Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
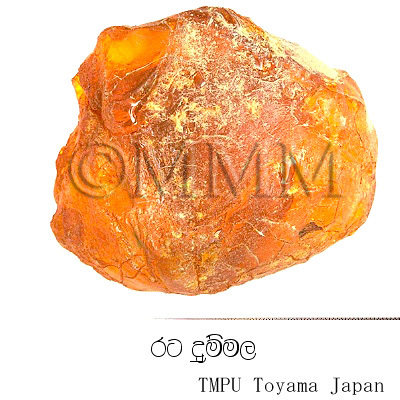
Crude drug name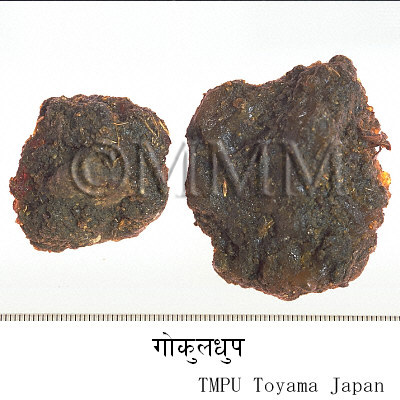 | Market name | Gokuldhup |
|---|---|---|
| Formal name | Guggulu | |
Other names Tips! | Guggul (T), Guggul (B), Guggul (H), Gugal (K), Guggulu, Gulgulu (M), Gumbulu (Te), Gukkal (Ta), Gugool (Ti), Gugul, Ratadummala (Sin) | |
| English name | Indian Bdellium | |
| Original plant name | Commiphora wightii (Arnott.) Bhandari (= Commiphora mukul (Hook. ex Stocks) Engl.), Indian Bdellium | |
| Family name | Burseraceae | |
| Used part | Classification | Plant origin | Sub classification | gum |
| Collection information | Kingdom of Nepal, Kathmandu | |
| Collection date | 1991/04/13 | |
| Collector | Tsuneo Namba, et al. | |
| TMPW No. | 14808 | |
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
27.7172453
85.3239605
Collection information
Kingdom of Nepal,Kathmandu
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Crude drug name | Ayurvedic name or Sanskrit name, English name | Guggulu, Indian Bdellium | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | Purapadapa, Rindi, Macana, Palankasa, Kausika, Jatayu, Sahika, Vayasari, Sivapriya, Dhupika, Pura, Durga, Mahisaksa, Arnakrama, Bhadrasriyam, Kalarasa, Nakuncara, Silakhya, Devadhupa, Kumbha, Ulukhalakam, Palankasa | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Commiphora wightii (Arnott.) Bhandari (= Commiphora mukul (Hook. ex Stocks) Engl.) | |||||
| Family name | Burseraceae | |||||
| Used part | Oleo-resin | |||||
| Distribution area | In Bellary, Mysore, Deccan, Khandesh, Kathiawar, Rajasthan and Berar. | |||||
| Remarks | Common. | |||||
| Common uses | The drug is astringent, bitter, stomachic, carminatvie, antiseptic, diaphoretic, diuretic, emmenagogue and expectorant. It is useful in amenorrhoea/amenorrhea, arthritis, diabetes, cough, dyspepsia, epilepsy and uterine affections. Powdered guggulu mixed with powdered root of Inula racemosa (Puskara guggul) is effective against hyperlipidemia and in ischaemic/ischemic heart diseases. Guggulu enriches the blood. Resin is used in the form of lotion for indolent ulcers and as a gargle in caries of the teeth, weak and spongy gums, pyorrhoea/pyorrhea alveolaris, chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis and ulcerated throat. It is an ingredient of an ointment for ulcers. Like all the oleo-resins, it causes an increase of leucocytes in the blood and stimulates phagocytosis. Inhalation of the fumes from burnt Guggulu is recommended in hay fever, acute and chronic nasal catarrh, chronic laryngitis, chronic bronchitis and phthisis. | |||||
| Therapeutic uses | Vrana (wounds), Apaci (glandular swellings), Meha (diabetic types), Asma (calculi), Vata (rheumatism), Kustha (skin diseases), Amamaruta (rheumatic fever), Granthi (tumour/tumor), Sopha (oedema), Gandamala (glandular swelling in the neck), Krmi (worms) | |||||
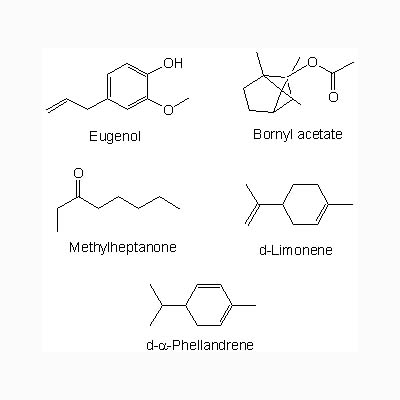
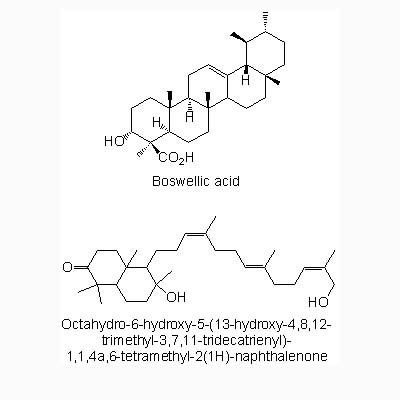
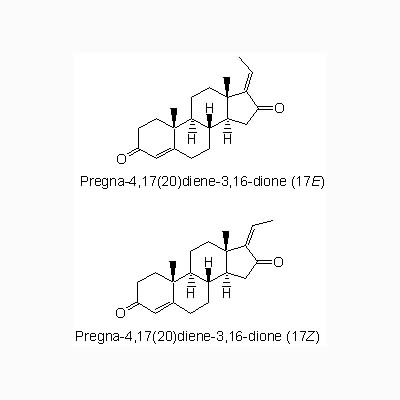
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds Methylheptanone (*C1), 13-(decahydro-2-hydroxy-2,5,5,8a-tetramethyl-6-oxo-1-naphthalena)-2,6,10-Trimethyl-2,6,10-Tridecatrienoic acid,(*C2), Octahydro-6-hydroxy-5-(13-hydroxy-4,8,12-trimethyl-3,7,11-tridecatrienyl)-1,1,4a,6-tetramethyl-2(1H)-naphthalenone (*C2) Monoterpenoids alpha-Pinene (*C1), Myrcene (*C1), Cadinene (*C1), Geraniol (*C1), d-alpha-Phellandrene (*C1), d-Limonene (*C1), Bornyl acetate (*C1), 1,8-Cineole (*C1), Linalool (*C1), Eugenol (*C1) Triterpenoids Myrrhanol A (*C3, *C4, *C8), Myrrhanol B (*C3), Myrrhanol C (*C3), Myrrhanone A (*C3, *C4, *C8), Myrrhanone B (*C3), Boswellic