Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hubei Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Wuhan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
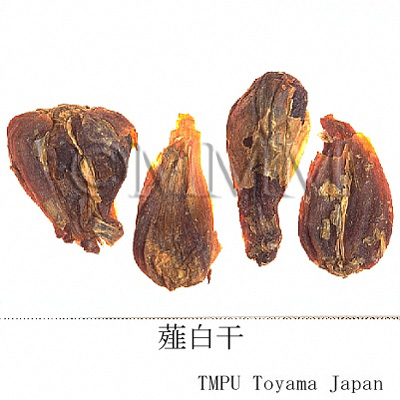
| Common name | 薤白, Xiebai, Allii Chinensis Bulbus (Non-JPS2022), Allii Macrostemonis Bulbus (CP2020), Allium Chinense Bulb (Non-JPS2022), Longstamen Onion Bulb (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 小根蒜,小根菜 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
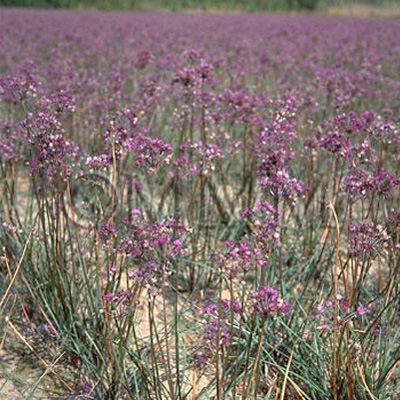
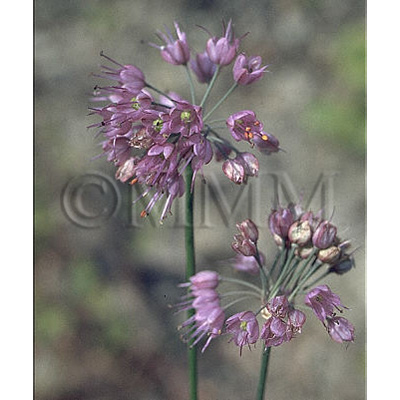
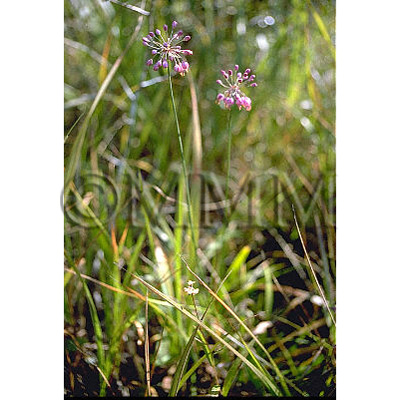
| Original plant name | Allium chinense G. Don, (Rakkyō) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | |||||
| Used part | bulb | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Xiebai is used as a stomachic, relieving stagnation of intestines and expectorant. It is applied for dyspnea due to chest pain, cardiac asthma and angina pectoris. It is also applied for burn externally as an antiphlogistic and germicide. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, lung, stomach and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To unblock yang, dissipate binds, and move qi and remove stagnation. [Indications] Chest impediment with heart pain, stuffiness, fullness and distending pain in epigastrium and abdomen, and tenesmus caused by diarrhea and dysentery. | |||||
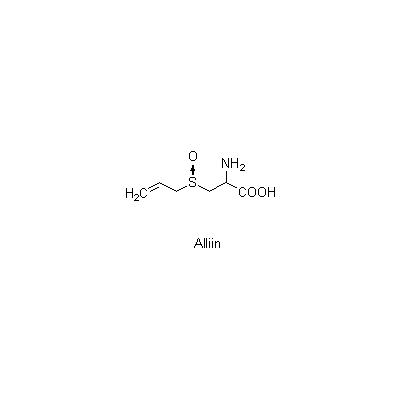
| Chemical constituent | Monosaccharides (*C1): Fructose, Glucose, Galactose, Galacturonic acid, Rhamnose Oligosaccharides (*C1): Sucrose Steroids (*C1,C2): Chinenoside II, Chinenoside III, Chinenoside IV, Chinenoside V Other sulfur containing compounds (*C1): Alliin, Diallyl disulfide | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Chest pain, Back pain, Feeling of pressure in the chest, Dyspnea, Angina pectoris, Expectoration of sputum, Diarrhea, Tenesmus | |||||
| Formulation | Karoto, Karogaihakuhakushuto | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook,p334. C2) Phytochemistry,41,283(1996). C3) Planta Med.,62,465(1996). | |||||
| Remarks | Allium chinense (Jap. name: Rakkyo) is produced in Zhejiang, Jiangsu and Anhui. Ningbo district of Zhejiang Prov. produces a lot of high quality "Xiebai". The bulb of A. macrostemon (Jap. name: Nobiru) is used in Northeast China, and called "Xiaogensuan" or "Xiaogencai". In Japan, it is often used as a substitute. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/19 | |||||