Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
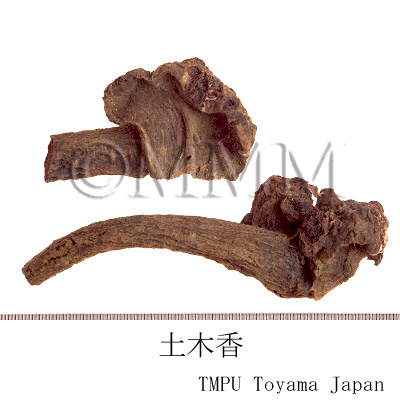
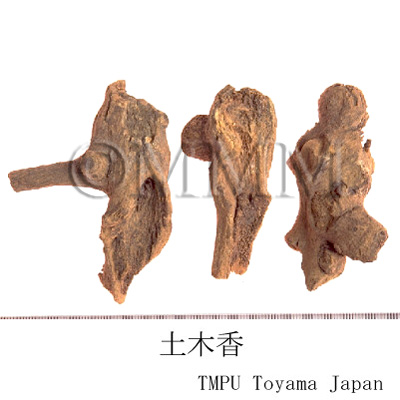
| Common name | 土木香, Tumuxiang, Inulae Radix (CP2020), Inula Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
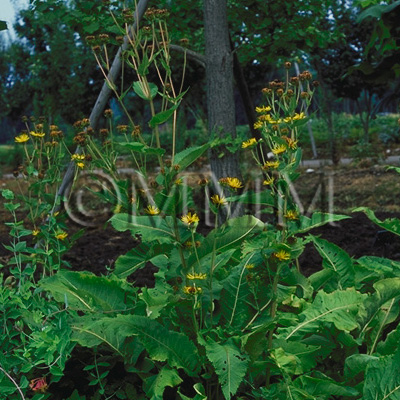
| Original plant name | Inula helenium L.1, Inula racemosa Hook. f., (Ōguruma1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Acting as a diuretic and diaphoresis, it is used for home remedy and insence making in place of Aucklandiae (Saussureae) Radix. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and spleen meridians. [Actions] To tortify the spleen and harmonize the stomach, move qi and relieve pain, and prevent miscarriage. [Indications] Distending pain in tpe chest, hypochondrium, epigastrium and abdomen; vormtmg, diarrhea and dysentery, chest or hypochondrium injury, pain caused by qi divergeny, threatened abortion. | |||||
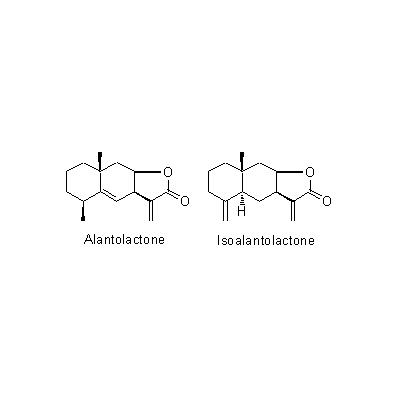
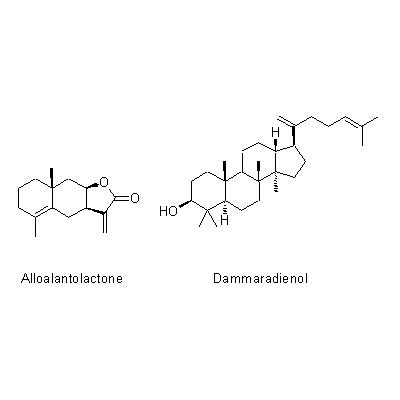
| Chemical constituent | Sesquiterpenoids I. helenium (*C1-C4): Alantolactone, Isoalantolactone, Dehydroalantolactone, Alloalantolactone, Dihydroisoalantolactone, 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone, 2-Oxoalantolactone I. racemosa (C4,C6-C9): Alantodiene, Alantolactone, Alloalantolactone, Isoalantodiene, Isoalloalantolactone, Inunal, Isoinunal, Neoalantolactone, Dihydroinunolide Triterpenoids I. helenium (*C5): Dammaradienol | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Anthelmintic | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Nausea, Vomitting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Tenesmus | |||||
| Formulation | Ureitsukito, Kagenshosaikoto, Kamikihito, Kikyoto, Kihito, Kyukihochuto, Kumibinroto, Kobokuto, Kowashakuyakuto, Goshitsusan, Sanshoin, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Jippito, Shakuyakuto, Jurokumiryukiin, Shobaito, Jinsoin, Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Chuseito, Chokoshiteito, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Haikanpo, Baimoto, Bunshoto, Boisan, Boito, Botanpisan, Honposhakuyakuto, Rogyokuto, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Saussureae Radix, Aristolochiae Radix, Vladimiriae Radix | |||||
| References | C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 40-42. C2)J. Am. Chem, Soc., 82, 2224 (1960). C3)Phytochemistry, 17, 1165 (1978). C4)J. Am. Chem. Soc., 79, 5721 (1957). C5)J. Chem. Soc., 2196 (1956). C6)Phytochemistry, 28, 2093 (1989). C7)J. Chem., Sect. B, 22, 286 (1983). C8)Phytochemistry, 24, 2007 (1985). C9)Indian J. Chem., Sect. B., 16, 27 (1978). | |||||
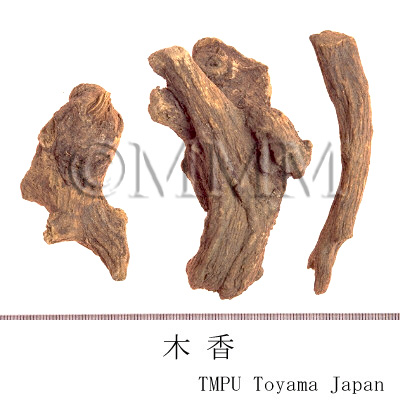
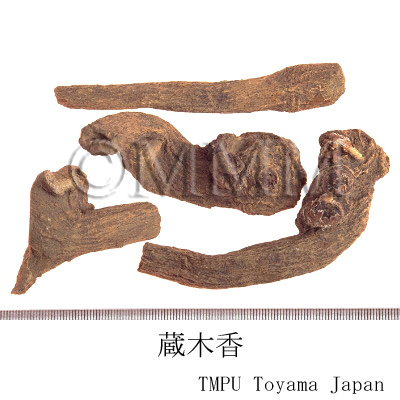
| Remarks | The real Muxiang (木香) is the root of Saussurea lappa Clarke (= Aucklandia lappa Decne.) of family Compositae. Inula helenium L. (Jap. name: Ōguruma) is a native of Europe and the root is applied to treat disease of chest (including chronic bronchitis, etc), alimentary disease and infectious disease (cold and tonsillitis). The root of Inula racemosa Hook. f. is called Cangmuxiang (Jap. name: 蔵木香, Zōmokkō) as well and frequently used in Tibetan Medicine. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/07/09 | |||||