Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
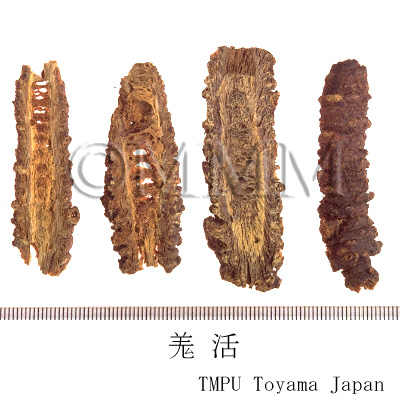
| Common name | 羌活, Qianghuo, Notopterygii Rhizoma (JP18), Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix (CP2020), Notopterygium (JP18), Incised Notopterygium Rhizome and Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
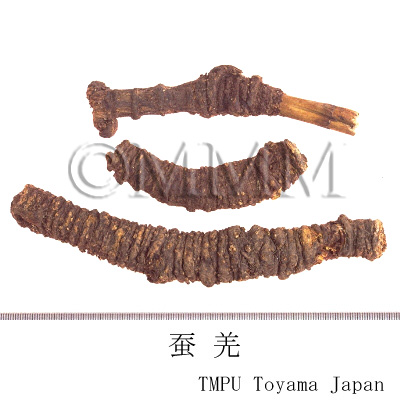
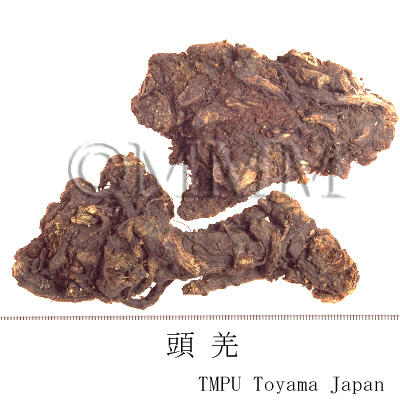
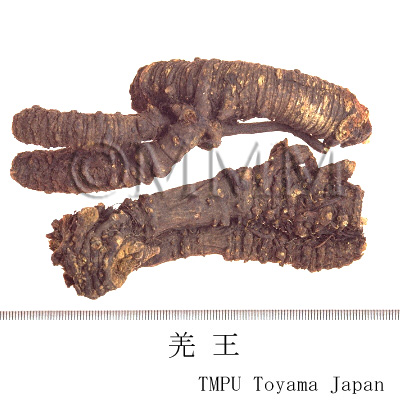
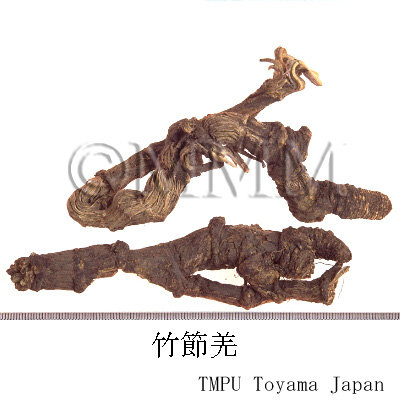
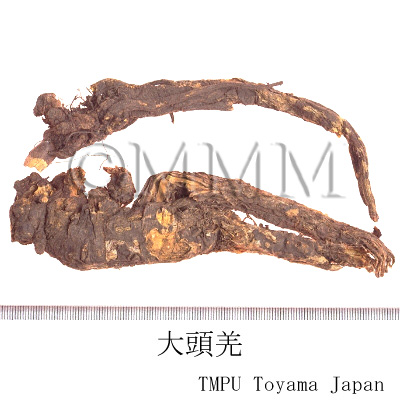
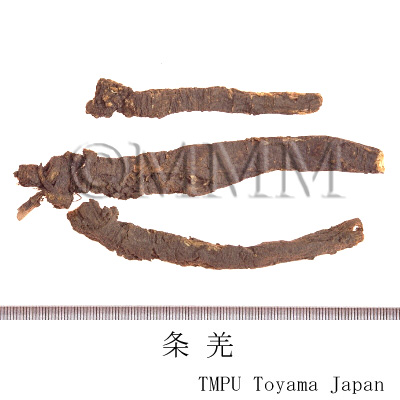
| Synonyms | 川羌, 西羌, 蚕羌, 頭羌, 竹節羌, 条羌 | |||||
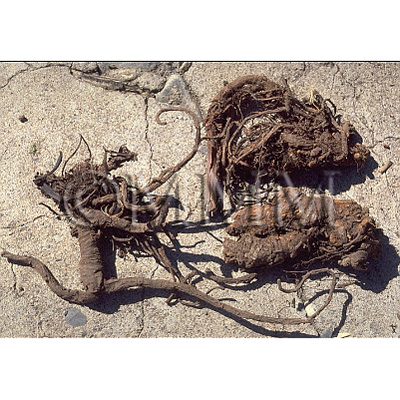
| crude drug image |
| |||||
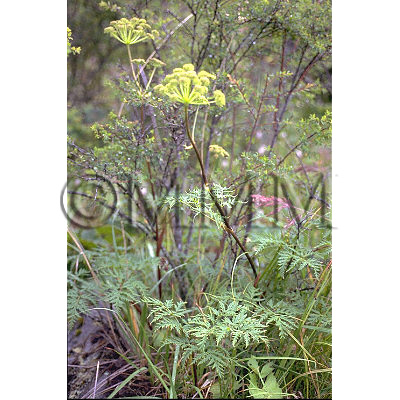
| Original plant name | Notopterygium incisum Ting ex H. T. Chang or Notopterygium forbesii Boiss. (B1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome and root | |||||
| Quality for selection | The best Qianghuo is Canqiang (Jap. name: Sankyō) which has rhizomes that resemble silkworms in shape. It is produced in Sichuan Province. | |||||
| Official compendium | JHMC (1989), CP (2020 ed.), JP XVIII | |||||
| Clinical application | As a painkiller, antispasmodic and metabolic promoter, Qianghuo is applied for headache, arthralgia, rheumatism, partial paralysis and general pain. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with warm property | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Bladder and kidney meridians. [Actions] To release the exterior and dissipate cold, dispel wmd and remove dampness and relieve pain. [Indications] Common cold caused by wind-cold headache and stiff nape, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, sore pain in the shoulder and back. | |||||