acid (*C5) Phenol derivatives 2-Propanoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)- (2S,3S,4R,5Z)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-tricosenyl ester (*C6), 2-Propanoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-(2S,3S,4R,5Z)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-pentacosenyl ester (*C6), 2-Propanoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-(2S,3S,4R,5Z)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-tetracosenyl ester (*C6), 2-Propanoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) (*C6), Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione (17Z) (*C7, *C9), Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione (17E) (Guggulsterone E, *C9, *C10) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Guggulu is said to reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels in hypercholestreomic subjects. | |||||
| Medical system | Ayurveda (Traditional Indian medicine) | |||||
| Traditional concept | Rasa (Taste) | Tikta (Bitter), Kasaya (Astringent), Katu (Pungent), Madhura (Sweet) | ||||
| Virya (Potency) | Usna (Hot) | |||||
| Guna (Quality) | Visada (Clear), Ruksa (Dry), Laghu (Light), Suksma (Minute), Picchila (Slimy) | |||||
| Vipaka (Post digestive taste) | Katu (Pungent) | |||||
| Karma (General action) | Bhagnasandhanakrt (fracture healing), Svarya (good for voice), Rasayana (rejuventive), Dipana (increasing digestive fire), Balya (strengthening), Kledahara (drying) | |||||
| Dosakarma (Action on dosa) | Decreases Kapha Vata, increases Pitta | |||||
| Dhatukarma(Action on body tissues) | Meda (adipose tissue) | |||||
| Mala (Action on excretory mechanism) | Sara (laxative) | |||||
| Traditional usage | 1. In obesity, use of "Rasanjana" (a type of collyrium), Brhatpancamula* (a group of five drugs), Guggulu (Commiphora wightii), Silajatu (asphalt) and Agnimantha (Premna mucronata) is beneficial. 2. Incase obesity has set in one should regularly use Silajatu, Guggulu, cow's urine, Triphala** (a group of three fruits), Lauhabhasma (processed iron powder), Rasanjana, honey, barley, Mudga (green gram), Kodrava (Paspalum scrobiculatum), Syamaka (Echinochloa frumentacea), etc. These are rough and reduce fat. 3. One should use Guggulu in ascitic types. 4. Use of Silajatu, urine, Guggulu, Triphala** and Snuhi (Euphorbia spp.) latex alleviates ascitic types. 5. One should use Guggulu with cow's urine or decoction of Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa) for oedema. 6. Guggulu or Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) should be taken with cow's urine for oedema. 7. Guggulu alone taken with urine or decoction of Punarnava, Devadaru (Cedrus deodara), Haritaki and Guduci (Tinospora cordifolia) alleviates oedema, anaemia, ascitis and obesity. 8. Guggulu, with urine is useful in oedema, with Khadira (Acacia catechu) decoction in skin diseases and with decoction of Brhatpancamula* (a group of five roots) or Agnimantha in obesity. 9. Guggulu destroys oedema taken with decoction Punarnava, Devadaru and Sunthi or decoction of Brhatpancamula* or Agnimantha in obesity. 10. Those suffering from oedema should use Guggulu with urine or Pippali (Piper longum) with milk or Haritaki or Sunthi mixed with jaggery. 11. Use of all rasayanas particularly Silajatu and Guggulu with milk is beneficial. 12. Guggulu is the best remedy for Vata covered by "medas" (obesity). 13. For sciatica, Rasna (Pluchea lanceolata), Guggulu are pounded with ghee and made into pills. It alleviates sciatica. 14. In arthritis, Guggulu or Guduci with Triphala** decoction with milk should be taken. 15. Guggulu with urine a good remedy for arthritis. 