Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
39.90419989999999
116.40739630000007
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Beijing
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
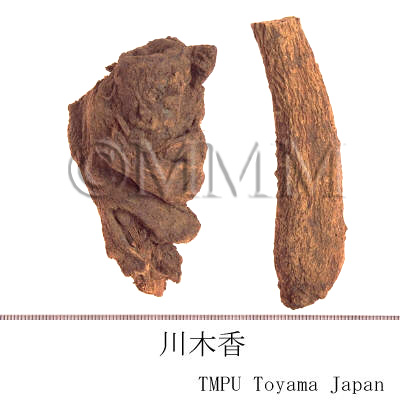
| Common name | 川木香, Chuanmuxiang, Vladimiriae Radix (CP2020), Common Vladimiria Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Vladimiria souliei (Franchet) Ling, Vladimiria souliei var. cinerea Ling | |||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Official compendium | CP(2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a stomachic and intestinal tonic, it is used to treat nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, parasite disease, etc. It is also used for making incense. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, large intestine, gallbladder meridians. [Actions] To move qi to relieve pain. [Indications] Distending pain in the chest, hypochondrium, epigasttrium and abdomen, borborigmus, diarrhea, and tenesmus. | |||||
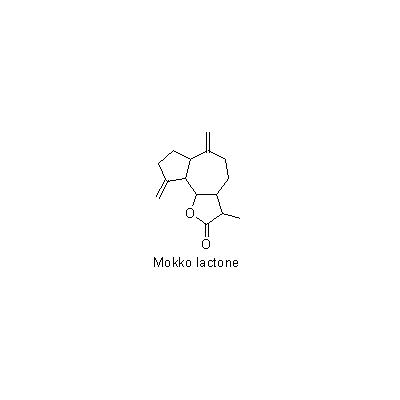
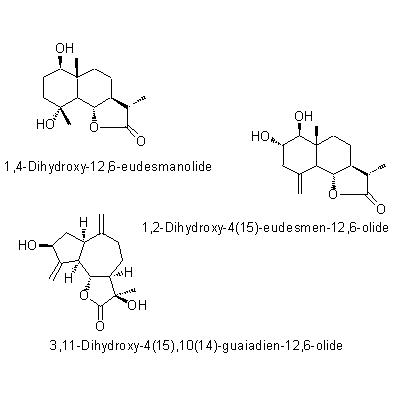
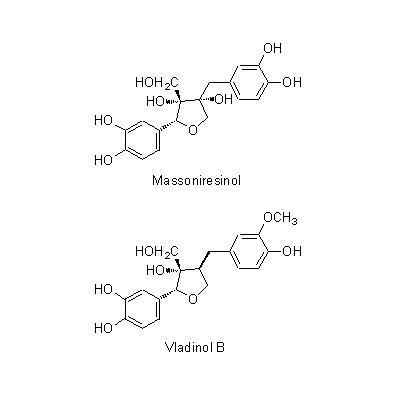
| Chemical constituent | Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Mokko lactone V. souliei (*C2): 1,4-Dihydroxy-12,6-eudesmanolide, 1,2-Dihydroxy-4(15)-eudesmen-12,6-olide, 3,11-Dihydroxy-4(15),10(14)-guaiadien-12,6-olide, 10,14-Dihydroxy-4(15)-guaien-12,6-olide, 10,14-Epoxy-4(15)-guaien-12,6-olide, 10alpha,14-Epoxy-3beta-hydroxy-12,6alpha-guaianolide Lignans & Neolignans V. souliei (*C3): Massoniresinol, Vladinol B, Vladinol D, Olivil | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Nausea, Vomitting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Tenesmus, Dyspepsia, Anorexia | |||||
| Formulation | Ureitsukito, Kagenshosaikoto, Kamikihito, Kikyoto, Kihito, Kyukihochuto, Kumibinroto, Kobokumaoto, Kowashakuyakuto, Goshitsusan, Sanshoin, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Jippito, Shakuyakuto, Jurokumiryukiin, Shobaito, Jinsoin, Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Chuseito, Chokoshiteito, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Haikanpo, Baimoto, Bunshoto, Boisan, Boito, Botanpisan, Honposhakuyakuto, Rogyokuto, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Saussureae Radix, Aristolochiae Radix, Inulae Radix, Inulae Racemosae Radix | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 40-42. C2)Phytochemistry, 29, 1209 (1990). C3)Planta Med., 56, 475 (1990). | |||||
| Remarks | The real Muxiang (木香) is the root of Saussurea lappa Clarke (= Aucklandia lappa Decne.) of family Compositae. Chuanmuxiang (Jap. name: 川木香, Senmokkō) is generally processed by roasting the top of the root. In the past, it was erroneously applied to Inula racemosa Hook. f. (Jap. name: Zōmokkō). The congenetic root of Vladimiria denticulata Ling. is circulated in the Chinese market under the name of Yueximuxiang (越西木香). | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/28 | |||||