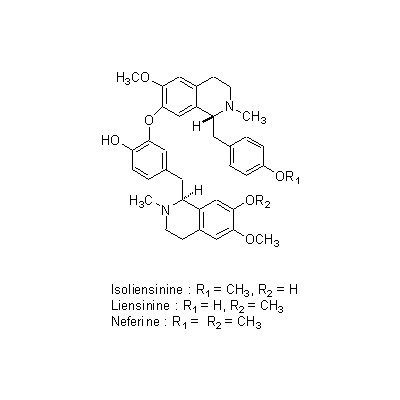
| Chemical constituent | Oligosaccharides (*C1): Raffinose(種子/seed) Polysaccharides (*C1): 澱粉/starch(種子/seed) Alkaloids (*C1): 幼芽/plumule: Methylcorypalline, Lotusine chloride, Demethylcoclaurine, Isoliensinine, Liensinine, Neferine, N-Nornuciferine, O-Nornuciferine, (+)-Pronuciferine 花床/blossom end:d-(-)-N-Norarmepavine, Liriodenine, N-Nornuciferine, Nuciferine Others (*C1): 種子の組成/seed composition:蛋白質/protein 16.6%, 脂肪/fat 2.0%, 炭水化物/carbohydrate 62.0%, Ca 0.089%, P 0.285%, Fe 0.0064% | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Vasodilator activity of coronary artery (methylcorypalline), relaxation of uterus smooth muscle (demethylcoclaurine). | |||||
| DNA sequence | M77033, M82396, M82397, M82398, M82399, M82400, M82401, M82402 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Bacterial diarrhea, Chronic diarrhea, Vomitting, Anorexia | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | Nelumbinis Semen,Nelumbinis Embryo/Nelumbinis Plumula,Nelumbinis Receptaculum, Nelumbinis Stamen,Nelumbinis Folium,Nelumbinis Rhizomatis Nodus | |||||
| References | C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 216-217. | |||||
| Remarks | Nelumbo nucifera Gaertner (Jap. name: 蓮, Hasu) is used as various medicines depending on its part, as follows.: fruit (the crude drug name: Shilianzi, Jap. name: Sekirenshi ), seed (Renniku), plumule which is in the center core of mature seed (Renshishin), fruit receptacle (Renbō), stamen (Renshu), leaf (Kayō), nodes of rhizome (Gūsetsu), etc. These are listed in the Pharmacopoeia of The People's Republic of China separately. - "Renshishin" (蓮子心, Nelumbinis Embryo/Nelumbinis Plumula) has effects of clearing the heat of heart, antipyretic, tranquilizer and quenching thirst. It cures vexation, thirst, hematemesis and pollution. The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China describes "Its action is removing heat from heart and calming the nerves, restoring the coordination between the heart and kidney, checking emission and arresting bleeding. It is applied for penetration of heat into the pericardium, impaired consciousness and delirium, break down of the normal physiological coordination between heart and kidney, insomnia and seminal emission, blood fever and hematemesis." - "Renbo" (蓮房, Nelumbinis Receptaculum) is used for hemostasis and removing blood stasis. It is applied for metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, hematuria, bleeding hemorrhoid, and hyperemesis after childbirth. - "Gūsetsu" (藕節, Nelumbinis Rhizomatis Nodus) is used for hemostasis and removing blood stasis. It is applied for hematemesis, hemoptysis, nasal hemorrhage, hematuria, metrorrhagia, and metrostaxis. - There are two varieties of Shilianzi in Chinese market at present, Tianshilianzi (Jap. name: 甜石蓮, Tensekiren) and Kushilianzi (Jap. name: 苦石蓮, Kusekiren). The former, Tensekiren, the fruit of Hasu, is the real one. The latter is the seed of Caesalpinia minax Hce. of family Leguminosae, which is called "Rouachintou" (老鴉枕頭) and produced in Yunnan and Guangxi. It can not be substituted. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2020/11/26 | |||||