Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Hubei Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
30.592849
114.30553899999995
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Wuhan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
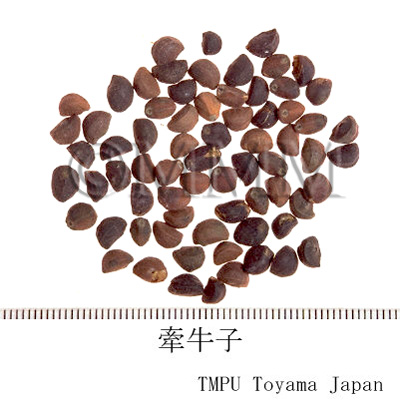
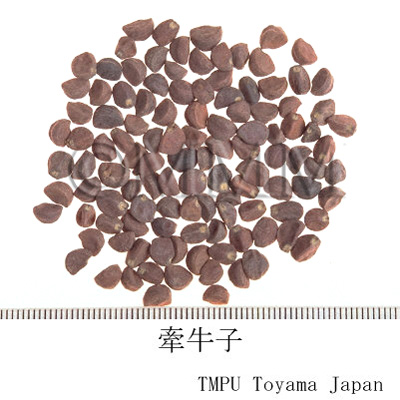
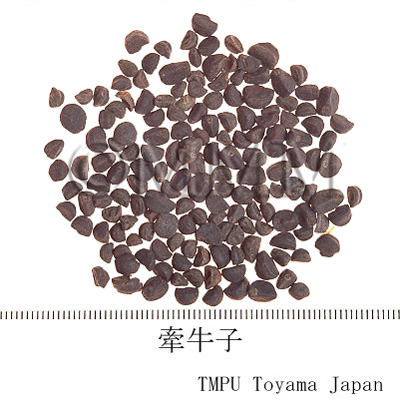
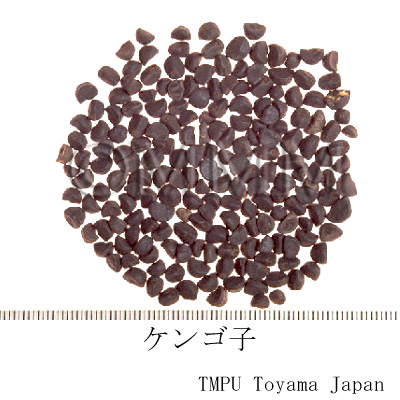
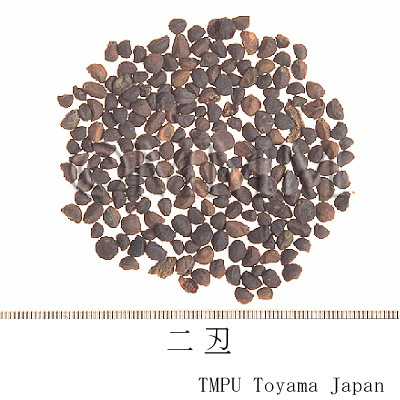
| Common name | 牽牛子, Qianniuzi, Pharbitidis Semen (JP18, CP2020), Pharbitis Seed (JP18, CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
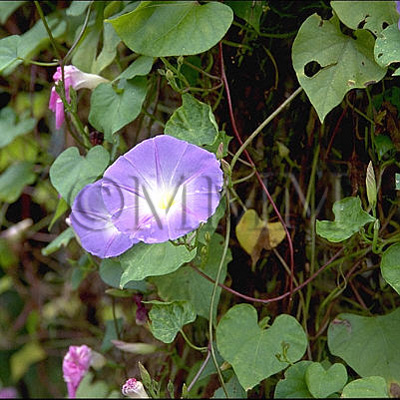
| Original plant name | Pharbitis nil Choisy1 or Pharbitis purpurea (L.) Voigt2, (Asagao1, Marubaasagao2) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Convolvulaceae | |||||
| Used part | mature seed | |||||
| Quality for selection | The size of good Qianniuzi is large. It sinks under water. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a mild laxative, laxative and diuretic, Qianniuzi is applied for ascites, constipation and oliguria, retention or stagnation of undigested food. It has anthelmintic action. Contraindicated for pregnant women and dyspeptic person. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Purgatives for removing water retention | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter; toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, kidney and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To purge water to relax the bowels, phlegm and flush away fluid retention, kill worms, remove accumulation. [Indications] Edema distention and fullness, constipation and annuria, phlegm-fluid retention, aggregation and accumulation, panting and cough caused by qi countflow, abdominal pain caused by worm accumulation. | |||||
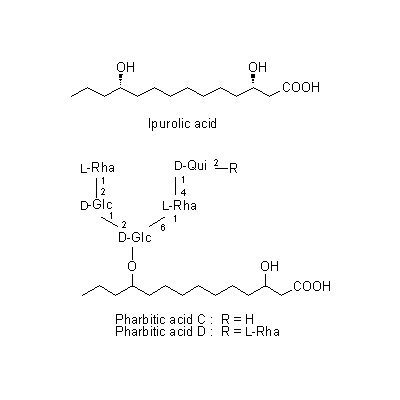
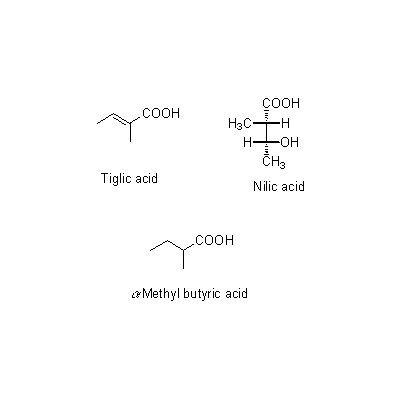
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Pharbitin 約/about 2% [pharbitic acid (ipurolic acid + glucose, rhamnose, quinovose) の糖部にtiglic adid, d-methyl-ethyl acetic acid, nilic acidが結合したもの] Plant hormones (*C1): Gibberellin (A3, A8, A26, A27, A29) およびそのglucoside(未熟種子/immature seed) 脂肪油約/fatty oil about 11% | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Cathartic, activating renal function. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF110949, U38310, AF110947, AF110948 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Edema, Ascites, Oliguria, Constipation, Abdominal pain, Cough, Roundworm | |||||
| Formulation | Kufugedokusan, Hachimisenkiho | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 302-304. | |||||
| Remarks | There are two kinds of Qianniuzi depending on the seed coat color. One is black and the other is white. The black one is more common than the white one for medicinal use, since it has a stronger effect. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines Pharbitis nil (Jap. name: Asagao) only. 0.1g at a time is taken, 1 to 3 times a day as a laxative. If the dosage is increased, it is used as a drastic aperient. Sometimes, the two original plants are included among genus Ipomoea and listed as Ipomoea nil (L.) Roth and I. purpurea (L.) Roth. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/02/28 | |||||