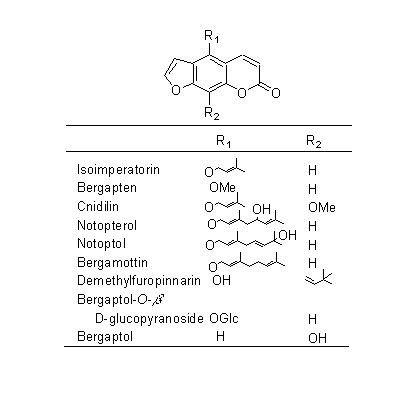
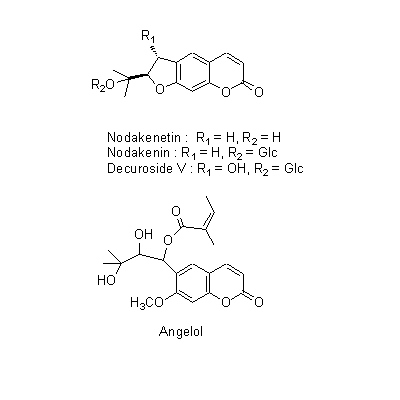
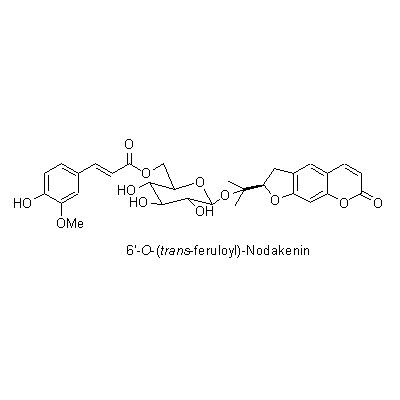
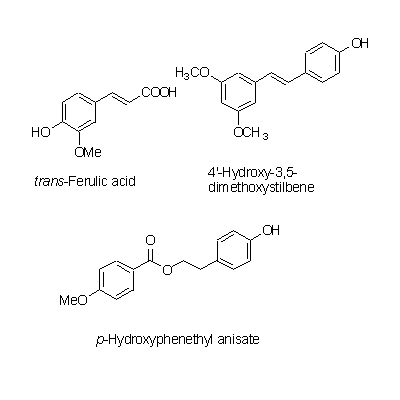
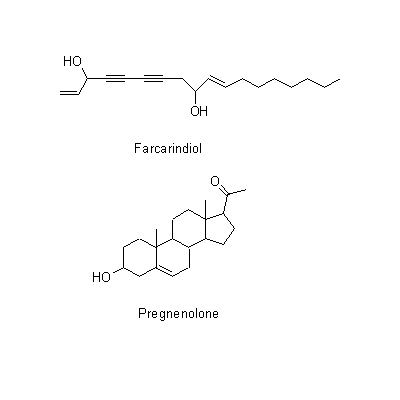
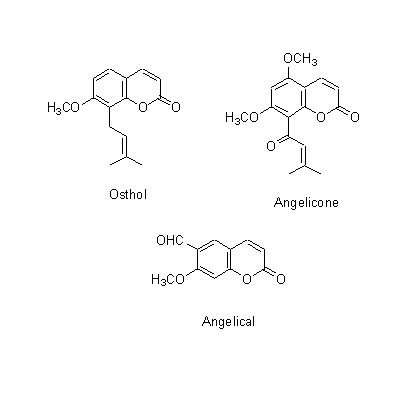
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Falcarindiol Steroid saponins & Sapogenins (*C1): Pregnenolone Phenylpropanoids (*C1): trans-Ferulic acid Coumarins (*C1): Isoimperatorin, Bergapten, Cnidilin, p-Hydroxyphenethyl anisate, Notopterol, Notoptol, Bergaptol, Nodakenetin, Nodakenin, Decuroside V, Bergamottin, 6'-O-(trans-feruloyl)-Nodakenin, Bergaptol-O-beta-glucopyranoside, Demethylfuropinnarin N. incisum (*C1): Angelical N. forbesii (*C2): Bergaptol-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 6'-O-trans-Feruloylnodakenin Stilbenes (*C1): 4'-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxystilbene | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known. | |||||
| DNA sequence | U78412, U78472; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Common cold, Chill, Fever, Headache, Swelling and pain of joint, Rheumatism | |||||
| Formulation | Kufugedokusan, Seishitsuketanto, Seijokentsuto, Senkyuchachosan, Sokeikakketsuto, Nijutsuto, Kamihassento, Jokinritsuansan, Senkanmeimokuto, Daibofuto, Tokinentsuto, Bunshinkiin, Orenshodokuin, Kijitsudaioto, Kufugedokusan, Kufushokutsuto, Kokikososan, Shin'isan, Jintanto | |||||
