Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
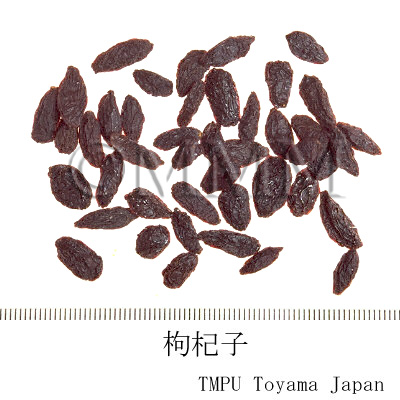
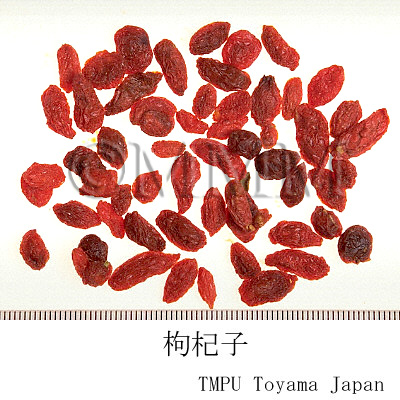
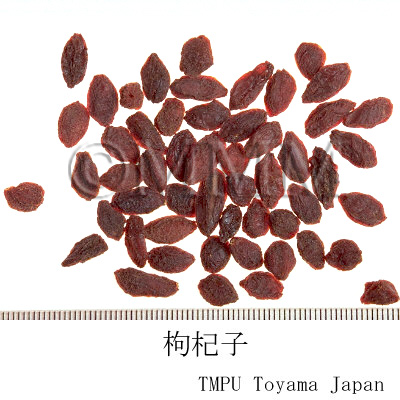
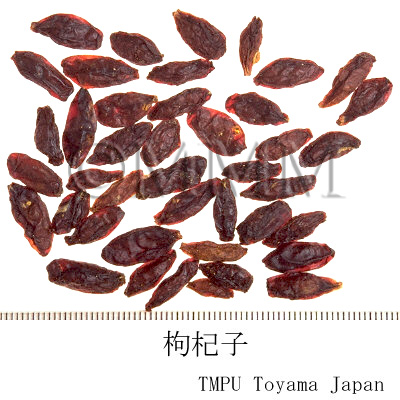
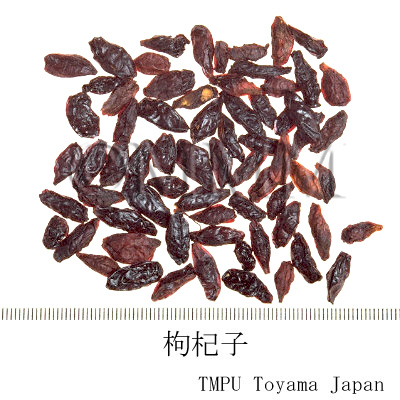
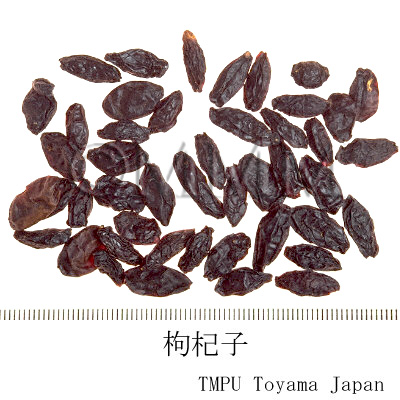
| Common name | 枸杞子, Gouqizi, Lycii Fructus (JP18, CP2020), Lycium Fruit (JP18), Barbary Wolfberry Fruit (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 寧夏枸杞,西枸杞,津枸杞 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
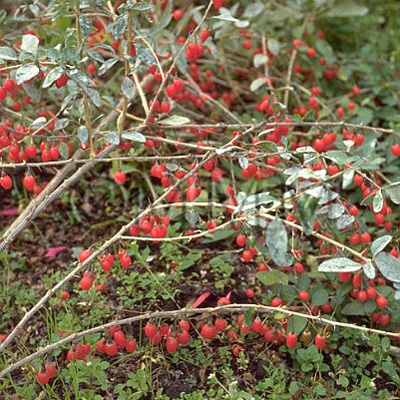
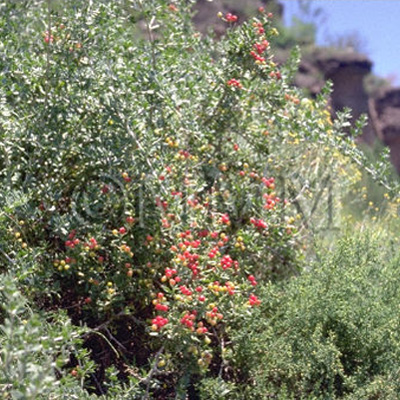
| Original plant name | Lycium chinense Miller1 or Lycium barbarum Linn.2, (Kuko1 or Nagabakuko2) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Solanaceae | |||||
| Used part | mature fruit | |||||
| Quality for selection | The fruit of L. barbarum L. (Xigouqi, Jap. name: Nagabakuko) is high quality and abundant. | |||||
| Official compendium | JHMC (1989), CP (2020 ed.), JP XVIII | |||||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, Gouqizi is applied for tonifying liver and kidney, exhaustion, aching of loins and knees, spiritless, dizziness, headache and diabetes. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Yin-vital essence | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and kidney meridians. [Actions] To nourish the liver and kidney, replenish essence to improve vision. [Indications] Consumptive disease with deficiency of essence, limp aching in the lower back and knees, dizziness and tinnitus, impotence, seminal emission, interior heat wasting-thirst, blood deficiency and sallow complexion, blurred vision. | |||||
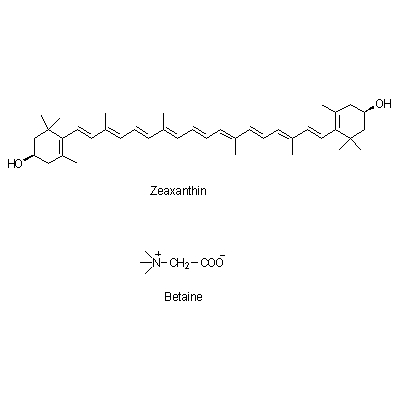
| Chemical constituent | Carotenoids L. chinense (*C1,C2): Zeaxanthin, Zeaxanthin dipalmitate (Physalien) Other nitrogen compounds L. chinense (*C1): Betaine (約/about 0.1%) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Decrease in blood pressure (inhibited by atropine and removal of vagus nerve). Suppression of hepatopathy induced by carbon tetrachloride. Parasympatholytic. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AB051022, AB036550, AB036579, AB036608, AB036637, AB036543, AB036572; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Lightheadedness, Vertigo, Ear buzzing, Decreaced vision, Heaviness and powerlessness in lumber and knee, Tiredness, Spermatorrhea, Dacryorrhea | |||||
| Formulation | Kogikujiogan | |||||
| Related drugs | Lycii Cortex and Lycii Folium | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 285-286. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook,p232. | |||||
| Remarks | - In China, the fruit of Lycium chinense is called Jingouqi and that of L. barbarum is called Xigouqi or Ningxiagouqi. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines these two kinds of fruits. The Pharmacopoeia of The People's Republic China defines the fruits of L. barbarum only. - Jikotsupi (Jap. name) is the root bark of the above and used to reduce fever. Sometimes, the trunk bark is also used for it. - Gouqi wine is applied to cure tiredness. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||