Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
39.90419989999999
116.40739630000007
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Beijing
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 青木香, Qingmuxiang, Radix Aristolochiae (CP1995) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 南木香, 土青木香 | |||||
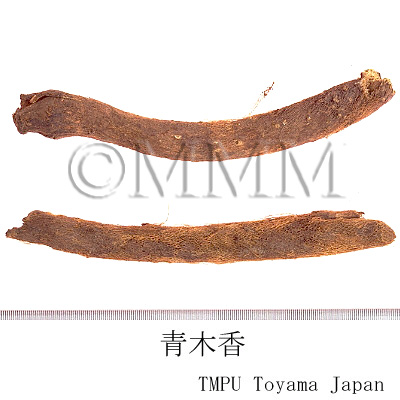
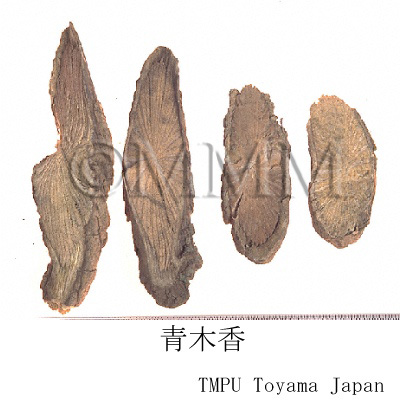
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc.1, Aristolochia contorta Bunge2, (Umanosuzukusa1, Marubanoumanosuzukusa2) | |||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (1995 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antidote, it is applied to distending pain in the chest, hypochondrium, epigastrium and abdomen. It is also used for colic pain, pain due to swelling, insect or snake bites and hypertension. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, spleen and kidney meridians. [Actions] To remove qi and activate blood, unblock the collaterals to relieve pain. [Indications] Stabbing pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness. | |||||
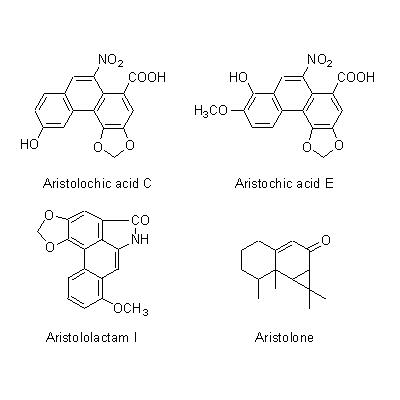
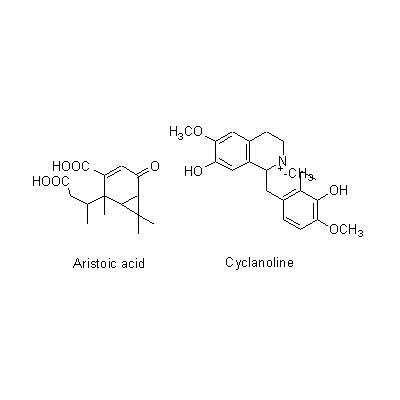
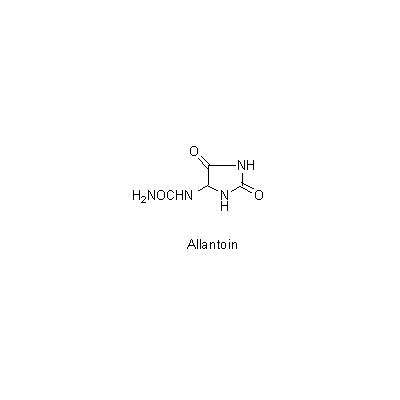
| Chemical constituent | Sesquiterpenoids A. debilis (*C1-C3): 1(10)-Aristolen-12-al, Aristolone, Aristoic acid, 9alpha-Hydroperoxy-1(10)-aristolen-2-one, 1alpha-Hydroxy-9-aristolen-8-one, Debilone, 3-Ishwaranone Alkaloids A. debilis (*C1,C5-C7): Aristolochic acid C, 7-Hydroxyaristolochic acid A, Aristolochic acid II, 7-Methoxyaristolochic acid A, Aristololactam I, Debilic acid, Cyclanoline A. contorta (*C4): Aristochic acid E Other nitrogen compounds A. debilis (*C1): Allantoin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Decrease in blood pressure. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Arthralgia, Edema, Hypertension | |||||
| Formulation | Ureitsukito, Kagenshosaikoto, Kamikihito, Kikyoto, Kihito, Kyukihochuto, Kumibinroto, Kobokuto, Kowashakuyakuto, Goshitsusan, Sanshoin, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Jippito, Shakuyakuto, Jurokumiryukiin, Shobaito, Jinsoin, Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Chuseito, Chokoshiteito, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Haikanpo, Baimoto, Bunshoto, Boisan, Boito, Botanpisan, Honposhakuyakuto, Rogyokuto, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Saussureae Radix, Vladimiriae Radix, Inulae Radix, Aristolochiae Fructus | |||||
| References | CP1995: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 1995 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 40-42. C2)Phytochemistry, 23, 1647 (1984). C3)Agric. Biol. Chem., 37, 341(1973). C4)Yaoxue Xuebao, 21, 702 (1986). C5)Yakugaku Zasshi, 79, 973 (1959). C6)Huaxue Xuebao, 39, 237 (1981). C7)Kexue Tongbao, 761, (1957). | |||||
| Remarks | The real Muxiang (木香) is the root of Saussurea lappa Clarke (= Aucklandia lappa Decne.) of family Compositae, which was called Qingmuxiang (Jap. name: 青木香, Seimokkō) in ancient times. At present, it is the root of Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc. (Jap. name: Umanosuzukusa) and A. contorta Bunge (Jap. name: Marubaumanosuzukusa) of family Aristolochiaceae. The aerial part of these two species are called Tianxianteng (天仙藤, Aristolochiae Herba) in China. It is used for promoting circulation of qi and blood, inducing diuresis and removing edema. It is applied to treat stomachache, abdominal pain, aching joints and edema in pregnancy. Qingmuxiang was listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (1995 edi.) but it was excluded from its 2000 edi. Tianxianteng was also excluded from its 2020 edi. Meantime, Qingmuxiang and Tianxianteng contain aristolochic acid, which may cause renal damage according to reports. Therefore it must be prescribed with care. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/28 | |||||