Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
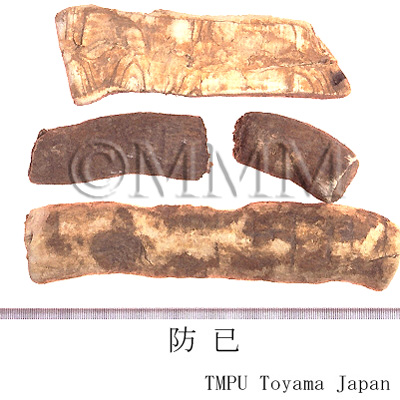
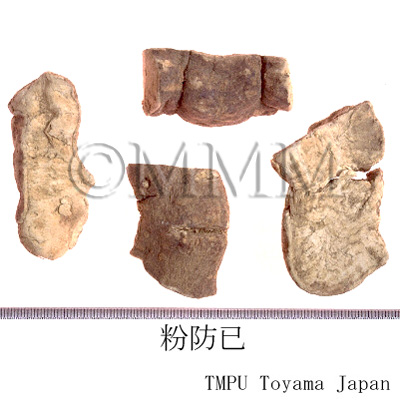
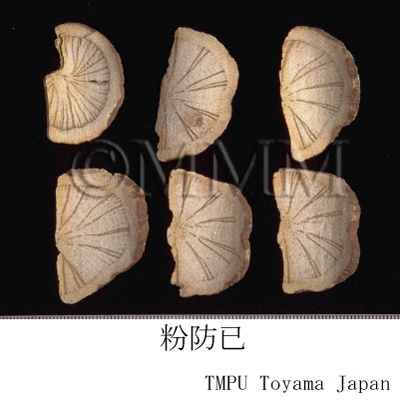
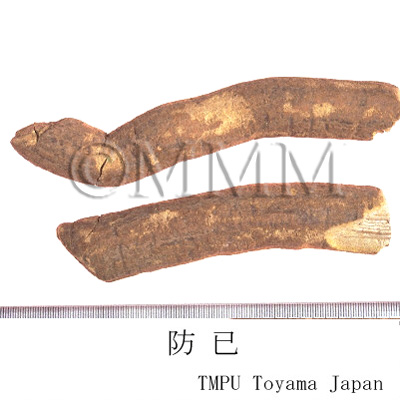
| Common name | 防已 (中国産/CN production), Fangji, Stephaniae Tetrandrae Radix (CP2020), Fourstamen Stephania Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 粉防已, 漢防已, 瓜防已 | |||||
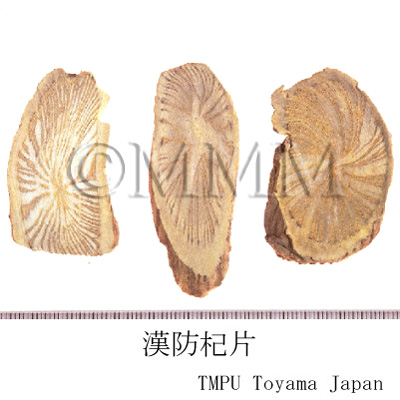
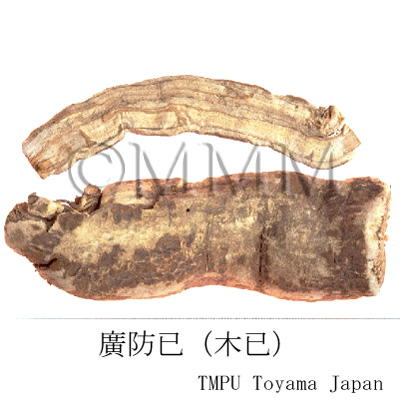
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Stephania tetrandra S. Moore (広防已 [Guangfangji]: Aristolochia fangchi Y.C.Wu ex L.D.Chou et S.M.Hwang), (Shimahasunohakazura) | |||||
| Family name | Menispermaceae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As diuretic and anodyne, it is applied to treat nerve pain, rheumatism, arthritis and edema. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Antirheumatics (dampness-eliminating) | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Bladder and lung meridians. [Actions] To dispel wind and relieve pain, and promote urination to alleviate edema. [Indications] Painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, edema and beriberi, inhibited urination, eczema, sore and toxin. | |||||
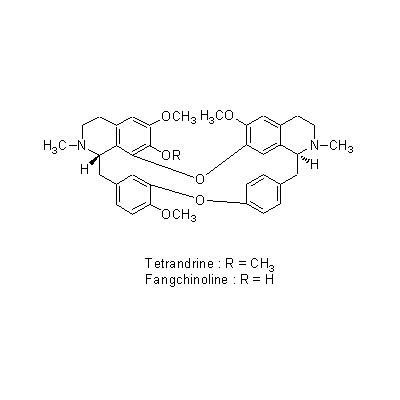
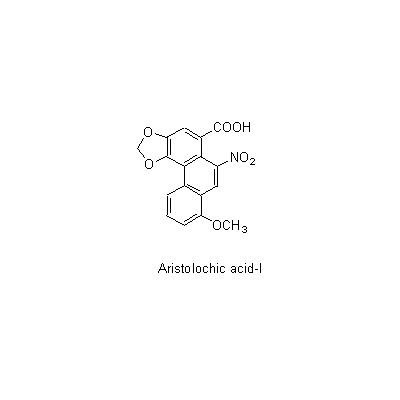
| Chemical constituent | Sesquiterpenoids A. fangchi (*C1): Aristolochic acid-I Isoquinoline alkaloids S. tetrandra (*C1): Tetrandrine, Dimethyltetrandrine, Fangchinoline | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory,analgesic,diuretic, antihypertensive, and anti ACE effect (bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AJ303202, AF206855, L12630, L24083; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Rheumatism, Arthritis, Arthralgia, Thirst, Edema, Pulmonary edema, Ascites, Beriberi, Eczema, Oliguria, Hypertension, Skin disease | |||||
| Formulation | Orenshodokuin, Shozokumeito, Jokinritsuansan, Seishitsuto, Zosonmokuboito, Sokeikakketsuto, Haikanpo, Boisan, Boito, Boiogito, Boijioto, Boibukuryoto, Mokuboito, Mokuboikyosekkokabukuryoboshoto, Rokumotsubushito | |||||
| Related drugs | Boi (produced in Japan), Qingfengteng, Mufangji, Guangfangji, Hanzhongfangji (see "Remarks") | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 78-81. | |||||
| Remarks | The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edition defines the roots of Stephania tetrandra as "Fangji". Its 2000 edition defines that of Aristolochia fangji as "Guangfangji". "Guangfangji" (Radix Aristolochiae Fangchi, Southern Fangchi Root ) is used for expelling wind to relieve pain, reducing fever and inducing diuresis. It is used for damp-heat with pain in the entire body, edema in the lower limb and difficulty in micturition. "Fangji" has the advantage of inducing diuresis and "Guangfangji" has the advantage of expelling wind. "Hanzhongfangji" is said to be derived from the root of Aristolochia heterophylla. The plants of Aristolochia spp. of family Aristolochiaceae contain aristolochic acid which is known to cause renal damage. In Japan, "Fangji" is called Boi or, sometimes, Boki. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/10/17 | |||||