Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Crude drug name_17423a.jpg/20000) | Market name | Ajmod |
|---|---|---|
| Formal name | Ajamoda | |
Other names Tips! | Ajamoda (T), Randhuni (B), Ajamoda (H), Ajamoda voma (K), Ayamodakam (M), Ashumadaga vomam (Te), Ashanta vomum (Ta), Asamodagam (Sin) | |
| English name | Ajamoda, Ajowan | |
| Original plant name | Trachyspermum roxburghianum (DC.) Wolf. (= Carum roxburghianum Benth. & Hook. f.), Ajamoda, Ajowan | |
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |
| Used part | Classification | Plant origin | Sub classification | fruit |
| Collection information | India, Dibrugarh, Assam | |
| Collector | Katsuko Komatsu | |
| TMPW No. | 17423 | |
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
27.4728327
94.91196209999998
Collection information
India,Dibrugarh, Assam
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Crude drug name | Ayurvedic name or Sanskrit name, English name | Ajamoda, Ajamoda, Ajowan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | Ajamoja, Moja, Markata dipya, Dipyaka, Kola, Hastimayura, Karavi, Amlamoda, Kharasva, Mayura, Brahmakusa, Locamastaka, Bastamoda, Markati, Gandhadala, Hastikaravi, Gandhapatrika, Mayuri, Sikhimoda, Madadhya, Vahnidipika, Brahmakosi, Visali, Hrdyagandha, Ugragandhika, Modini, Phalamukhya, Vasucandrabhidha | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Trachyspermum roxburghianum (DC.) Wolf. (= Carum roxburghianum Benth. & Hook. f.) | |||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||
| Used part | Fruits | |||||
| Distribution area | Cultivated throughout India, also in gardens. | |||||
| Remarks | Commonly cultivated. | |||||
| Common uses | Fruits of this drug are acrid, bitter, thermogenic, antispasmodic, carminative, stimulant, tonic, stomachic and anthelmintic. They are used in the treatment of flatulence, anorexia, dyspepsia, bronchitis, asthma, hiccough, vomiting and pain in the bladder. They are used as a cardio-tonic and emmenagogue. They have antibiotic and diuretic properties. They are rich in calcium and iron. | |||||
| Therapeutic uses | Sula (abdominal colic), Krmi (worms), Netra roga (eye diseases), Chardi (vomiting), Hikka (hicough), Vasti ruja (pain in urinary bladder), Udara (ascites), Danta roga (tooth diseases), Gulma (intestinal tumours/tumors), Sukla ruja (reproductive disorders), Adhmana (abdominal distension), Aruci (lack of taste) | |||||
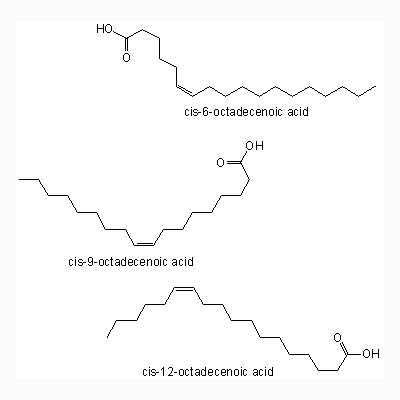
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids Cis-6-octadecenoic acid (*C1), Cis-9-octadecenoic acid (*C1), Cis-12-octadecenoic acid (*C1) Others Verbascoside (*C2), 6-O-alpha-L-(2"-O-trans-p-Coumaroyl-rhamnopyranosylcatapol (*C2), 6-O-alpha-L-(2"-O-cis-p-Coumaroyl-rhamnopyranosylcatapol (*C2), 6-O-alpha-L-(3"-O-trans-p-Coumaroyl-rhamnopyranosylcatapol (*C2), Premcoryoside (*C2), Premnafolioside (*2) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | The crystalline ketonic substance exhibited powerful antispasmodic activity; the action was particularly marked on the smooth-muscle of the rabbit's gut. The esential oil and the crystalline substance were found to lower the blood pressure in dogs and rats; the effect was due to the direct action on the blood vessels.The oil produced a marked diuretic effect in rabbits. The fruits left after the extraction of essential oil showed pronounced cardio-tonic activity. | |||||
| Medical system | Ayurveda (Traditional Indian medicine) | |||||
| Traditional concept | Rasa (Taste) | Katu (Pungent), Tikta (Bitter) | ||||
| Virya (Potency) | Usna (Hot) | |||||
| Guna (Quality) | Laghu (Light), Ruksa (Dry), Tiksna (Sharp) | |||||
| Vipaka (Post digestive taste) | Katu (Pungent) | |||||
| Karma (General action) | Dipana (increasing digestive fire), Pacana (digesting undigested), Vidahi (causing excess burning), Vrsya (aphrodisiac), Balakari (promoting strength) | |||||