16. In arthritis, one should take Silajatu or Guggulu or Pippali or Sunthi (dry ginger) with urine or decoction of Dasamula***. 17. One should use regularly Haritaki, Guggulu and Silajatu with urine for rheumatic fever. 18. Intake of Guggulu with equal quality of Trikatu**** (a group of three pungents), Citraka (Plumbago zeylanica), Musta (Cyperus rotundus), Triphala** and Vidanga (Embelia ribes) destroys all disorders caused by fat tissue, Kapha and rheumatic fever. 19. The diseases can be controlled by regular use of Silajatu, Guggulu and honey in arthritis. 20. Use of all rejuvenative drugs particularly of Silajatu and Guggulu with milk is beneficial. 21. The patient should use Silajatu, Guggulu, Sunthi and Devadaru with decoction of the group of drugs according to predominance of dosa. 22. In all types and conditions of abscess, Guggulu should be used with suitable decoctions. 23. In abscess caused by Vata, Guggulu or Castor oil should be taken. 24. Similarly in abscess caused by Kapha, Guggulu should be taken with urine. 25. Guggulu should be used with Triphala** decoction in wounds, skin diseases, sinus and fistula in ano. The same with Kancanara (Bauhinia racemosa), Triphala** and Pippali is useful in tumours/tumors of the neck. 26. Intake of Guggulu and Vidanga mixed with Triphala** and Khadira decoction destroys fistula in ano. 27. One should take Guggulu or castor oil with cow's urine. By this chronic scrotal enlargement caused by Vata is destroyed. 28. Guggulu with decoction of Vasa (Adhatoda vasica), Nimba (neem), Patola (Trichosanthes cucumerina), Triphala**and Guduci controls gastritis. --------------------------- Brhatpancamula* contains five roots of trees i.e., Bilva, Agnimantha, Syonaka, Patala, and Gambhari. It pacifies Vata Dosa and Kapha Dosa. It improves appetite and digestion. It is used for the treatment of the diseases related to the digestive and musculoskeletal systems. Triphala**, a group of three fruits, i.e., Amalaka, Bibhitaki, and Haritaki. It is beneficial for increasing appetite, improving eyesight, and treating chronic intermittent fever. Dasamula*** is a formulation consisting of the ten roots of ten medicinal plants categorized as Brhatpancamul and Laghupancamula. It is generally useful in Tridoṣa and particularly in Vata. It alleviates fever, oedema, vatika disorders and debility. Trikatu****, a group of three pungents: Pippali, Marica and Sunthi. It supports digestion and the overall gastric function. | |||||
| Formulation | Yogaraja guggulu, Kaisora guggulu, Triphala guggulu, Goksuradi guggulu, Candraprabha vati, Guggulu tiktaka Kasaya, Guggulu tiktaka ghrtam, Guggulu pancapala curnam, Navakarsika guggulu, Arogyavardhini. | |||||
| Comments | According to Raja nighantu, Guggulu grows near deserts. There are five types. Hemabha, Mahisaksatulya, Padmaragopama, Bhrngabha, Kumudadyuti. According to Bhavaprakasa, 5 types are Mahisaksa - with blackish colour and used for elephants, Mahanila - blue coloured also used for elephants, Kumuda - lotus coloured, used for horse, Padma - peal coloured, used for horse, Hiranya - golden coloured and used for human. Mahisaksa is also used in medicines for human. The best variety is identified as, that which burns in the fire, when heated melts, dissolves in water and looks like milk. Old, fire coloured, slimy with different colours should be discarded. New Guggulu is nourishing and the old one is very scraping (Lekhana). Unctuous, like gold, having appearance like ripe Jambu is new. It loses its quality when stored for long period. It should be purified before using by boiling it in Milk or Triphala decoction. Similarly it can be purified in decoction of Dasamula and Amrta. Turmeric, Neem decoction is also used for purifying this. If used in more than prescribed quantity it causes cataract, dryness of mouth, infertility, emaciation, unconsciousness, roughness of the body. While taking Guggulu one should avoid sour taste, food having sharp quality, indigestion, sexual intercourse, mental worries, sunlight, alcohol, anger. Its leaves are sweet, rough, pungent, cold, heavy, blocking and increases Kapha and Vata. This is included in the Eladi gana of Susruta. | |||||
