Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
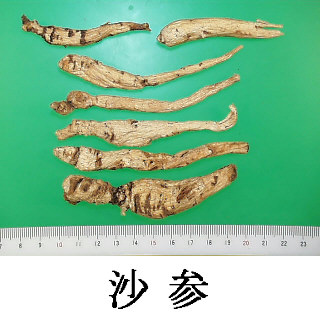
| Common name | 沙参, Shashen, Adenophorae Radix (Non-JPS2022, CP2020), Adenophora Root (Non-JPS2022), Fourleaf Ladybell Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 南沙参 | |||||
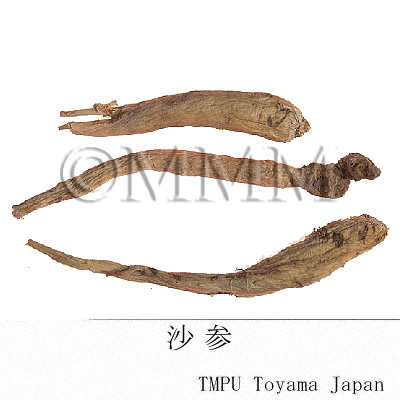
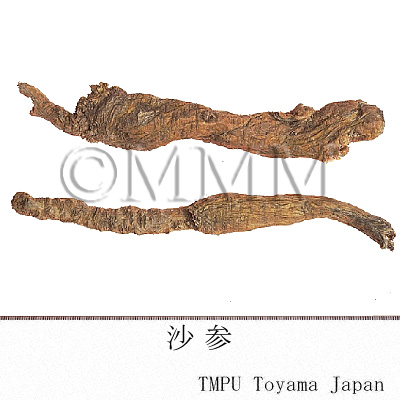
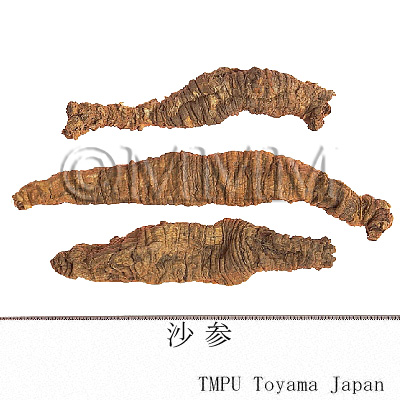
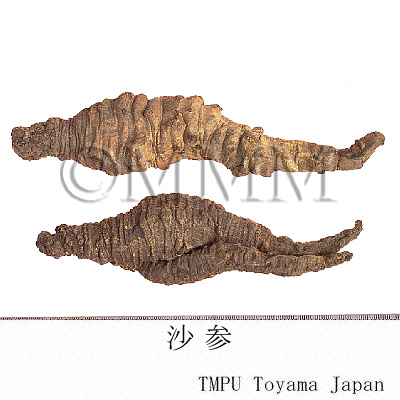
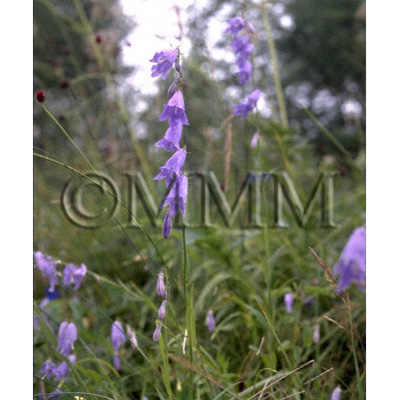
| crude drug image |
| |||||
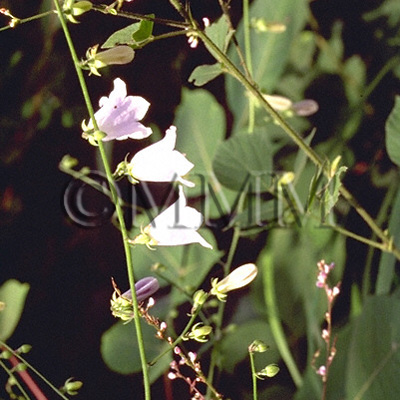
| Original plant name | Adenophora tetraphylla Fischer, Adenophora stricta Miquel1, Adenophora hunanensis Nannfeldt or Adenophora triphylla A. De Candolle, (Marubanoninjin1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Campanulaceae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Shashen is enlarged and corn shaped. The internal is dense and white. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antitussive, expectorant and tonic, shashen is applied for invalid's chronic cough, stridor, phthisis and oliguria. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Yin-vital essence | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To nourish yin, clear heat, boost the stomach, engender fluid, resolve phlegm, and tonify qi. [Indications] Lung heat and dry cough, cough caused by yin consumptive disease, dry cough with greasy phlegm, stomach yin deficiency, reduced food intake, vomiting, deficiency of qi and yin, heat vexation and dry mouth. | |||||
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids A. stricta subsp. sessilifolia (*C1): Sessilifolic acid 3-O isovalerate, Lupenone, 24-Methylene cycloartanol Sterols A. stricta subsp. sessilifolia (*C1): beta-Sitosteryl pentadecanoate, beta-Sitosteryl palmitate, beta-Sitosterol, Ikshusterol, beta-Sitosteryl glucoside | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF090712, AF090713; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Cough, Dry cough, Thirst, Fever, Chronic bronchitis | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | Beishashen (binfangfeng), Manshen (see "Remarks") | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) Shoyakugaku Zasshi,44,98-100(1990). | |||||
| Remarks | Chinese "Shashen" consists of southern and northern "Shashen". Southern "Shashen" is from the plants of family Campanulaceae of genus Adenophora and northern "Shashen" is the barked root of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt et Miquel of family Umbelliferae (Jap. name: Hamabohu). Southern "Shashen" has strong behavior of removing phlegm, while northern "Shashen" has strong effect of nourishing Yin. Korean "Shashen" is the root of Codonopsis lanceolata (Sieb. et Zucc.) Trautv. of family Campanulaceae. In Korea, this species is called "Totok" which is the origin of Japanese "Totoki". Japanese "Shashen" is mostly the root of Adenophora triphylla A.DC. var. japonica Hara (Jap. name: Tsuriganeninjin). | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/19 | |||||