Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
31.2303904
121.47370209999997
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Shanghai City
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
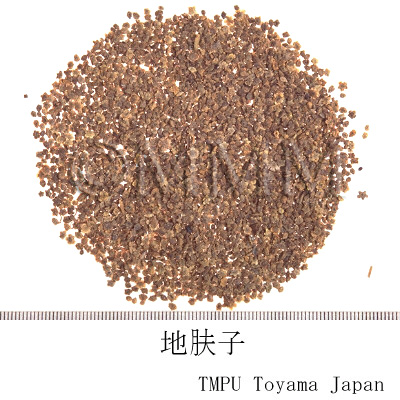
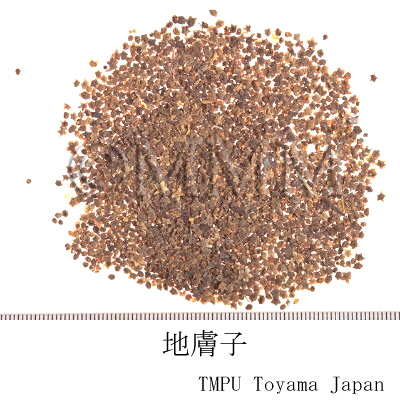
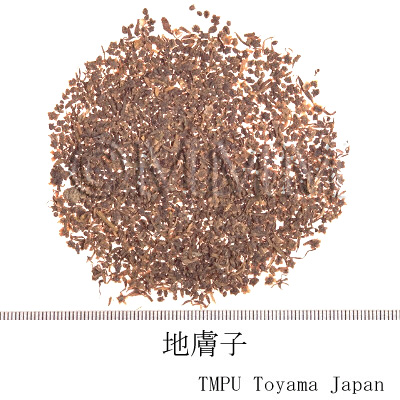
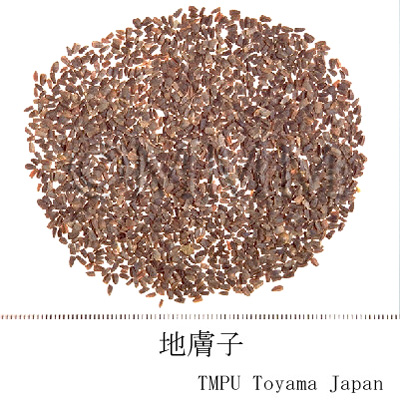
| Common name | 地膚子, Difuzi, Kochiae Fructus (CP2020), Belvedere Fruit (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
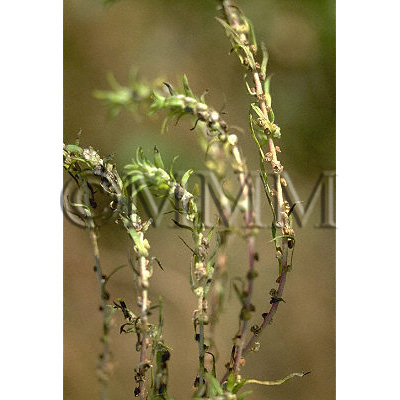
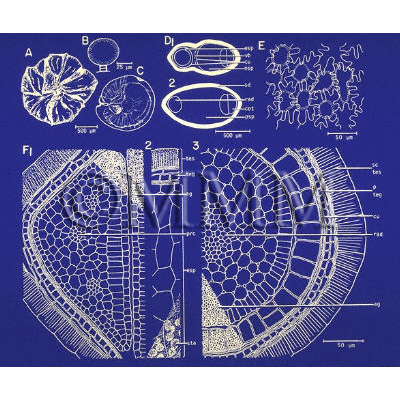
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
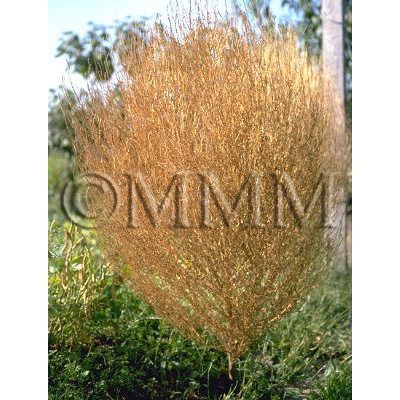
| Original plant name | Kochia scoparia (L.) Schrader (B1), (Hōkigi) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Chenopodiaceae | ||||||
| Used part | mature fruit | ||||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antidote and diuretic, it is employed for the treatment of gonorrhea, difficulty in urination, edema, beriberi, skin lesion of dampness type, scabies, etc. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diuretics removing dampness | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Kidney and bladder meridians. [Actions] To clear heat and drain dampness, and dispel wind to relieve itching. [Indications] Slow and painful urination, pudenda! itching, vaginal discharge, rubella, eczema, itching of skin. | ||||||
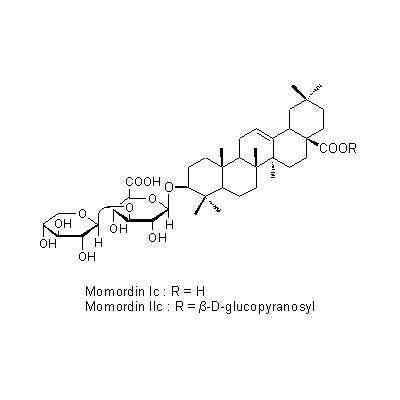
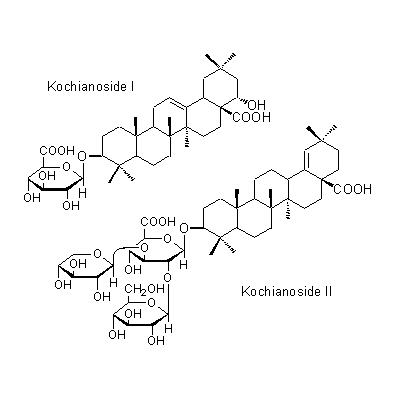
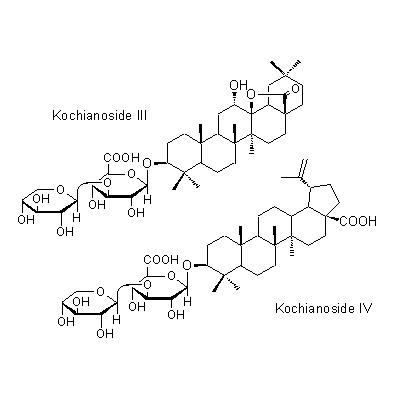