| Dosakarma (Action on dosa) | Decreases Kapha Vata | |||||
| Dhatukarma(Action on body tissues) | Sukla (reproductive tissue) | |||||
| Mala (Action on excretory mechanism) | Malastambhakari (blocking) | |||||
| Avayava (Action on organ) | Hrdya (good for heart), Netra (eye), Vasti (bladder), Danta (tooth), Jathara (stomach) | |||||
| Traditional usage | 1. Milk with ghee, honey and the powder of sugar, Ajamoda (Trachyspermum roxburghianum), Aralu (Ailanthus excelsa), Madhuka (Liquorice) should be taken in diarrhoea/diarrhea associated with pain. 2. Patha (Cissampelos pariera), Ajamoda, Kutaja (Holarrhena pubescens), Utpala (Nymphaea nouchali), Sunthi (dry ginger), Pippali (Piper longum) all in equal quantity taken with tepid water controls diarrhoea/diarrhea. 3. Goat's ghrta processed with Yavaksara (alkali of Hordeum vulgare), Ajamoda, Citraka (Plumbago zeylanica) and Amalaka (Phyllanthus emblica) mixed with honey is useful in the disorder caused by Vata and hoarseness of voice. 4. In case of gravels the following formulation is used. Bones of heron, camel and ass, Goksura (Tribulus terrestris), Talapatri (Curculigo orchioides), Ajamoda and the root bark of Kadamba (Anthocephalus indicus) and Bilva (Aegle marmelos) mixed together are taken with wine or warm water. 5. In impurity of breast milk, the child should be given to lick ghee mixed or cooked with the powder of Rasna (Pluchea lanceolata), Ajamoda, Sarala (Pinus roxburghii) and Devadaru (Cedrus deodara) along with sugarcandy. | |||||
| Formulation | Ajamoda arka, Ajamodadi curna, Ajamodadi vataka, Hinguastaka curna | |||||
| Related drugs | 1. Apium graveolens L. 2. Carum stictocarpum Benth. | |||||
| Comments | - Synonyms like Ajamoda, Bastamoda denotes an association of goat with this plant. Dipyaka, Vahni dipika denote its capacity to increase digestive functions. The synonyms suffixed or prefixed with gandha denotes its strong smell. - This is included in the Sula prasamana, Dipaniya gana by Caraka and Pippalyadi by Susruta. | |||||
| References | Reference book Tips! | [2] Indian Medicinal Plants - A Compendium of 500 species, Varier, P.S., Orient Longman Ltd. Chennai (Madras) Vol. 5 (Repr.1997), pp 299-303. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants, 1956. Chopra, R.N., Nayar, S.L. and Chopra, I.C., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi. - New Edition (1996) National Institute Science Communication; Supplement p 245. Illustrated Manual of Herbal Drugs Used in Ayurveda, 1996. Sarin, Y.K., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi p 202. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India, Part I, Vol I, Ed. I, 1989. Govt. of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Dept. of Health, New Delhi p 2. Indian Medicinal Plants (Second Edition), Vols. 1-5, 1993. Kirtikar, K.R. and Basu. B.D., Periodical Experts Book Agency, Delhi Vol. 2, p 1204. Plants in Ayurveda (A Compendium of Botanical and Sanskrit Names), 1997. Abdul Kareem, M., Foundation for Revitalisation of Local Health Traditions, Bangalore 1625. Dravyagunavijnana, Vols. 1-5, reprint 1998. Sharma, P.V., Chowkhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi Vol. 2, pp 497-498. Classical uses of Medicinal Plants, 1996. Sharma, P.V., Chaukhambha Visvabharati, Varanasi p 8. | ||||
| Research paper | *C1 Chaudri, T. A., Ahmad, I, Muhammad, D. and Ahmed, M.; Pak. J. SCi. Ind. Res., 44, 75-78 (2001). *C2 Otsuka, H., Watanabe, E., Yuasa, K., Ogimi, C., Takushi, A. and Takeda, Y.; Phytochemistry, 32, 983-86 (1993). *C3 Yuasa, K., Ide, T., Otsuka, H. and Takeda, Y.; J. Nat. Prod., 56, 1695-99 (1993). | |||||
| Remarks | Karfas is a Arabic/Urudu name for Trachyspermum roxburghianum. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/11/16 | |||||


_17372a.jpg/20000)
_8548a.jpg/20000)