Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hubei Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Wuhan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
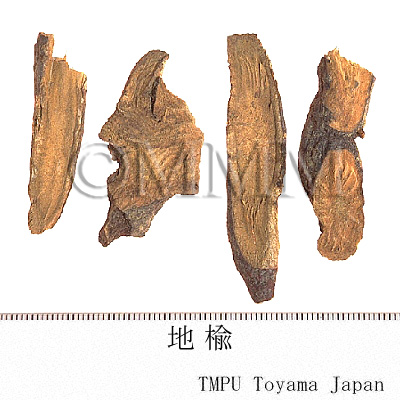
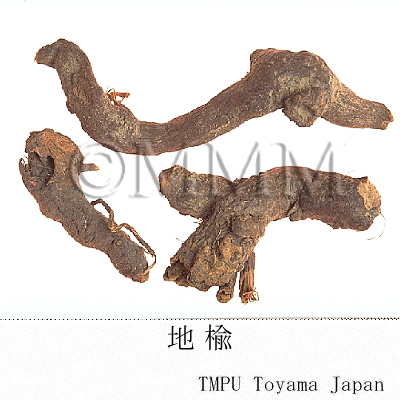
| Common name | 地楡, Diyu, Sanguisorbae Radix (CP2020), Garden Burnet Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
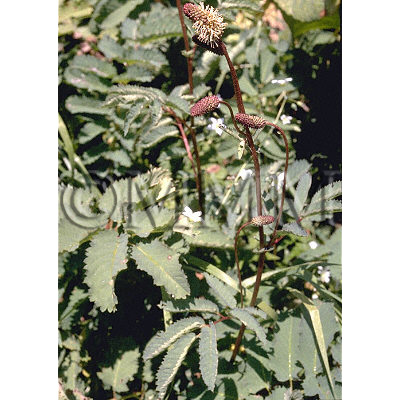
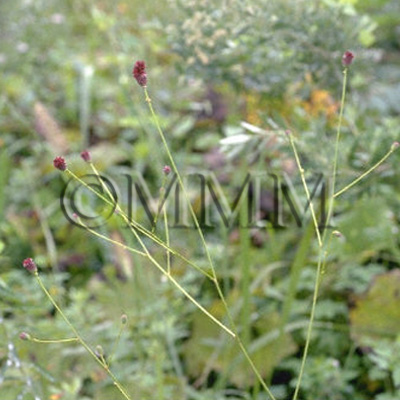
| Original plant name | Sanguisorba officinalis L.1, Sanguisorba officinalis L. var. longifolia (Bert.) Yu et Li or the variant species, (Waremokō1 and its varietas) (B1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rosaceae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Quality for selection | The external of a good one is dark brown with longitudinal wrinkles and the internal is white. It is fresh, and the shape is fusiform and axial. The both ends are elongated. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an astringent and hemostatic, it is applied for bloody dysentery, hemorrhoids, metrorrhagia, hematemesis, hemoptysis, melena, hypermenorrhea and hematochezia. For external use, it works wonders for dermatitis, mucitis, eczema, incised wound and burns. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Hemostatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; bittter, sour and agtringent. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To cool the blood to stanch bleeding , remove toxin and promote wound healing. [Indications] Bloody stool, hemorrhoid. bleeding, blood dysentery, flooding and spotting, scald and burn, swelling abscess, sore and toxin. | |||||
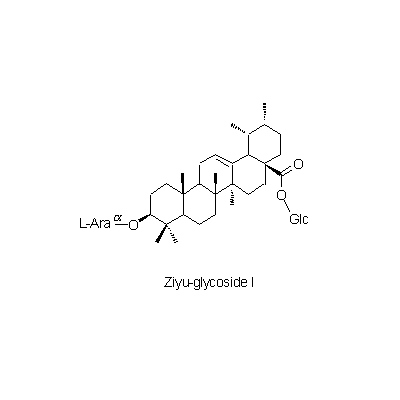
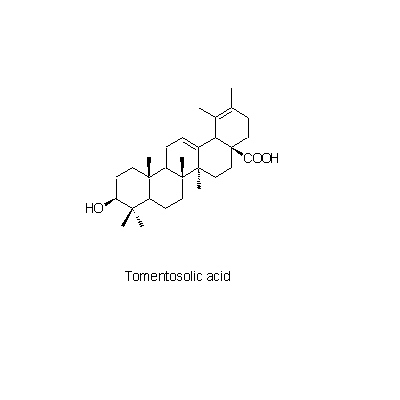
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Sanguisorbin (ゲニン/genin = Tomentosolic acid), Ziyu-glycoside I, Ziyu-glycoside II (ゲニン/genin = Pomolic acid) Carotenoids & Vitamin A (*C1): Vitamin A (approx. 0.04%) Tannins (*C1): Tannin (approx. 17%) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Suppression of bacteria (ethanol extract: Escherichia coli, myxomycete, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus, Salmonella typhi, paratyphoid bacillus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa), antibacterial (Neisseria meningitidis). Antiinflammatory, suppression of apoptosis induced by the renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, restoration of renal function (administration in advance) (P1), improving the renal function due to LPS ( administration in advance, NO production system) (P2). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF183533, AF183556 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematuria, Hematochezia, Bleeding hemorrhoids, Hemorrhagic diarrhea, Irregular vaginal bleeding, Hypermenorrhea, Pyogenic dermatosis, Eczema, Incised wound, Burn | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1)Shoyakugaku Zasshi, 39, 301-311 (1985). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 70-71. P1)J. Trad. Med., 16, 97-101 (1999). P2)Biol. Pharm. Bull., 22, 1327-1330 (1999). | |||||
| Remarks | The original plant of Diyu (地楡) is Sanguisorba officinalis. The variants include var. longifolia (Bert.) Yu et Li, var. carnea (Fisch.) Regel ex Maxim. (Jap. name: Ezowaremokō), var. glandulosa (Kom.) Worosch and var. longifolia (Kitag.) Yu et Li. Besides the above, the root of following plants are used for medicinal purposes: S. tenuifolia Fisch. ex Link and S. tenuifolia Fisch. ex Link var. alba Trautv. et Meyer (Nagabonoshirowaremokō in Jap.) in northeast of China, S. applanata Yu et Li and its variants in Yantai of Shandong, S. alpina Bunge in a part of Ningxia. Also, the rhizome of Polygonum bistorta L. of family Polygonaceae (Ibukitoranoo in Jap.) is called Diyu in Guiyang of Guizhou and the rhizome of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. (Itadori in Jap.) is called "Tudiyu" (土地楡, Dochiyu in Jap.) in southern Sichuan. As for the rest, in Xinyang of Henan the rhizome of Astilbe chinensis Maxim. ex Fr. et Sav. of family Saxifragaceae is called "Zidiyu" (紫地楡, Shichiyu in Jap.) or "Chidiyu" (赤地楡, Sekichiyu in Jap.) which is also the name for the root of Geranium strictipe Kunth of family Geraniaceae in Kunming of Yunnan. Additionally, in a part of Yunnan, the root of Potentilla peduncularis D. Don of family Rosaceae and P. siemersiana Lehm. are called "Baidiyu" (白地楡, Hakuchiyu in Jap.). However, all of them are misused for Diyu. In Korean market, most Diyu/Jiyu is the blended roots of S. officinalis L., S. officinalis L. var. longifolia (Bert.) Yu et Li and S. tenuifolia Fisch. ex Link var. alba Trautv. et Meyer. (B1) | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/28 | |||||