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids (*C1, C2, C3): Momordin Ic, Momordin IIc, Kochianoside I, Kochianoside II, Kochianoside III, Kochianoside IV, Scoparianoside A, Scoparianoside B, Scoparianoside C | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Relieving the itching (momordin Ic), suppression of alcohol and sugar absorption (momordin Ic). | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 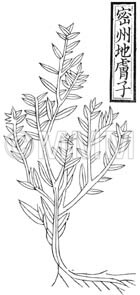 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Dysuria, Urodynia, Itching, Scabies, Eczema, Urticaria, Vulvitis, Vaginitis | ||||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | ||||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1) Shoyakugaku Zassh, 39(3), 190-203(1985). B2) Shoyakugaku Zassh, 36(1), 6-10(1982). C1) Yakugaku Zasshi, 117(4), 193-201(1997). C2) Chem. Pharm. Bull., 45(6), 1052-1055(1997). C3) ibid., 45(8), 1300-1305(1997). | ||||||
| Remarks | The real Difuzi (地膚子) is thought to be the mature fruit of Kochia scoparia (L.) Schrad. of family Chenopodiaceae (Jap. name: Hōkigi). However, Chenopodium album L. (Jap. name: Shiroakaza), C. ficifolium Smith (Jap. name: Koakaza) and C. ambrosioides L. (Jap. name: Kearitasō) were also distributed in the market (B1). All of them belong to the same family as Difuzi. In addition, the fruit of Leonurus japonicus Houttuyn of family Labiatae (Jap. name: Mehajiki) and L. sibiricus L. (Jap. name: Hosobamehajiki) were found under the name of Difuzi in the Hong Kong market (B2). The fruit of Mehajiki or Hosobamehajiki is the original plant of "Chongweizi" (茺蔚子). The medicinal effects of Difuzi and Chongweizi are completely different except that both of them are used for eye problems. Chenopodium or Leonurus is not appropriate for use under the name of Difuzi derived from either genus. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/01/13 | ||||||