Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
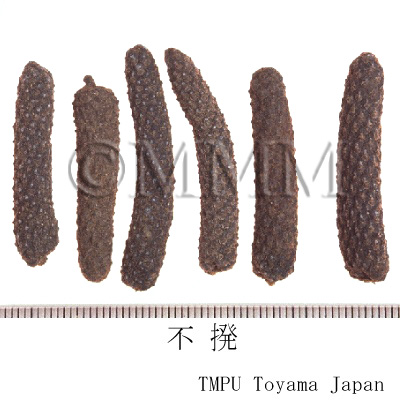
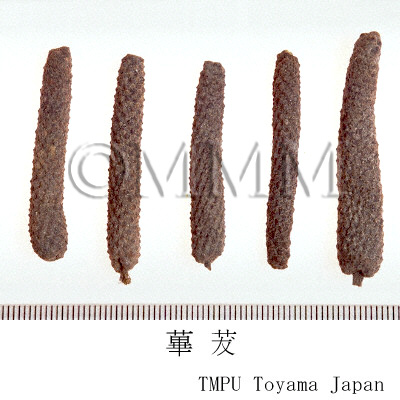
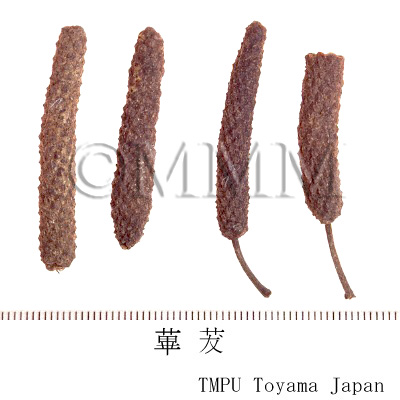
| Common name | 蓽撥, Bibo, Piperis Longi Fructus (CP2020), Long Pepper (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
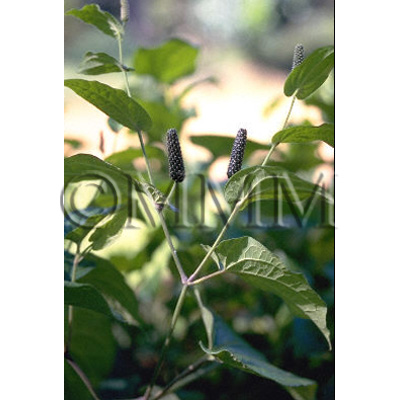
| Original plant name | Piper longum Linn., (Hihatsu) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Piperaceae | |||||
| Used part | immature spike | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an aromatic stomachic, analgesic, antidiarrheal and antitussive, it is employed to treat headache, toothache, diarrhea, vomiting, etc. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Hot; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Stomach and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To warm the middle energizer, dissipate cold, direct qi downward and relieve pain. [Indications] Cold pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, vomiting, diarrhea, and qi stagnation, caused by congealing cold, chest bi disorder, heart pain, headache, and toothache. | |||||
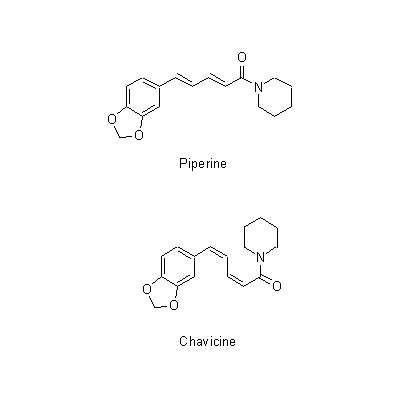
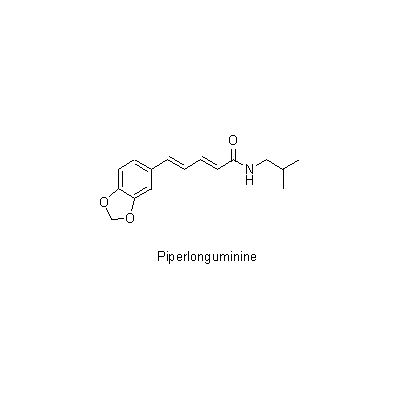
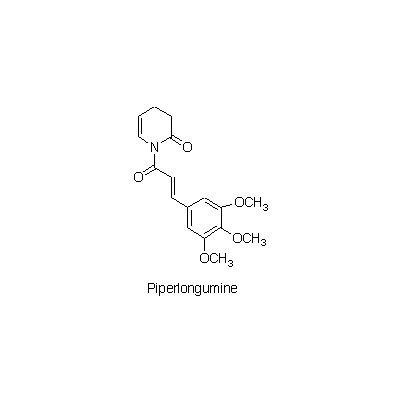
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C2): 8-Heptadecene, Heptadecane Sesquiterpenoids (*C2): Germacrene D, ar-Curcumene, beta-Caryophyllene Other aromatic derivatives (*C1): Piperine, Chavicine, Piperlongumine, Piperlonguminine | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedation, antiinflammatory, antimalarial (moderate effect), inducing GST (beta-caryophyllene), decrease serum triglyceride levels, antiinflammatory (ar-curcumene). | |||||
| DNA sequence | L41586 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Upper abdominal pain, Headache, Toothache, Diarrhea, Vomiting | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | "Pippali" in Ayurveda and "Pi-pi-ling" in Tibetan medicine | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, p 291. C2) J. Essent. Oil Res., 12, 603-608 (2000). | |||||
| Remarks | In India, the root called "Pippali-moolam", as well as the fruit "Pippali" is used for medicine which is a detoxicant for snakebite and other venoms. However, the root is not used in China. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/06/12 | |||||