Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Crude drug name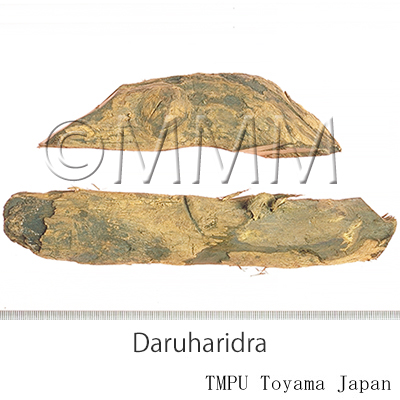 | Market name | DARUHARIDRA |
|---|---|---|
| Formal name | Daruharidra | |
Other names Tips! | Daruhaldi (T), Daruharidra (B), Daruhaldi (H), Skyerba (Ti) | |
| English name | Indian Barberry | |
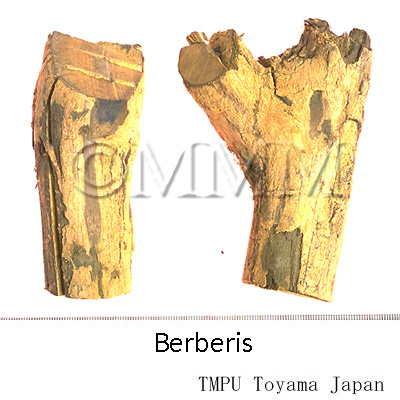
| Original plant name | Berberis lycium Royle, Berberis asiatica Roxb. ex DC., Indian Barberry | |
| Family name | Berberidaceae | |
| Used part | Classification | Plant origin | Sub classification | root |
| Collection information | India, Kolkata, West Bengal | |
| Collection date | 2000/12/19 | |
| Collector | Katsuko Komatsu | |
| TMPW No. | 20535 | |
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
22.572646
88.36389499999996
Collection information
India,Kolkata, West Bengal
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Crude drug name | Ayurvedic name or Sanskrit name, English name | Daruharidra, Indian Barberry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | Darvi, Parjanya, Katankateri, Pacampacanya, Kaleyakam, Hemapalamsika, Pitadaru, Pitahvacandanam, Pita, Himam, Darunisa, Kaliyakam, Haridru, Pitadaru, Kapitakam, Sthiraraga, Kamini, Kamavati, Darupita, Karkatakini, Pitacandanam, Hemakanti, Katankati | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Berberis lycium Royle, Berberis asiatica Roxb. ex DC. | |||||
| Family name | Berberidaceae | |||||
| Used part | Root | |||||
| Distribution area | Himalayas from Himachal Pradesh occurring at 600-2700m, eastwards to Bhutan and Assam at 1500-1800 m and on Parasnath hills in Bihar, Pachmarhi in Madhya Pradesh and Mount Abu in Rajasthan. It is also grown on hedges. The roots are collected in fairly large quantities in Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh and Tehri-Garhwal of Uttar Pradesh and sold in the drug market of Chamba, Dehra Dun and Haridwar. | |||||
| Remarks | Common. | |||||
| Common uses | This is useful in jaundice, haemorrhoids/hemorrhoids, urino-genital disorders and skin diseases. | |||||
| Therapeutic uses | Vrana (wounds), Meha (diabetic types), Kandu (itching), Visarpa (erysipelas), Netrakarna asya roganut (Curing disorders of ear, nose, mouth), Visa (poison), Kustha (skin diseases) | |||||
| Chemical constituent | Others Alkaloid, 4%; berberine, 2.09%; palmatine; berbamine, jatrorrhizine, oxyacathine, oxyberberine. Berberine chloride and berberine tannate are official in the Japanese pharmocopoeia. | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | The roots are reported to possess anti-cancer activity. Berberine hydrochloride and sulphate help in the diagnosis of latent malaria by releasing the parasites into the blood stream. Berberine is useful in the treatment of oriental sores caused by Leishmania tropica Wright. The alkaloid berberine is used as a superior intestinal antiseptic and bitter stomachic. Dihydro berberine is used in brain tumour. The drug is locally obtained in various ways. A thick extract is made from the root bark, roots and the lower stem wood, by boiling them with water. This is strained and evaporated till a dark brown sticky mass of the consistency of the opium is obtained. The product is called rasaut, rasavanti or rasanjan. | |||||
| Medical system | Ayurveda (Traditional Indian medicine) | |||||
| Traditional concept | Rasa (Taste) | Tikta (Bitter), Katu (Pungent) | ||||
| Virya (Potency) | Usna (Hot) | |||||
| Guna (Quality) | Ruksa (Dry), Laghu (Light) | |||||
| Vipaka (Post digestive taste) | Katu (Pungent) | |||||
| Dosakarma (Action on dosa) | Decreases Kapha, Pitta | |||||
| Avayava (Action on organ) | Netra (eyes), Karna (ear), Asya (mouth) | |||||
| Traditional usage | 1. One suffering from jaundice should take in morning cooled decoction of Triphala* (a group of three fruits), Guduci (Tinospora cordifolia), Darvi (Berberis lycium or B. asiatica), Nimba (neem) mixed with honey. 2. Darvi or Rasanjana (a product of Darvi) taken with cow's urine checks leprosy. 3. Darvi and Rasanjana should be used in various ways such as bath, intake, paste, rubbing, dusting and processing of oil and ghee for alleviation of skin diseases. 4. Decoction of Darvi, Khadira (Acacia catechu) and Nimba destroys skin disease. 5. In wounds oil cooked with Darvi, Vidanga (Embelia ribes) and Kampillaka (Mallotus philippinensis) is useful and in that having predominance of Kapha and Pitta, ghrta cooked with Durva (Cynadon dactylon) juice is efficacious. 6. In dysuria caused by Pitta, Darvi with Amalaka (Phyllanthus emblica) juice mixed with honey should be taken. 7. In the diseases cased by Kapha paste of Darvi should be taken with cow's urine. This is efficacious in scrotal enlargement. 8. Extract of Darvi with honey destroys the diseases of mouth, disorders of blood and sinus. 