| Related drugs | Wakyōkatsu (和羌活, Araliae Cordatae Radix), Dokukatsu (独活, Araliae Cordatae Rhizoma) | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1)Nat.Med.,49,409(1995). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 89-91. C2)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,38,2498(1990). | |||||
| Remarks | Kenkyōkatsu, produced in Korea, is the root or rhizome of Ostericum koreanum Kitagawa (= Angelica koreana Maxim.) of family Umbelliferae (Jap. name: Chosen'oniudo) or Ostericum grosseserratum Kitagawa (= Angelica uchiyamana Yabe) (Jap. name: Nioiudo). Both Kenkyōkatsu and Chōkyōkatsu, produced in Japan, are the roots or rhizomes of Angelica pubescens Maxim. (Jap. name: Shishiudo). Recently however, Japanese Qianghuo (Jap. name: Wakyōkatsu) is the slender roots of Aralia cordata Thunb. of family Araliaceae. Chinese Qianghuo is the root of genus Angelica of family Umbelliferae. Both Qianghuo and Duhuo (Araliae Cordatae Rhizoma) have benefits of expelling wind and removing dampness. They relieves pain and removes palsy as well. Qianghuo is a medicine of Taiyang meridians. It has the advantage of expelling dryness and diaphoresis, and should be used for exterior syndrome due to wind cold, while Duhuo has no effect of diaphoresis. Duhuo is a drug of Yin Minimum Kidney Meridian, and used with Xixin (Asiasari Radix), which has a beneficial effects on headache resulting from Yin Minor Channel. In ancient times, it was said "Qianghuo cures hives and Duhuo cures latent wind. Qianghuo tends to specialize in the exterior and Duhuo tends to specialize in the interior." | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/03/29 | |||||