| References | Reference book Tips! | [2] Indian Medicinal Plants - A Compendium of 500 species, Varier, P.S., Orient Longman Ltd. Chennai (Madras) Vol. 2 (Repr.1997), pp 164-172. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants, 1956. Chopra, R.N., Nayar, S.L. and Chopra, I.C., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi. - New Edition (1996) National Institute Science Communication; Supplement p 75. Illustrated Manual of Herbal Drugs Used in Ayurveda, 1996. Sarin, Y.K., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi p 330. Ayurvedic Drugs and Their Plant Sources, 1994. Sivarajan, V.V. and Balachandran, I., Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi p 394. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India, Part I, Vol I, Ed. I, 1989. Govt. of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Dept. of Health, New Delhi p 43. Plants in Ayurveda (A Compendium of Botanical and Sanskrit Names), 1997. Abdul Kareem, M., Foundation for Revitalisation of Local Health Traditions, Bangalore 54. Dravyagunavijnana, Vols. 1-5, reprint 1998. Sharma, P.V., Chowkhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi Vol. 2, pp 54-58. Classical uses of Medicinal Plants, 1996. Sharma, P.V., Chaukhambha Visvabharati, Varanasi p 124. | ||||
| Research paper | *C1 Saxena, V. K. and Sharma, R. N.; J. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci., 20, 55-56 (1998). *C2 Andre, P., Lhermite, S. and Pellicier, F.; PCT Int. Appl. WO 9710196 A1, 28pp (1997). *C3 Kawahara, Y., Shimoda, H. and Yoshikawa, M.; Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho JP 2002234834 A2, 9pp (2002). *C4 Kimura, I., Yoshikawa, M., Kobayashi, S., Matsuda, H. and Sugihara, Y.; PCT Int. Appl. WO 2002069952 A1, 48 pp (2002). *C5 Jauch, J.; PCT Int. Appl. WO 2002085921 A2, 40 pp (2002). *C6 Zhu, N., Rafi, M. M., Li, D., LaVoie, E. J., DiPaola, R. S., Badmaev, V., Ghai, G., Rosen, R. T. and Ho, C-T.; ACS Symposium Series, 803 (Quality Management of Nutraceuticals), 281-91 (2002). *C7 Yusui, K. H.; Indian IN 166998 A, 12pp (1990). *C8 Kimura, I., Yoshikawa, M., Kobayashi, S., Sugihara, Y., Suzuki, M., Oominami, H., Murakami, T., Matsuda, H. and Doiphode, V. V.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 11, 985-89 (2001). *C9 Mesrob, B., Nesbitt, C., Misra, R. and Pandey, R. C.; J. Chromatogr., B: Biomed. Sci. Appl., 720, 189-96 (1998). *C10 Sarkhel, S., Yadava, U., Prakas, P., Jain, G. K., Singh, S. and Maulik, P. R.; Acta Crystallographica, Section E, E57, 285-86 (2001). | |||||
| Remarks | An Ayurvedic preparation, Thyrocap, having guggul as one of the constituents, is used to control simple and diffuse goiter. Kancanaraguggulu a composite preparation containing the resin is used in the treatment of swellings like galaganda, gandamala, granthi etc. Guggul is one of the constituents of an Ayurvedic drug Rumalaya, used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Another drug, Laksa guggulu, having guggulu is used for fractures, and Arogyavardhini vati is reported to control the parasite Entamoeba hystolitica in the intestinal and hepatic amoebiasis. Resin is also used in a shampoo against head parasites. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2025/01/20 | |||||