9. Smoking should be used with sticks made of Darvi, Ingudi (Balanites roxburghii), Danti (Baliospermum montanum), Kinihi (Albizia procera) and Tulasi (Ocimum sanctum) for coryza. 10. Milk boiled with Darvi cooled and mixed with a little rock salt should be used for washing eyes. 11. Decoction made of Darvi 40 gms with water 640 ml reduced to one eighth is mixed with honey and used for washing. It is useful in inflammation of eyes caused by all dosas. 12. In night blindness, stick made of Rasanjana, Haridra, Darvi leaves of Jati (Jasminum officinale) and Nimba mixed with liquid cow dung is used as collyrium. 14. Decoction of Darvi mixed with honey should be taken followed by intake of rice water. 15. Incase of poisoning, Haridra and Darvi are used as paste etc. 16. In soft chancre paste of Rasanjana, Sirisa (Albizia lebbeck), Haritaki (Terminalia bellirica) mixed with honey should be used. 17. In "Prameha" (polyuria), Darvi juice mixed with honey is beneficial. 18. Oil cooked with Durva juice or Kampillaka or paste of Darvi bark is an excellent healing of wounds. Rasanjana (Semi solid extract of Darvi): 19. In bleeding piles, Rasanjana boiled with milk until it becomes semi-solid. Then one fourth powder of Nimba leaves is added to it and made into pills. 20. Rasanjana is very good for obesity. 21. In obesity, Rasanjana, Brhatpancamula** (a group of five roots), Guggulu (Commiphora mukul), Silajatu (asphalt), and decoction of Agnimantha (Premna mucronata) are useful. 22. Darvi or Rasanjana with cow's urine checks leprosy. 23. Rasanjana should be taken internally for a month and also applied as paste externally. 24. In soft chancre, Rasanjana mixed with Sirisa and Haritaki and also honey should be applied externally. It destroys "upadamsa" (a genital condition). 25. Rasanjana, Haridra, Darvi, Manjista (Rubia cordifolia), Nimba leaves, Trivrt (Operculina turpethum), Tejovati (Zanthoxylum armatum) and Danti paste of these drugs destroys sinus. 26. Oil cooked with Rasanjana, Ativisa (Aconitum heterophyllum), Musta (Cyperus rotundus) and Devadaru (Cedrus deodara) should be used as snuff. | |||||
| Formulation | Darvyadi kvatha, Darvyadi taila, Darvyadi leha, Darvi ghrta, Khadirarista, Candanadi vati, Sudarsana curna; Punarnava mandura | |||||
| Related drugs | 1. Coscinium fenestratum Colebr. (Menispermaceae) 2. Berberis lycium Royle (Berberidaceae) | |||||
| Comments | There is a controversy regarding the usage of Berberis asiatica as the source of Daruharidra. In South India, Coscinium fenestratum is used as Daruharidra. Most of the authors correlate to Berberis lycium, B. asiatica is used as a substitute for this. The synonyms suffixed or prefixed with "Pita" or "Haridra" indicate the yellowish colour of this plant. Pacampaca denotes the preparation called Rasanjana made out of this. This is included in Arsoghna, Kandughna, Lekhaniya gana of Caraka and Haridradi, Mustadi, Laksadi of Susruta. | |||||
| References | Reference book Tips! | [2] Indian Medicinal Plants - A Compendium of 500 species, Varier, P.S., Orient Longman Ltd. Chennai (Madras) Vol. 2 (Repr.1997), pp 191-193. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants, 1956. Chopra, R.N., Nayar, S.L. and Chopra, I.C., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi. - New Edition (1996) National Institute Science Communication; Supplement p 36. Illustrated Manual of Herbal Drugs Used in Ayurveda, 1996. Sarin, Y.K., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi pp 26-29. Plants in Ayurveda (A Compendium of Botanical and Sanskrit Names), 1997. Abdul Kareem, M., Foundation for Revitalisation of Local Health Traditions, Bangalore 230. Dravyagunavijnana, Vols. 1-5, reprint 1998. Sharma, P.V., Chowkhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi Vol. 2, pp 437-439. Classical uses of Medicinal Plants, 1996. Sharma, P.V., Chaukhambha Visvabharati, Varanasi p 190. | ||||
| Remarks | In the Unani system of medicine the drug Rasaut is used for the treatment of leprosy. Root and root bark of Berberis lycium Royle (Berberidaceae) is the usual adulterant. Daruharidra originating from Jammu & Kashmir and Kullu valley of Himachal Pradesh consists predominantly the root of this species. Some consider Daruhaldi/Daruharidra as Berberis aristata DC. Berberine hydrochloride and sulphate found in the roots find application in the preparation of drugs for cholera, diarrhoea/diarrhea, dysentery and eye troubles. They are administered orally in conjunction with salts and some fluids. A drug preparation from the root called Rasaut is regarded as bitter, tonic and is reported to be used as cholagogue, stomachic, laxative, diaphoretic, antipyretic and antiseptic. It is administered externally in painful eye affections, indolent ulcers and haemorrhoids/hemorrhoids. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/01/16 | |||||